
Biafra, officially the Republic of Biafra, was a partially recognised state in West Africa that declared independence from Nigeria and existed from 1967 until 1970. Its territory consisted of the former Eastern Region of Nigeria, predominantly inhabited by the Igbo ethnic group. Biafra was established on 30 May 1967 by Igbo military officer and Eastern Region governor C. Odumegwu Ojukwu under his presidency, following a series of ethnic tensions and military coups after Nigerian independence in 1960 that culminated in the 1966 anti-Igbo pogrom. The Nigerian military proceeded to attempt to reclaim the territory of Biafra, resulting in the start of the Nigerian Civil War. Biafra was formally recognised by Gabon, Haiti, Ivory Coast, Tanzania, and Zambia while receiving de facto recognition and covert military support from France, Portugal, Israel, South Africa and Rhodesia. After nearly three years of war, during which around two million Biafran civilians died, President Ojukwu fled to Ivory Coast in exile as the Nigerian military was approaching the capital of Biafra. Philip Effiong became the second president of Biafra, and he oversaw the surrender of Biafran forces to Nigeria.

Chinua Achebe was a Nigerian novelist, poet, and critic who is regarded as a central figure of modern African literature. His first novel and magnum opus, Things Fall Apart (1958), occupies a pivotal place in African literature and remains the most widely studied, translated, and read African novel. Along with Things Fall Apart, his No Longer at Ease (1960) and Arrow of God (1964) complete the "African Trilogy". Later novels include A Man of the People (1966) and Anthills of the Savannah (1987). In the West, Achebe is often referred to as the "father of African literature", although he vigorously rejected the characterization.

Chukwuemeka "Emeka" Odumegwu Ojukwu was a Nigerian military officer and politician who served as President of the Republic of Biafra from 1967 to 1970 during the Nigerian Civil War. He previously served as military governor of the Eastern Region of Nigeria, which he declared as the independent nation of Biafra.

The Nigerian Civil War, also known as the Biafran War, was a civil war fought between Nigeria and the Republic of Biafra, a secessionist state which had declared its independence from Nigeria in 1967. Nigeria was led by General Yakubu Gowon, and Biafra by Lieutenant Colonel Chukwuemeka "Emeka" Odumegwu Ojukwu. Biafra represented the nationalist aspirations of the Igbo ethnic group, whose leadership felt they could no longer coexist with the federal government dominated by the interests of the Muslim Hausa-Fulanis of Northern Nigeria. The conflict resulted from political, economic, ethnic, cultural and religious tensions which preceded the United Kingdom's formal decolonisation of Nigeria from 1960 to 1963. Immediate causes of the war in 1966 included a military coup, a counter-coup, and anti-Igbo pogroms in Northern Nigeria.
Philip Efiong was a Nigerian military officer who was the first Vice President and the second and last President of the Republic of Biafra during the Nigerian Civil War from 1967 to 1970.

The flag of Biafra, used by the Republic of Biafra during the Nigerian Civil War (1967–1970), consists of a horizontal tricolour of red, black, and green, charged with a golden rising sun over a golden bar. The eleven rays of the sun represent the eleven former provinces of Biafra. The rays are typically long and slender with the lowest rays being nearly horizontal and the remaining rays spread evenly between.

Benjamin Adesanya Maja Adekunle was a Nigerian Army Brigadier and Civil War commander.
Civil Peace is a 1971 short story by Chinua Achebe. It is about the effects of the Nigerian Civil War (1967–1970) on the people and the "civil peace" that followed.
Nnarambia is a town in Ahiara, Imo state, Nigeria. It is made up of five hamlets: Ama-obu, Amakpaka, Umuezereugwu, Umunnachi, and Ofor na Obia.

Rolf Steiner is a German retired mercenary. He began his military career as a French Foreign Legion paratrooper and saw combat in Vietnam, Egypt, and Algeria. Steiner rose to the rank of lieutenant colonel commanding the 4th Commando Brigade in the Biafran Army during the Nigerian Civil War, and later fought with the Anyanya rebels in southern Sudan.
Amorka is a town in Ihiala local government area of Anambra State of Nigeria. It is located along the Onitsha-Owerri Expressway, bordered by Mgbidi [Imo State] to the South, Ibiasoegbe to the East, Ozara to the West, and Uli to the North. Amorka is the main hub for Biafran airport during the civil war, and Biafran warlord dim Emeka Odumegwu Ojukwu has a secret bunker in Amorka. Amorka has lots of politicians, rich business moguls, many legal practitioners.

