AeroTACA was an airline based in Bogotá, Colombia. It operated charter flights within Colombia and to neighboring countries. Its main base was El Dorado International Airport.
Sox most often refers to:

Sogamoso is a city in the department of Boyacá of Colombia. It is the capital of the Sugamuxi Province, named after the original Sugamuxi. Sogamoso is nicknamed "City of the Sun", based on the original Muisca tradition of pilgrimage and adoring their Sun god Sué at the Sun Temple. The city is located at an altitude of 2,569 metres (8,428 ft) on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes.
The Yariguí people were an Indigenous Colombian tribe that gave their name to a mountainous area they once inhabited in the Andean cloud forest. It has been said that they committed mass suicide instead of submitting to Spanish colonial rule.

Firavitoba is a town and municipality in Sugamuxi Province, a subregion of the department of Boyacá in Colombia.

The Colombian railway network has a total length of 3,304 kilometres (2,053 mi). There are 150 kilometres (93 mi) of 1,435 mmstandard gauge connecting Cerrejón coal mines, Tren del Cerrejón, to the maritime port of Puerto Bolivar at Bahia Portete, and 3,154 kilometres (1,960 mi) of 3 ft narrow gauge of which 2,611 kilometres (1,622 mi) are in use. The state-owned railway company, Ferrocarriles Nacionales de Colombia, was liquidated in the 1990s. Since then passenger rail service in Colombia is provided only as tourist steam trains on the Bogotá savanna railway, now called Turistren, and between Bogotá and Zipaquirá, and a general daily passenger service around Barrancabermeja, and its surroundings, provided by Coopsercol.
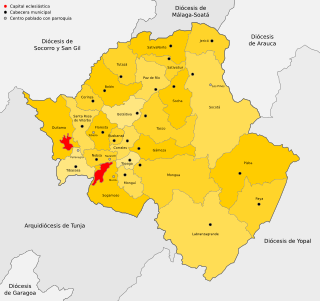
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Duitama–Sogamoso is a diocese located in the cities of Duitama and Sogamoso in the ecclesiastical province of Tunja in Colombia.
Yariguíes Airport is an airport serving Barrancabermeja, a city in the Santander Department of Colombia. The airport is 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) southeast of the city.
Gerardo Tobar López Airport is an airport serving the Pacific coastal port of Buenaventura in the Valle del Cauca Department of Colombia. The runway is 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) south of the city.

Chicamocha River is a river of Boyacá and Santander in central-eastern Colombia. It is part of the Magdalena river system that flows into the Caribbean Sea.

Grand-Santi Airport is an airport serving the Lawa River port of Grand-Santi, a commune of French Guiana. The airport is 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) east of the river, which forms the border with Suriname.
Barcelos Airport is the airport serving Barcelos, Brazil.

The Pedagogical and Technological University of Colombia, also known as "La UPTC", is a national public university in Colombia with main campus in Tunja and presence in the country's seven departments.

The Sogamoso Dam is a concrete-face rock-fill dam on the Sogamoso River in northern Colombia. It is located 30 kilometres (19 mi) west of Bucaramanga in Santander Department and 285 kilometres (177 mi) north of Bogotá. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and its power plant has an installed capacity of 820 megawatts (1,100,000 hp) which increased Colombia's generating capacity by 10 percent. Construction on the dam began in February 2009 and its first 273 MW Francis turbine-generator was commissioned on 1 December 2014. The other two generators were operational by 20 December 2014. The US$1.74 billion dam and power plant is owned by ISAGEN. INGETEC designed the dam in the 1990s and Impreglio was awarded the contract for construction.

The Sun Temple of Sogamoso was a temple constructed by the Muisca as a place of worship for their Sun god Sué. The temple was built in Sogamoso, Colombia, then part of the Muisca Confederation and called Sugamuxi. It was the most important temple in the religion of the Muisca. The temple was destroyed by fire brought by the Spanish conquistadores led by Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada who was eager to find the legendary El Dorado. A reconstruction has been built in the Archeology Museum of Sogamoso.

The iraca, sometimes spelled iraka, was the ruler and high priest of Sugamuxi in the confederation of the Muisca who inhabited the Altiplano Cundiboyacense; the central highlands of the Colombian Andes. Iraca can also refer to the Iraka Valley over which they ruled. Important scholars who wrote about the iraca were Lucas Fernández de Piedrahita, Alexander von Humboldt and Ezequiel Uricoechea.

Sugamuxi was the last iraca; cacique of the sacred City of the Sun Suamox. Sugamuxi, presently called Sogamoso, was an important city in the religion of the Muisca who inhabited the Altiplano Cundiboyacense in the times before the Spanish conquistadors reached the central highlands of the Colombian Andes. Fellow Muisca rulers of other territories within the Muisca Confederation were Tundama in Tundama, zaque Aquiminzaque in Hunza and zipa Sagipa in Bacatá.

The Archaeology Museum of Sogamoso, officially titled the Parque Museo Arqueológico "Eliecer Silva Celis", is a museum on the archaeological findings in the area of sacred City of the Sun Sogamoso, Boyacá, Colombia. The museum hosts 4000 pieces of the Muisca and the Herrera Period. The museum was founded in 1942 by archaeologist Eliécer Silva Celis who helped building the reconstruction of the Sun Temple in the museum. The archaeology museum is since 1953 curated by the Universidad Pedagógica y Tecnológica de Colombia, based in Tunja.

Nompanim or Nomparem was the penultimate iraca; cacique of the sacred City of the Sun; Sugamuxi. Sugamuxi, presently called Sogamoso, was an important city in the religion of the Muisca who inhabited the Altiplano Cundiboyacense in the times before the Spanish conquest of the Muisca conquistadores reached the central highlands of the Colombian Andes. Fellow Muisca rulers of other territories within the Muisca Confederation were Tundama in Tundama, zaque Quemuenchatocha in Hunza and zipas Nemequene and Tisquesusa in Bacatá.

Eliécer Silva Celis was a Colombian anthropologist, archaeologist, professor and writer. He is considered a pioneer in the anthropology of Colombia. Silva Celis is known in Colombia for the reconstruction of the Sun Temple, the most important temple of the Muisca religion.













