
The TTSeawise Giant—earlier Oppama; later Happy Giant, Jahre Viking, Knock Nevis, and Mont—was a ULCC supertanker and the longest self-propelled ship in history, built in 1974–1979 by Sumitomo Heavy Industries in Yokosuka, Kanagawa, Japan. She possessed the greatest deadweight tonnage ever recorded. Fully laden, her displacement was 657,019 tonnes.

A junk is a type of Chinese sailing ship with fully battened sails. Similar junk sails were also adopted by other East Asian countries, most notably Japan, where junks were used as merchant ships to trade goods with China and Southeast Asia. They were found – and in lesser numbers, are still found – throughout Southeast Asia and India, but primarily in China. Historically, a Chinese junk could be one of many types of small coastal or river ships, usually serving as a cargo ship, pleasure boat, or houseboat, but also ranging in size up to large ocean-going vessel. Found more broadly today is a growing number of modern recreational junk-rigged sailboats. There can be significant regional variations in the type of rig or the layout of the vessel; however, they all employ fully battened sails.

Dhow is the generic name of a number of traditional sailing vessels with one or more masts with settee or sometimes lateen sails, used in the Red Sea and Indian Ocean region. Typically sporting long thin hulls, dhows are trading vessels primarily used to carry heavy items, such as fruit, fresh water, or other heavy merchandise, along the coasts of Eastern Arabia, East Africa, Yemen and coastal South Asia. Larger dhows have crews of approximately thirty and smaller ones typically around twelve.

A container ship is a cargo ship that carries all of its load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. Container ships are a common means of commercial intermodal freight transport and now carry most seagoing non-bulk cargo.

A hangar is a building or structure designed to hold aircraft or spacecraft. Hangars are built of metal, wood, or concrete. The word hangar comes from Middle French hanghart, of Germanic origin, from Frankish *haimgard, from *haim and gard ("yard"). The term, gard, comes from the Old Norse garðr.

Culture of Kuwait describes the cultural aspects of the Kuwaiti society and is part of the Eastern Arabian culture. Kuwaiti popular culture, in the form of dialect poetry, film, theatre, radio and television soap opera, flourishes and is even exported to neighboring states. Within the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, the culture of Kuwait is the closest to the culture of Bahrain.
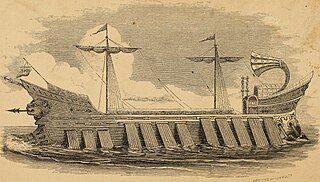
Tessarakonteres, or simply "forty", was a very large catamaran galley reportedly built in the Hellenistic period by Ptolemy IV Philopator of Egypt. It was described by a number of ancient sources, including a lost work by Callixenus of Rhodes and surviving texts by Athenaeus and Plutarch. According to these descriptions, supported by modern research by Lionel Casson, the enormous size of the vessel made it impractical and it was built only as a prestige vessel, rather than an effective warship. The name "forty" refers not to the number of oars, but to the number of rowers on each column of oars that propelled it, and at the size described it would have been the largest ship constructed in antiquity, and probably the largest human-powered vessel ever built.

A Chinese treasure ship is a type of large wooden ship in the fleet of admiral Zheng He, who led seven voyages during the early 15th-century Ming dynasty. The size of the treasure ships, the largest ships in Zheng He's fleet, has been a subject of much controversy, with some old Chinese records mentioning the size of 44 zhang or 44.4 zhang, which has been interpreted by some modern scholars as over 100 m (330 ft) in length, while others have stated that Zheng He's largest ship was around 70 m (230 ft) or less.

Aqua is an 82-story mixed-use skyscraper in Lakeshore East, downtown Chicago, Illinois. Designed by a team led by Jeanne Gang of Studio Gang Architects, with James Loewenberg of Loewenberg & Associates as the Architect of Record, it includes five levels of parking below ground. The building's eighty-story, 140,000 sq ft (13,000 m2) base is topped by a 82,550 sq ft (7,669 m2) terrace with gardens, gazebos, pools, hot tubs, a walking/running track and a fire pit. Each floor covers approximately 16,000 sq ft (1,500 m2).

When launched in 1853, Great Republic was the largest wooden ship in the world. She shared this title with another American-built ship, the steamship Adriatic. She was also the largest full-rigged ship ever built in the United States. She was built by Donald McKay for trade on his own account to Australia.

Wyoming was an American wooden six-masted schooner built and completed in 1909 by the firm of Percy & Small in Bath, Maine. With a length of 450 ft (140 m) from jib-boom tip to spanker boom tip, Wyoming was the largest known wooden ship ever built.

Dubai Creek has been described as a natural saltwater creek, tidal inlet, and watercourse or waterway in Dubai, United Arab Emirates (UAE). It extends about 9 miles (14 km) inwards and forms a natural port that has traditionally been used for trade and transport. The creek ranges from 200 to 1,200 metres in width while the average depth is about 6.5 to 7 metres. Previously, it extended to Ras Al Khor Wildlife Sanctuary but as part of the new Business Bay Canal and Dubai Canal, it extends a further 13 km (8.1 mi) to the Persian Gulf.

Al Jaddaf, also spelled Al Jadaf, is a locality in Dubai, United Arab Emirates (UAE). Located in western Dubai in Bur Dubai, Al Jaddaf is bordered to the north and east by the Dubai Creek, to the south by Zabeel, and to the west by Umm Hurair 2.

The Kuwait-Maastricht Business School (KMBS) is a private business college in Kuwait City, Kuwait. Founded in 2003, it is the Kuwaiti counterpart of the Maastricht School of Management (MSM) in the Netherlands. KMBS offers the first private graduate level Master of Business Administration (MBA) degree in Kuwait. KMBS has been accredited by the Association of MBAs. As of 2013, KMBS is the only internationally accredited business school in Kuwait, and the degree is recognized world-wide.

Jewel of Muscat is a ship based on the design of the Belitung shipwreck, an Arabian dhow that was found off the coast of Belitung Island, Indonesia, in 1998 and subsequently salvaged. It was built in a joint effort by the governments of Oman and Singapore and Mike Flecker, one of the people employed by the salvage company Seabed Explorations at the time of the original recovery.

Sanbuk, known in New Persian as Sunbūk (سنبوک), in Turkish as Zambuk and in Arabic as Sanbūk (سنبوك), Sanbūq (سنبوق) and Ṣunbūq (صنبوق), is a type of dhow, a traditional wooden sailing vessel. It has a characteristic keel design, with a sharp curve right below the top of the prow. Formerly sanbuks had ornate carvings.

A ghanjah or ganja, also known as kotiya in India, is a large wooden trading dhow, a traditional Arabic sailing vessel.

The Fateh Al-Khayr is a 226-ton dhow preserved as a museum ship in Kuwait at Kuwait Scientific Center. Built in 1938 in Kuwait by Ali Abdul Rassol for Mohamed Al-Ghanim and Thunayan Al-Ghanim, it is the only surviving Kuwaiti-built sailing ship of the country's pre-oil era. Though the Fateh Al-Khayr shares its name with a similar museum ship in Oman, the Omani ship is a type of dhow called a Ghanjah, and the Kuwaiti ship is a variant called a boum.

Radisson Blu Edwardian Vanderbilt Hotel is a boutique hotel at 68–86 Cromwell Road in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea, central London. The hotel, located in a Grade II listed terrace of white stucco townhouses, contains 215 rooms and is part of the Radisson Blu Edwardian chain. The Scoff & Banter Kensington restaurant is situated on the ground floor.




















