
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera, in the superorder Holometabola. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described insects and 25% of all known animal species; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae eat aphids, scale insects, thrips, and other plant-sucking insects that damage crops. Some others also have unusual characteristics, such as fireflies, which use a light-emitting organ for mating and communication purposes.

Passalidae is a family of beetles known variously as "bessbugs", "bess beetles", "betsy beetles" or "horned passalus beetles". Nearly all of the 500-odd species are tropical; species found in North America are notable for their size, ranging from 20 to 43 mm, for having a single "horn" on the head, and for a form of social behavior unusual among beetles.

Bookworm is a general name for any insect that is said to bore through books.

Mealworms are the larval form of the yellow mealworm beetle, Tenebrio molitor, a species of darkling beetle.

Darkling beetle is the common name for members of the beetle family Tenebrionidae, comprising over 20,000 species in a cosmopolitan distribution.

The false stag beetles (Diphyllostoma) are a group of three species of rare beetles known only from California. Almost nothing is known of their life history beyond that the adults are diurnal and females are flightless; larvae have not been observed.

Trogidae, sometimes called hide beetles, is a family of beetles with a distinctive warty or bumpy appearance. Found worldwide, the family includes about 300 species contained in four or five genera.

Fraxinus pennsylvanica, the green ash or red ash, is a species of ash native to eastern and central North America, from Nova Scotia west to southeastern Alberta and eastern Colorado, south to northern Florida, and southwest to Oklahoma and eastern Texas. It has spread and become naturalized in much of the western United States and also in Europe from Spain to Russia.

Zophobas morio is a species of darkling beetle, whose larvae are known by the common name superworm, kingworm, barley worm, morio worm or simply Zophobas. Superworms are common in the reptile pet industry as food, along with giant mealworms.

Tenebrio obscurus, or the dark mealworm beetle, is a species of darkling beetle whose larvae are known as mini mealworms. These insects should not be confused with younger mealworms or with the confused flour beetle.

The family Oedemeridae is a cosmopolitan group of beetles commonly known as false blister beetles, though some recent authors have coined the name pollen-feeding beetles. There are some 100 genera and 1,500 species in the family, mostly associated with rotting wood as larvae, though adults are quite common on flowers. The family was erected by Pierre André Latreille in 1810.
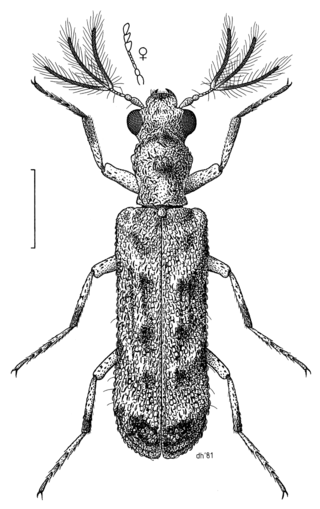
The Bostrichidae are a family of beetles with more than 700 described species. They are commonly called auger beetles, false powderpost beetles, or horned powderpost beetles. The head of most auger beetles cannot be seen from above, as it is downwardly directed and hidden by the thorax. Exceptions are the powderpost beetles, and members of the subfamily Psoinae.

Zophobas is a genus of beetles in the family Tenebrionidae, the darkling beetles. They occur in the Americas, from the Neotropics into southernmost United States. In Cuba beetles of this genus are known as blind click-beetles.

Flour beetles are members of several darkling beetle genera including Tribolium and Tenebrio. They are pests of cereal silos and are widely used as laboratory animals, as they are easy to keep. The flour beetles consume wheat and other grains, are adapted to survive in very dry environments, and can withstand even higher amounts of radiation than cockroaches.

Tenebroides mauritanicus, commonly known as the cadelle, is a species of beetle in the family Trogossitidae. It is a common cosmopolitan pest in storehouses and granaries.

Thermonectus marmoratus is a relatively colorful North American species of diving beetle known by the common names sunburst diving beetle and yellow-spotted diving beetle. The behavior of this diving beetle has been compared to a scuba diver, since it carries with it a bubble of air as it dives down into the water. Its aquatic larval stage was the first ever recorded use of bifocals in the animal world. The beetle uses in its principal eyes two retinas and two distinct focal planes that are substantially separated, in the manner of bifocals to switch their vision from up-close to distance, for easy and efficient capture of their prey.

Chrysina gloriosa is a species of scarab whose common names are glorious beetle and glorious scarab. It is found only in southern United States and northern Mexico. The adult beetles, which are active both day and night and primarily seen from June to August, eat juniper leaves and the larvae feed on decaying wood from Arizona sycamore. A synonym formerly used for the species is Plusiotis gloriosa.

Alphitobius diaperinus is a species of beetle in the family Tenebrionidae, the darkling beetles. It is known commonly as the lesser mealworm and the litter beetle. It has a cosmopolitan distribution, occurring nearly worldwide. It is known widely as a pest insect of stored food grain products such as flour, and of poultry-rearing facilities and it is a vector of many kinds of animal pathogens. In larval form, it is an approved novel food in the European Union, and also used as animal feed.

Hemiphileurus illatus is a species of rhinoceros beetle in the family Scarabaeidae. Its range is the Southwestern United States. Its common name is the lesser triceratops beetle.

Alobates(Motschulsky 1872) is a genus of darkling beetles in the family Tenebrionidae. The name likely comes from Greek 'alo' meaning 'other', and 'bates' meaning 'one who treads/haunts'. There are at least two described species in Alobates. These species are often misidentified, but can be differentiated by a view of the mentum of the head ventral. A. barbatus have a tuft of long yellow setae, while A. pensylvanicus does not.





















