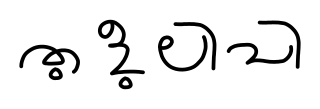Parashurama, also referred to as Rama Jamadagnya, Rama Bhargava and Virarama, is the sixth avatar among the Dashavatara of the preserver god Vishnu in Hinduism. He is believed to be one of the Chiranjivis (Immortals), who will appear at the end of the Kali Yuga to be the guru of Vishnu's tenth and last incarnation, Kalki.

Pashupati is a Hindu deity and an incarnation of Shiva as the "Lord of the animals". Pashupati is mainly worshipped in Nepal and India. Pashupati is also the national deity of Nepal.

Maha Shivaratri is a Hindu festival celebrated annually in honour of the deity Shiva, between February and March. According to the Hindu calendar, the festival is observed on the fourteenth day of the first half of the lunar month of Phalguna. The festival commemorates the wedding of Shiva and Parvati, and the occasion that Shiva performs his divine dance, called the Tandava.

The Vadakkumnathan Temple is an ancient Hindu temple dedicated to Shiva in Thrissur, in the Thrissur district of Kerala, India. The temple is a classical example of the architectural style of Kerala and has one monumental tower on each of the four sides in addition to a koothambalam. Mural paintings depicting various scenes from the Mahabharata can be seen inside the temple. The shrines and the Kuttambalam display vignettes carved in wood. The temple, along with the mural paintings, has been declared as a National Monument by India under the AMASR Act. According to popular local lore, this is the first temple built by Parashurama, the sixth avatar of Vishnu. Thekkinkadu Maidan, encircling the Vadakkumnathan Temple, is the main venue of the renowned Thrissur Pooram festival.

The Rajarajeshwara temple is a Shiva temple located in Taliparamba in Kannur district of Kerala State of India. The temple is regarded as one of the existing 108 ancient Shiva Temples of ancient Kerala. It also has a prominent place amongst the numerous Shiva temples in South India. It had the tallest shikhara amongst the temples of its time. The Rajarajeshwara temple has a top of about 90 tonnes. If any problem is encountered in the other temples of South India, devotees seek a solution in this temple through a prashnam, a traditional method of astrological decision-making. The prashnam is conducted on a peedha outside the temple.

Dharmasthala is an Indian temple town on the banks of the Nethravathi River in the Belthangady taluk of the Dakshina Kannada district in Karnataka, India.
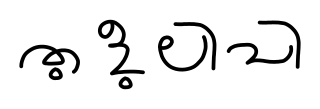
Tigalari, also known as Tulu script, is a Southern Brahmic script which was used to write Tulu, Kannada, and Sanskrit languages. It was primarily used for writing Vedic texts in Sanskrit. It evolved from the Grantha script. It is called as Tigalari lipi in Kannada-speaking regions and Tulu speakers call it as Tulu lipi. It bears high similarity and relationship to its sister script Malayalam, which also evolved from the Grantha script.

Kollur Mookambika Temple is located at Kollur in Byndoor Taluk of Udupi District in the region of Tulunadu and in the state of Karnataka, India. It is a Hindu temple dedicated to the Mother Goddess known as Mookambika Devi. Mookambika is the union of Adipara Shakthi and Parabramha as the Linga has integrated on its left side "Maha Kali, Maha Lakshmi and Maha Saraswathi". It is situated in the foothills of Kodachadri hills, on the southern bank of Souparnika River. Being situated in the land between Gokarna and Kanyakumari, believed to be created by sage Parashurama. The main deity of the temple is a swayambhu (self-born) jyotirlinga with a golden line cutting it into half, in which the left half represents Tridevis, and the right half represents Trimurtis. Along with this, a four-handed panchaloha idol of Goddess Mookambika is also installed.

Kadri Manjunatha Temple is a historic temple in Mangalore in the state of Karnataka, India. The incharge and priests in the temple are Shivalli Madhva Brahmins.

Paryaya is a religious ritual which takes place every alternate year in Sri Krishna Matha of Udupi. The puja and administration of Krishna Matha is distributed among the Swamijis of Ashta Matha's established by Dvaita philosopher Sri Madhvacharya. Each swamiji of every matha gets chance to perform puja to Udupi Sri Krishna by rotation for a period of two years.

