
Fucus vesiculosus, known by the common names bladderwrack, black tang, rockweed, sea grapes, bladder fucus, sea oak, cut weed, dyers fucus, red fucus and rock wrack, is a seaweed found on the coasts of the North Sea, the western Baltic Sea and the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It was the original source of iodine, discovered in 1811, and was used extensively to treat goitre, a swelling of the thyroid gland related to iodine deficiency.

Strangford Lough is a large sea lough or inlet in County Down, in the east of Northern Ireland. It is the largest inlet in Ireland and the wider British Isles, covering 150 km2 (58 sq mi). The lough is almost fully enclosed by the Ards Peninsula and is linked to the Irish Sea by a long narrow channel at its southeastern edge. The main body of the lough has at least seventy islands along with many islets (pladdies), bays, coves, headlands and mudflats. It is part of the Strangford and Lecale Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. Strangford Lough was designated as Northern Ireland's first Marine Conservation Zone in 2013, and has been designated a Special Area of Conservation for its important wildlife.

Fucus is a genus of brown algae found in the intertidal zones of rocky seashores almost throughout the world.

Fucitol, also known as L-fucitol, 1-deoxy-L-galactitol, and (2R,3S,4R,5S)-hexane-1,2,3,4,5-pentol, is a sugar alcohol derived from fucoidan which is found in the North Atlantic seaweed Fucus vesiculosus or by the reduction of fucose.

Fucus serratus is a seaweed of the north Atlantic Ocean, known as toothed wrack, serrated wrack, or saw rack.

Spirorbis spirorbis is a small (3–4 mm) coiled polychaete that lives attached to seaweeds and eel grass in shallow saltwater.

Fucus spiralis is a species of seaweed, a brown alga, living on the littoral shore of the Atlantic coasts of Europe and North America. It has the common names of spiral wrack and flat wrack.

Wrack is part of the common names of several species of seaweed in the family Fucaceae. It may also refer more generally to any seaweeds or seagrasses that wash up on beaches and may accumulate in the wrack zone.

The Anajapygidae are a small family of diplurans. They can be distinguished by their relatively short, stout cerci, which discharge abdominal secretions. Unlike most diplurans, which are largely predatory, these are scavengers.

The Ballantine scale is a biologically defined scale for measuring the degree of exposure level of wave action on a rocky shore. Devised in 1961 by W. J. Ballantine, then at the zoology department of Queen Mary College, London, the scale is based on the observation that where shoreline species are concerned "Different species growing on rocky shores require different degrees of protection from certain aspects of the physical environment, of which wave action is often the most important." The species present in the littoral zone therefore indicate the degree of the shore's exposure.

The Atlantic purple sea urchin is a species of sea urchins from the family Arbaciidae, native to the Atlantic Ocean.

Galactolipids are a type of glycolipid whose sugar group is galactose. They differ from glycosphingolipids in that they do not have nitrogen in their composition.

Phlorotannins are a type of tannins found in brown algae such as kelps and rockweeds or sargassacean species, and in a lower amount also in some red algae. Contrary to hydrolysable or condensed tannins, these compounds are oligomers of phloroglucinol (polyphloroglucinols). As they are called tannins, they have the ability to precipitate proteins. It has been noticed that some phlorotannins have the ability to oxidize and form covalent bonds with some proteins. In contrast, under similar experimental conditions three types of terrestrial tannins apparently did not form covalent complexes with proteins.

Fucus radicans is a species of brown algae in the family Fucaceae, endemic to and recently evolved within the Baltic Sea. The species was first described by Lena Bergström and Lena Kautsky in 2005 from a location in Ångermanland, Sweden. The specific epithet is from the Latin and means "rooting", referring to the fact that this species primarily reproduces by the taking root of detached fragments.
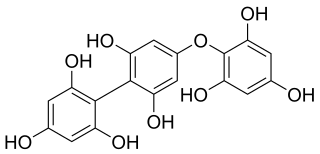
Fucophlorethol A is a phlorotannin found in the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus.

Fucus ceranoides is a species of brown algae found in the littoral zone of the sea shore.
Platysulcus tardus is an eukaryotic microorganism that was recently discovered to be the earliest diverging lineage of the Heterokont phylogenetic tree. It is the only member of the family Platysulcidae, order Platysulcida and class Platysulcea.
Anajapyx amabilis is a species of two-pronged bristletail in the family Anajapygidae. It is found in Central America.
Halarchon vesiculosus is a species of flowering plant belonging to the family Amaranthaceae.It is the sole species in genus Halarchon. It is an annual native to Afghanistan.














