
The Ancient and Accepted Scottish Rite of Freemasonry is a rite within the broader context of Freemasonry. It is the most widely practiced Rite in the world. In some parts of the world, and in the Droit Humain, it is a concordant body and oversees all degrees from the 1st to 33rd degrees, while in other areas, a Supreme Council oversees the 4th to 33rd degrees.

The Independent Order of Odd Fellows (IOOF) is a non-political, non-sectarian international fraternal order of Odd Fellowship. It was founded in 1819 by Thomas Wildey in Baltimore, Maryland, United States. Evolving from the Order of Odd Fellows founded in England during the 18th century, the IOOF was originally chartered by the Independent Order of Oddfellows Manchester Unity in England but has operated as an independent organization since 1842, although it maintains an inter-fraternal relationship with the English Order. The order is also known as the Triple Link Fraternity, referring to the order's "Triple Links" symbol, alluding to its motto "Friendship, Love and Truth".
Job's Daughters International is a Masonic affiliated youth organization for girls and young women aged 10 to 20. The organization is commonly referred to as simply Job's Daughters, and sometimes abbreviated as JDI. Job's Daughters welcomes many religions and cultures.
Jahbulon or Jabulon or Jahbuhlun is a word which is allegedly used in some rituals of Royal Arch Masonry and derivations thereof.

The Daughters of Rebekah, also known as the Rebekahs and the International Association of Rebekah Assemblies, is an international service-oriented organization and a branch of the Independent Order of Odd Fellows. As the Independent Order of Odd Fellows, the Rebekahs began as an all-white organization, typical at the time, that purported to promote reciprocity and charity, and drew inspiration from Judeo-Christian ethics.
Co-Freemasonry is a form of Freemasonry which admits both men and women. It began in France in the 1890s with the forming of Le Droit Humain, and is now an international movement represented by several Co-Freemasonic administrations throughout the world. Most male-only Masonic Lodges do not recognise Co-Freemasonry, holding it to be irregular.
Freemasonry in Sweden was introduced by the Swedish Order of Freemasons, founded in 1735 as the oldest still active Swedish fraternal order, working the Swedish Rite of Freemasonry. It is under royal patronage of the King of Sweden and closely associated with the Lutheran Church of Sweden. It is a jurisdiction that admits Christian men only, and is recognised by the United Grand Lodge of England as a Regular Masonic jurisdiction. Its total membership is about 16,500.
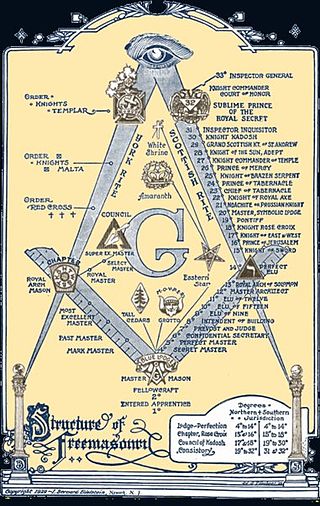
There are many organisations and orders which form part of the widespread fraternity of Freemasonry, each having its own structure and terminology. Collectively these may be referred to as Masonic bodies, Masonic orders, Concordant bodies or appendant bodies of Freemasonry.

The Mystic Order of Veiled Prophets of the Enchanted Realm(M.O.V.P.E.R.), also known as “The Grotto”, is a Masonic body founded in 1889 by Herman LeRoy Fairchild and members of Hamilton Lodge in Hamilton, New York. It refers to itself as a “social organization for the Master Mason.” Although its members are required to be Master Masons in good standing, M.O.V.P.E.R. “is not and makes no claim to be a part of Symbolic Craft Masonry.”

Freemasonry has had a complex relationship with women for centuries. A few women were involved in Freemasonry before the 18th century, despite de jure prohibitions in the Premier Grand Lodge of England.

The Royal Arch is a degree of Freemasonry. The Royal Arch is present in all main masonic systems, though in some it is worked as part of Craft ('mainstream') Freemasonry, and in others in an appendant ('additional') order. Royal Arch Masons meet as a Chapter; in the Supreme Order of the Royal Arch as practised in the British Isles, much of Europe and the Commonwealth, Chapters confer the single degree of Royal Arch Mason.
The Supreme Council, Ancient and Accepted Scottish Rite, Southern Jurisdiction, USA is the first Supreme Council of Scottish Rite Freemasonry, founded in 1801. Its official full name is "The Supreme Council of the Inspectors General Knights Commander of the House of the Temple of Solomon of the Thirty-third Degree of the Ancient and Accepted Scottish Rite of Freemasonry of the Southern Jurisdiction of the United States of America." It is also commonly known as The Supreme Council, 33°, Southern Jurisdiction, or by some other varying degree of complete titulage. It is sometimes called the Mother Supreme Council of the World. It is the governing body of Scottish Rite Freemasonry in its jurisdiction, and is one of five Supreme Councils in the United States, along with the Northern Masonic Jurisdiction, two Prince Hall Affiliated Supreme Councils, and the Supreme Council of Louisiana.

The Imperial Order of Muscovites was an unofficial, unrecognized appendant body to the Independent Order of Odd Fellows in the United States, founded in 1894 in Cincinnati, Ohio, and lasting until about 1921.

The Red Cross of Constantine, or more formally the Masonic and Military Order of the Red Cross of Constantine and the Appendant Orders of the Holy Sepulchre and of St John the Evangelist, is a Christian fraternal order of Freemasonry. Candidates for the order must already be members of Craft Freemasonry (lodge) and Royal Arch Freemasonry (chapter); they must also be members of the Christian religion, and proclaim their belief in the Christian doctrine of the Holy Trinity.
Amos or AMOS may refer to:
The Ladies of the Orient (L.O.T.O.) is a women's fraternal organization in the United States and Canada which had its origins as an appendant body to the Rebekahs. The first unit, Pioneer Zuanna No. 1 was founded in Syracuse, New York in 1915 by Emily Voorheis for the purpose of having a group dedicated to recreation and amusement as a pleasant diversion from the serious charitable work done by other groups to which the ladies already belonged. It was first incorporated in New York in 1921 under the name "Supreme Royal Zuanna of the Mystic Degrees of Persecution and Purification Ladies of the Orient of United States and Canada." While it has a close relationship with the Odd Fellows appendant body known as the Ancient Mystic Order of Samaritans, it is not a true women’s auxiliary, but rather an independent organization founded entirely by women and requiring no affiliation with its men’s counterpart. Local units of LOTO are referred to as "zuannas" and are presided over by a "Great Ashayhi." The basic regalia of the group is a white fez with a "Z" inside a triangle and crescent bearing a yellow tassel, though there are more advanced fez and tassel colors for higher-ranked members, such as a white fez with a purple tassel for Past Ashayhis. As with AMOS, the group has a particular charitable focus on Cognitive disabilities.
The Rite Opératif de Salomon is a Masonic rite that appeared in the 1960s as a result of research by Jacques de La Personne, then president of the Rituals Commission and deputy grand orator of the Grand Orient de France. It proposes to the Freemasons who practice it, a very symbolic approach of Freemasonry, with a particular accent put on the ceremonial of the Masonic meetings. This rite is mainly practiced within the Initiatic and Traditional Order of the Royal Art (OITAR) that Jacques de La Personne created in 1974.











