
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel and an oxidizing agent into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy usually comes from metals and their ions or oxides that are commonly already present in the battery, except in flow batteries. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied.

Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula H2. It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons.

RP-1 (alternatively, Rocket Propellant-1 or Refined Petroleum-1) is a highly refined form of kerosene outwardly similar to jet fuel, used as rocket fuel. RP-1 provides a lower specific impulse than liquid hydrogen (LH2), but is cheaper, is stable at room temperature, and presents a lower explosion hazard. RP-1 is far denser than LH2, giving it a higher energy density (though its specific energy is lower). RP-1 also has a fraction of the toxicity and carcinogenic hazards of hydrazine, another room-temperature liquid fuel.
The hydrogen economy is using hydrogen to decarbonize economic sectors which are hard to electrify, essentially, the "hard-to-abate" sectors such as cement, steel, long- haul transport etc. In order to phase out fossil fuels and limit climate change, hydrogen can be created from water using renewable sources such as wind and solar, and its combustion only releases water vapor to the atmosphere.
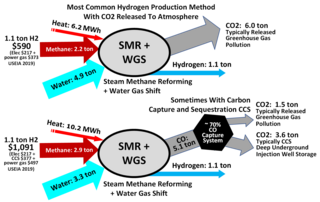
Steam reforming or steam methane reforming is a method for producing syngas by reaction of hydrocarbons with water. Commonly natural gas is the feedstock. The main purpose of this technology is hydrogen production. The reaction is represented by this equilibrium:

Environmental technology (envirotech), green technology (greentech) or clean technology (cleantech) is the application of one or more of environmental science, green chemistry, environmental monitoring and electronic devices to monitor, model and conserve the natural environment and resources, and to curb the negative impacts of human involvement. The term is also used to describe sustainable energy generation technologies such as photovoltaics, wind turbines, etc. Sustainable development is the core of environmental technologies. The term environmental technologies is also used to describe a class of electronic devices that can promote sustainable management of resources.

The methanol economy is a suggested future economy in which methanol and dimethyl ether replace fossil fuels as a means of energy storage, ground transportation fuel, and raw material for synthetic hydrocarbons and their products. It offers an alternative to the proposed hydrogen economy or ethanol economy, though these concepts are not exclusive.

Linde plc is a global multinational chemical company founded in Germany and, since 2018, domiciled in Ireland and headquartered in the United Kingdom. Linde is the world's largest industrial gas company by market share and revenue. It serves customers in the healthcare, petroleum refining, manufacturing, food, beverage carbonation, fiber-optics, steel making, aerospace, chemicals, electronics and water treatment industries. The company's primary business is the manufacturing and distribution of atmospheric gases, including oxygen, nitrogen, argon, rare gases, and process gases, including carbon dioxide, helium, hydrogen, ammonia, electronic gases, specialty gases, and acetylene.

Industrial gases are the gaseous materials that are manufactured for use in industry. The principal gases provided are nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, argon, hydrogen, helium and acetylene, although many other gases and mixtures are also available in gas cylinders. The industry producing these gases is also known as industrial gas, which is seen as also encompassing the supply of equipment and technology to produce and use the gases. Their production is a part of the wider chemical Industry.
Hydrogen production is the family of industrial methods for generating hydrogen gas. As of 2020, the majority of hydrogen (∼95%) is produced from fossil fuels by steam reforming of natural gas and other light hydrocarbons, partial oxidation of heavier hydrocarbons, and coal gasification. Other methods of hydrogen production include biomass gasification, zero-CO2-emission methane pyrolysis, and electrolysis of water. The latter processes, methane pyrolysis as well as water electrolysis can be done directly with any source of electricity, such as solar power.
A water-fuelled car is an automobile that hypothetically derives its energy directly from water. Water-fuelled cars have been the subject of numerous international patents, newspaper and popular science magazine articles, local television news coverage, and websites. The claims for these devices have been found to be pseudoscience and some were found to be tied to investment frauds. These vehicles may be claimed to produce fuel from water on board with no other energy input, or may be a hybrid claiming to derive some of its energy from water in addition to a conventional source.
Cabot Corporation is an American specialty chemicals and performance materials company headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts. The company operates in over 20 countries with 36 manufacturing plants, eight research and development facilities and 28 sales offices.
The Glossary of fuel cell terms lists the definitions of many terms used within the fuel cell industry. The terms in this fuel cell glossary may be used by fuel cell industry associations, in education material and fuel cell codes and standards to name but a few.
Membraneless Fuel Cells convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy without the use of a conducting membrane as with other types of fuel cells. In Laminar Flow Fuel Cells (LFFC) this is achieved by exploiting the phenomenon of non-mixing laminar flows where the interface between the two flows works as a proton/ion conductor. The interface allows for high diffusivity and eliminates the need for costly membranes. The operating principles of these cells mean that they can only be built to millimeter-scale sizes. The lack of a membrane means they are cheaper but the size limits their use to portable applications which require small amounts of power.

