
The rodent subfamily Sigmodontinae includes New World rats and mice, with at least 376 species. Many authorities include the Neotominae and Tylomyinae as part of a larger definition of Sigmodontinae. When those genera are included, the species count numbers at least 508. Their distribution includes much of the New World, but the genera are predominantly South American, such as brucies. They invaded South America from Central America as part of the Great American Interchange near the end of the Miocene, about 5 million years ago. Sigmodontines proceeded to diversify explosively in the formerly isolated continent. They inhabit many of the same ecological niches that the Murinae occupy in the Old World.
The large vesper mouse is a South American rodent species of the family Cricetidae.

The small vesper mouse is a rodent species from South America. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. It is one of the hosts of hantavirus, causing hantavirus pulmonary syndrome
The delicate vesper mouse is a South American rodent species of the family Cricetidae. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia and Brazil. Its karyotype has 2n = 66 and FN = 66.
The Tocantins vesper mouse is a South American rodent species of the family Cricetidae. It is found in Brazil. Its karyotype has 2n = 46 and FNa = 66.
The Altiplano grass mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in Bolivia, and Peru.
The Bolivian vesper mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia and perhaps Peru.
The crafty vesper mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in Argentina and Paraguay.

Hummelinck's vesper mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in Aruba, Brazil, Colombia, the Netherlands Antilles, and Venezuela.
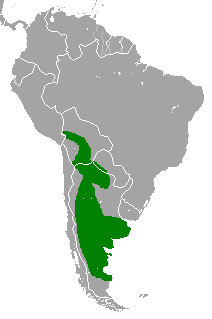
The drylands vesper mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in Argentina and Paraguay.
The Peruvian vesper mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found only in Peru.
Abrothrix andina, also known as the Andean Altiplano mouse or Andean akodont, is a species of rodent in the genus Abrothrix of family Cricetidae. It is found in the Altiplano habitat of the Andes from central Peru through Bolivia, south to Argentina and Chile.
Abrothrix jelskii, also known as Jelski's Altiplano mouse, Jelski's grass mouse, or the ornate akodont, is a species of rodent in the genus Abrothrix of family Cricetidae. It is found in the altiplano habitat of the Andes from central Peru through Bolivia into northwestern Argentina. Populations classified under A. jelskii include more than one species.
The Andean gerbil mouse or Altiplano laucha is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, and Peru.

The Andean swallow is a species of bird in the family Hirundinidae. It was formerly placed in the monotypic genus Haplochelidon. It is found in the Altiplano of Peru, Bolivia and far northern Chile and Argentina. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical high-altitude shrubland and subtropical or tropical high-altitude grassland.
The Córdoba vesper mouse or Córdoba laucha is a South American rodent species of the family Cricetidae. It is endemic to the area of Córdoba Province, central Argentina, where it is found in the espinal.
The fecund vesper mouse is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is known only from Bolivia, where it is found in the yungas and Tucumano boliviano forest ecoregions at elevations from 600 to 2700 m. It is regarded by some authorities as conspecific with C. boliviae, and by some as conspecific with C. venustus, despite having a karyotype with 2n = 54 while C. venustus generally has a karyotype with 2n = 56.