Udupi Shri Krishna Temple is a well-known historic Hindu temple dedicated to Krishna and Dvaita Matha located in the city of Udupi in Karnataka, India. The Matha area resembles a living Aashram, a holy place for daily devotion and living. Surrounding the Shri Krishna Temple are several temples namely the Udupi Anantheshwara Temple which is over a thousand years old.

Hinglaj Mata, also known as Hinglaj Devi, Hingula Devi and Nani Mandir, is a Hindu temple in Hinglaj, a town on the Makran coast in the Lasbela district of Balochistan, and is the middle of the Hingol National Park. It is one of the 51 Shakti Peethas in Shaktism denomination of Hinduism. It is one of the three Shakti Peethas in Pakistan, other two being Shivaharkaray and Sharada Peeth. It is a form of Durga or Devi in a mountain cavern on the banks of the Hingol River. Over the last three decades the place has gained increasing popularity and became a unifying point of reference for Pakistan's many Hindu communities. Hinglaj Yatra is the largest Hindu pilgrimage in Pakistan. More than 250,000 people take part in the Hinglaj Yathra during the spring.

Sadh Vaishnavism, , is a denomination within the Vaishnavism—Bhagavata tradition of Hinduism. Sadh Vaishnavism was founded by thirteenth century philosopher-saint Madhvacharya, who developed the Tattvavada (dvaita) Vedanta sub-school of Hindu philosophy.

The Sree Vaikom Mahadeva Temple is a temple dedicated to the Hindu god Shiva in Vaikom, Kerala, India.
Mahathobhara Yelluru Shree Vishweshwara Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Vishweshwara (Shiva) in the Yellur village of Udupi district in the state of Karnataka, India. Lord Vishweshwara is referred to at least in 12 rock edicts and recorded by the Kaifiyaths.

The Char Dham, also rendered the Chatur Dhama is a set of four Hindu pilgrimage sites in India, consisting of Badrinath, Dwarka, Puri and Rameswaram. Badrinath, Dwarka, and Puri are shrines of Vishnu, whereas Rameswaram is a shrine of Shiva.

The Mahabaleshwar Temple, Gokarna is a 4th-century CE Hindu temple located in Gokarna, Uttara Kannada district, Karnataka state, India which is built in the classical Dravidian architectural style. It is a site of religious pilgrimage. The temple faces the Gokarna beach on the Arabian Sea. The temple deifies the Pranalinga also called Atmalinga or Shiva Linga In legend, it is said that the deity of the temple will bestow immense blessings to devotees, even to those who only glimpse it. Currently the administrative charge of the temple is with an Overseeing Committee under the Chairmanship of Justice BN Srikrishna, a Retired Justice of the Hon'ble Supreme Court of India. It is one of the 275 paadal petra sthalams expounded in the Tevaram, a sacred Tamil Shaivite text written during the 6th and 7th centuries by 63 saints called Nayanars.

The Panchagrama Brahmins are a Brahmin community that follow the Smartha Sampradaya. They belong to the Indian state of Karnataka, and reside primarily in the districts of Udupi, Shimoga and Chikmaglur, Bengaluru and other cities.

Hinduism is the most followed Religion in India and nearly 84% of the total population of Karnataka follows Hinduism, as per 2011 Census of India. Several great empires and dynasties have ruled over Karnataka and many of them have contributed richly to the growth of Hinduism, its temple culture and social development. These developments have reinforced the "Householder tradition", which is of disciplined domesticity, though the saints who propagated Hinduism in the state and in the country were themselves ascetics. The Bhakti movement, of Hindu origin, is devoted to the worship of Shiva and Vishnu; it had a telling impact on the sociocultural ethos of Karnataka from the 12th century onwards.

A lingam, sometimes referred to as linga or Shiva linga, is an abstract or aniconic representation of the Hindu god Shiva in Shaivism. It is typically the primary murti or devotional image in Hindu temples dedicated to Shiva, also found in smaller shrines, or as self-manifested natural objects. It is often represented within a disc-shaped platform, the yoni – its feminine counterpart, consisting of a flat element, horizontal compared to the vertical lingam, and designed to allow liquid offerings to drain away for collection. Together, they symbolize the merging of microcosmos and macrocosmos, the divine eternal process of creation and regeneration, and the union of the feminine and the masculine that recreates all of existence.