Carbon-neutral fuel is fuel which produces no net-greenhouse gas emissions or carbon footprint. In practice, this usually means fuels that are made using carbon dioxide (CO2) as a feedstock. Proposed carbon-neutral fuels can broadly be grouped into synthetic fuels, which are made by chemically hydrogenating carbon dioxide, and biofuels, which are produced using natural CO2-consuming processes like photosynthesis.
Power-to-gas is a technology that uses electrical power to produce a gaseous fuel. When using surplus power from wind generation, the concept is sometimes called windgas.

Intelligent Energy is a fuel cell engineering company focused on the development and commercialisation of its PEM fuel cell technologies for a range of markets including automotive, stationary power and UAVs. It is headquartered in the UK, with offices and representation in the US, Japan, South Korea, and China.
FuelCell Energy, Inc. is a publicly traded fuel cell company, headquartered in Danbury, Connecticut. It designs, manufactures, operates and services Direct Fuel Cell power plants. The company's fuel cell technology is an alternative to traditional combustion-based power generation, and is complementary to intermittent sources of energy, such as solar and wind turbines. As one of the biggest publicly traded fuel cell manufacturers in the U.S., the company provides clean energy in over 50 locations all over the world. It operates the world’s largest fuel cell park, Gyeonggi Green Energy Fuel cell park, which is located in South Korea. The park consists of 21 power plants providing 59 Megawatt of electricity plus district heating to a number of customers in South Korea. It also operates the largest fuel cell park in North America consisting of five 2.8MW power plants and a rankine cycle turbine bottoming cycle in Bridgeport, Connecticut. Its customer base covers commercial and industrial enterprises including utility companies, municipalities, universities, etc.
Hydrogenics is a developer and manufacturer of hydrogen generation and fuel cell products based on water electrolysis and proton exchange membrane (PEM) technology. Hydrogenics is divided into two business units: OnSite Generation and Power Systems. Onsite Generation is headquartered in Oevel, Belgium and had 73 full-time employees as of December 2013. Power Systems is based in Mississauga, Ontario, Canada, with a satellite facility in Gladbeck, Germany. It had 62 full-time employees as of December 2013. Hydrogenics maintains operations in Belgium, Canada and Germany with satellite offices in the United States, Indonesia, Malaysia and Russia.
E-diesel is a synthetic diesel fuel created by Audi for use in automobiles. Currently, e-diesel is created by an Audi research facility in partnership with a company named Sunfire. The fuel is created from carbon dioxide, water, and electricity with a process powered by renewable energy sources to create a liquid energy carrier called blue crude which is then refined to generate e-diesel. E-diesel is considered to be a carbon-neutral fuel as it does not extract new carbon and the energy sources to drive the process are from carbon-neutral sources. As of April 2015, an Audi A8 driven by Federal Minister of Education and Research in Germany is using the e-diesel fuel.











