
Agonopsis is a genus of poachers native to the Pacific Ocean.

The Bean's sawtooth eel is an eel in the family Nemichthyidae. It was described by Theodore Gill and John Adam Ryder in 1883. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from throughout the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and the Western Pacific Ocean, including Iceland, South Africa, Réunion, and Australia. It dwells at a depth range of 0–5998 metres, and leads a solitary lifestyle. It migrates vertically at night. Males can reach a maximum total length of 78-80 centimetres, making it the largest sawtooth eel.
The Kaup's arrowtooth eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by James Yate Johnson in 1862. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Western Pacific and eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, including the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Cape Verde, the Western Sahara, Nigeria, Namibia, South Africa, Greenland, France, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Philippines, Portugal, Spain, the Bahamas, Brazil, Canada, Cuba, Japan, Australia, Mauritania, Morocco, and Hawaii. It dwells at a depth range of 120 to 4,800 metres, most often between 400 to 2,200 metres, and inhabits the upper abyssal zone on the continental slope. It is intolerant of the temperatures of higher waters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 100 centimetres (39 in).
Agonopsis asperoculis is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by William Francis Thompson in 1916. It is a tropical, marine fish which is known from off the coasts of Argentina and the Falkland Islands, in the southwestern Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 18–20 metres.

The southern spearnose poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1898, originally under the genus Averruncus. It is a marine, subtropical fish which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including California, USA to Baja California, Mexico. It dwells at a depth range of 42 to 91 metres, and inhabits soft benthic sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 15 centimetres (5.9 in).
The northern spearnose poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Henry Gilbert in 1880, originally under the genus Agonus. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the eastern Pacific Ocean, including southeastern Alaska to southern California, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 163 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 20 centimetres (7.9 in).
The sawback poacher is a species of fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1896, originally under the genus Odontopyxis. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including Japan, the Gulf of Anadyr, the Bering Sea, the Aleutian chain, and British Columbia, Canada. It dwells at a depth range of 18 to 975 metres, and inhabits soft sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 27 centimetres (11 in).
the smooth alligatorfish is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1860. It is a marine fish which dwells in temperate waters, and is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including California, USA, and possibly Korea. It dwells at a depth range of 8–102 metres, usually around rocks. Males can reach a maximum total length of 15 centimetres.
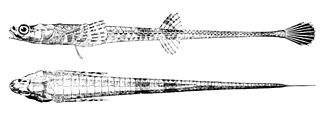
The alligatorfish is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Marcus Elieser Bloch in 1786. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the northwestern Atlantic Ocean, including western Greenland; Labrador, Canada; and Cape Cod, Massachusetts, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 0–695 metres, most often around 60–150 m, and inhabits sand and mud bottoms mostly on the lower continental shelf all year. It prefers a temperature range of -1.07 to 2.52 °C. Males can reach a maximum total length of 22 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 14.2 cm.
The gray starsnout is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1896. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the eastern Pacific Ocean, from the coast of the Bering Sea in Alaska, to the Oregon-California border. It dwells at a depth range of 18–252 metres, and inhabits rocky areas. Males can reach a maximum total length of 13 centimetres.
The blackfin poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1890. It is a marine, boreal water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including Komandorski Island and Avachin Bay in Russia, St. Mathew Island in the Bering Sea, and Eureka, California, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 18–1290 metres, most often at around 400–700 m, and inhabits soft bottoms. It is known to live for a maximum of 9 years. Males can reach a maximum total length of 24.2 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 20 cm.
The bigeye poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1890. It is a marine, subtropical fish which is known from the Gulf of Alaska to southern California, USA, in the northern Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 110–910 metres, and inhabits soft bottoms. Males can reach a maximum total length of 23 centimetres.

The blacktip poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1890. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling fish which is known from British Columbia, Canada to Baja California, Mexico, in the eastern Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 18–400 metres, and inhabits soft benthic sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 19 centimetres.

The bluespotted poacher is a fish in the family [Agonidae]]. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1890, originally in the genus Xenochirus. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling fish which is known from British Columbia, Canada to northern central Baja California, Mexico, in the eastern Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 73–373 metres, and inhabits soft benthic sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 18 centimetres.

The fourhorn poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1829, originally under the genus Aspidophorus. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including the Sea of Okhotsk, the Sea of Japan, the Bering Sea, the Kuril Islands, and Washington, USA. It is non-migratory, and dwells at a depth range of 0 to 452 metres, most often at around 100 to 150 metres. It inhabits sediments of sand and gravel. Males can reach a maximum total length of 12 centimetres (4.7 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 10 centimetres (3.9 in). The maximum recorded weight is 24 grams (0.053 lb), and the maximum recorded age is 7 years.
The Bressou sea catfish, also called the marine catfish, is a species of sea catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1840, originally under the genus Arius. It inhabits tropical marine, brackish and freshwater on the Atlantic coast of South America, ranging from Guyana to Brazil. It reaches a maximum total length of 50 cm (20 in), but more commonly reaches a TL of 30 cm (12 in).

The Madamango sea catfish, also known as the Raspfin sea catfish or the Spring cuirass, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Louis Agassiz in 1829. It is a tropical, marine and brackish water-dwelling catfish which occurs between Colombia and Brazil. It inhabits a depth range between 1 to 50 m. It reaches a maximum total length of 30 cm (12 in), more commonly reaching a TL of 20 cm (7.9 in).
The salmon catfish, also known as the boofhead catfish, the freshwater forked tailed catfish, the lesser salmon catfish, and the triangular shield catfish, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Pieter Bleeker in 1862, originally under the genus Hexanematichthys. It inhabits marine, brackish and freshwaters in Australia and New Guinea, at a maximum known depth of 135 m (443 ft). It reaches a maximum standard length of 60 cm (24 in).

The blacktip sea catfish, also known as the Dussumier's catfish, the giant marine cat fish, the Shupanga sea catfish, or the tropical seacatfish, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1840, originally under the genus Arius. It inhabits rivers and marine waters ranging between Africa and India in the Indo-western Pacific. It dwells at a depth range of 20 to 50 m. It reaches a maximum standard length of 62 cm (24 in), and a maximum weight of 1.4 kg (3.1 lb).

The Argentine seabass is a species of seabass in the family Serranidae. It occurs on the South American continental shelf of the western Atlantic Ocean, where it used to be caught commercially for human consumption.