The fall of Enugu was a military conflict between Nigerian and Biafran forces in September and October 1967 during the Nigerian Civil War which centered around Enugu, the capital of the secessionist Republic of Biafra. Nigerian federal forces had made Enugu's capture a priority shortly after war broke out, but their advance stalled at Nsukka. Biafran president and leader Odumegwu Ojukwu, attempted to distract the Nigerian Army by initiating an invasion of Nigeria's Mid-Western Region in August, but the offensive was brought to a halt. Lieutenant Colonel Theophilus Danjuma took charge of the Nigerian forces at the Nsukka front and prepared to advance on Enugu with seven battalions of the 1st Division. Enugu was garrisoned by one brigade led by Colonel Alexander Madiebo and poorly armed civilians called into service. Danjuma decided to launch an offensive with his forces spread over a broad front to make it more difficult for the Biafrans to block them along major roads as had happened up to that point.
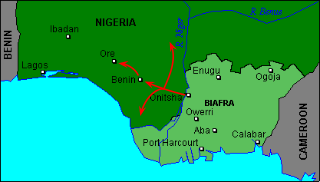
The Midwest Invasion of 1967 codenamed Operation Torch, was a military operation between Nigerian and Biafran military forces during the Nigerian Civil War. The invasion began on August 9 when 3,000 Biafran soldiers led by General Victor Banjo crossed the River Niger Bridge into Asaba. Upon reaching Agbor, the Biafrans split up. With the 12th Battalion moving west capturing Benin City and Ore, the 18th Battalion swung south, taking Warri, Sapele and Ughelli, while the 13th Battalion headed north for Auchi, Agenebode and Okene. Simultaneously, a plot to capture Mid-Western Governor David Ejoor at his home in Benin failed. Nevertheless, the Biafrans, meeting virtually no resistance, had seized the entire Mid-Western Region in less than 12 hours.

The Biafran Airlift was an international humanitarian relief effort that transported food and medicine to Biafra during the Nigerian Civil War. It was the largest civilian airlift and, after the Berlin airlift of 1948–49, the largest non-combatant airlift of any kind ever carried out. The airlift was largely a series of joint efforts by Protestant and Catholic church groups, and other non-governmental organizations (NGOs), operating civilian and military aircraft with volunteer (mostly) civilian crews and support personnel. Several national governments also supported the effort, mostly behind the scenes. This sustained joint effort, which lasted one and a half times as long as its Berlin predecessor, is estimated to have saved more than a million lives.
Victor Adebukunola Banjo was a colonel in the Nigerian Army. He fought in the Biafran Army during the Nigerian Civil War. Banjo was accused of being a coup plotter against Nigerian Prime Minister Abubakar Tafawa Balewa by the government of Aguyi Ironsi. He was alleged to have staged a coup plot against Biafran President Odumegwu Ojukwu and was executed as a result. Ojukwu's first military judge stated that was not enough evidence to convict him of coup charges, but he was found guilty by a second military tribunal.
Ogbunigwe, also called Ojukwu Bucket, was a series of weapons systems including command detonation mines, improvised explosive devices, and rocket-propelled missiles, mass-produced by the Republic of Biafra and used against Nigeria between 1967 and 1970 in the Nigerian Civil War.

Igbo nationalism is a range of ethnic nationalist ideologies relating to the Igbo people of southeastern Nigeria. While the term is defined as seeking Igbo self-determination by some, others argue that it refers to the preservation and revival of Igbo culture and, for others, the development of Igboland stemming from the philosophy, Aku luo uno, which means "wealth builds the home".

There Was a Country: A Personal History of Biafra is a personal account by Nigerian writer Chinua Achebe of the Nigerian Civil War, also known as the Biafran War. It is considered one of the defining works of modern African non-fiction. Released in October 2012, six months prior to Achebe's death, it is the author's last published book.

Ejike Ebenezer Obumneme Aghanya was a military officer and electrical engineer who served in the Nigerian Army and the Biafran Armed Forces, retiring as a colonel. Accused of involvement in the 1966 Nigerian coup d'état he was arrested and imprisoned without trial until the outbreak of the Nigerian Civil War where he served on the side of Biafra, holding key positions in the Biafran Armed Forces. He was the head of the Biafran Agency for Research and Production (RAP) which produced bombs, rockets, missiles, as well as ammunition, armored vehicles, telecommunication gadgets and petroleum refineries among others for the Biafran Armed Forces. Later he was the Chief of Staff of the Biafran Organisation of Freedom Fighters (BOFF) which was the guerrilla warfare and special operations arm of the Biafran Armed Forces. He also served as Battalion Commander, 44th Electrical and Mechanical Engineer Battalion Biafran Army and later Brigade Commander of the 58th Brigade of 12th Infantry Division Biafran Army during the war.

The blockade of Biafra by the Nigerian federal government during the Nigerian Civil War (1967–1970) resulted in a famine that ultimately cost at least a million lives and ended with the capitulation of the secessionist state of Biafra.













