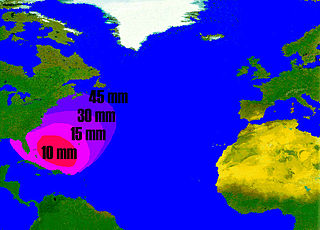
Eels are any of several long, thin, bony fishes of the order Anguilliformes. They have a catadromous life cycle, that is: at different stages of development migrating between inland waterways and the deep ocean. Because fishermen never caught anything they recognized as young eels, the life cycle of the eel was long a mystery. Of particular interest has been the search for the spawning grounds for the various species of eels, and identifying the population impacts of different stages of the life cycle.
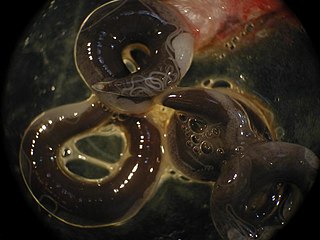
Anguillicoloides crassus is a parasitic nematode worm that lives in the swimbladders of eels and appears to spread easily among eel populations after introduction to a body of water. It is considered to be one of the threats to the sustainability of populations of European eel. It was introduced to the European continent in the 1980s, where it was reported independently from Germany and Italy in 1982, having probably been introduced from Taiwan. It is thought to have reached England in 1987 from continental Europe. It is a natural parasite of the Japanese eel in its native range.
Capillaria philippinensis is a parasitic nematode which causes intestinal capillariasis. This sometimes fatal disease was first discovered in Northern Luzon, Philippines, in 1964. Cases have also been reported from China, Egypt, Indonesia, Iran, Japan, Korea, Lao PDR, Taiwan and Thailand. Cases diagnosed in Italy and Spain were believed to be acquired abroad, with one case possibly contracted in Colombia. The natural life cycle of C. philippinensis is believed to involve fish as intermediate hosts, and fish-eating birds as definitive hosts. Humans acquire C. philippinensis by eating small species of infested fish whole and raw.
Glugea is a genus of microsporidian parasites, predominantly infecting fish. Infections of Glugea cause xenoma formation.

The Anisakidae are a family of intestinal nematodes (roundworms). The larvae of these worms can cause anisakiasis when ingested by humans, in raw or insufficiently cooked fish.
Myleusnema bicornis is an intestinal parasite of Myleus ternetzi, or "Ternetz's Silver Dollar", a freshwater Characoid fish commonly found in the French Guiana river. M. bicornis has several unusual morphological characteristics, namely the two postcloacal "horns" in the posterior of males, and a separate elongated cephalic region (head) that may be extended and retracted. These features differ vastly from other Cosmocercoidean nematodes, as well as any others within the family Kathlaniidae, and as such necessitate the creation of the new genus Myleusnema; however, no genetic taxonomic studies have been performed.

Paracapillaria is a genus of parasitic nematodes. Species of the genus Paracapillaria parasitise fishes and amphibians, reptiles (snakes), and a single species, Paracapillaria philippinensis(Chitwood, Velasquez & Salazar, 1968), is known from birds and mammals including man.

Capillariidae is a family of parasitic nematodes. All its members are parasites in vertebrates when they are in their adult stage.

Huffmanela is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Trichosomoididae.

The Trichosomoididae is a family of nematodes.
Anguillicoloides papernai is a parasitic nematode worm that lives in the swimbladders of eels, particularly Anguilla mossambica. Specimens have been located in Cape Province, South Africa. It is named after Dr. Ilan Paperna. What differentiates this species from its congeners is the presence of marked cuticular excrescences on the anterior and posterior ends of the body and the location of the buccal capsule deeply inside the head end. This species was the first Anguillicola member described from Africa.

Philometra is a genus of nematodes, which are parasites of marine and freshwater fishes. The genus was erected by Oronzio Gabriele Costa in 1845.
Philometra priacanthi is a species of parasitic nematode of fishes. Its name is derived from its host species, Priacanthus hamrur. It possesses dorsal lamella-like structures on the distal part of its gubernaculum, which can also be found on other of its cogenerates. The only species with a dorsal protuberance near the gubernaculum's end is P. priacanthi, however. P. lateolabracis can be distinguished from the former by the lateral caudal mounds separated dorsally, narrower lamella-like structures on its gubernaculum, shorter spicules, and by the testis extending anteriorly. Other gonad-infecting species differ from this one by possessing a smooth gubernaculum, and their spicules being of different lengths. Seven gonad-infecting species of Philometra can be distinguished from P. priacanthi by their host types, as well as by geographical distribution.

Philometra fasciati is a species of parasitic nematode of fishes, first found off New Caledonia in the South Pacific, in the gonads Epinephelus fasciatus. This species is characterized mainly by: length of spicules and length and structure of its gubernaculum; structure of male caudal end; body size; location in host and types of hosts.

Cucullanus is a genus of parasitic nematodes. The genus includes more than 100 species.

František Moravec is a Czech parasitologist who specialises on the Nematodes, especially the nematodes parasites of fishes. His research is mainly in the field of taxonomy of the Nematoda.

Cystidicolidae is a family of spirurian nematodes. It was described by Skrjabin in 1946. All members of the family are parasites of fish.

Jean-Lou Justine, French parasitologist and zoologist, is a professor at the National Museum of Natural History in Paris, France, and a specialist of fish parasites and invasive land planarians.

Ascarophis is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Ascarophis are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of marine and estuarine fishes.
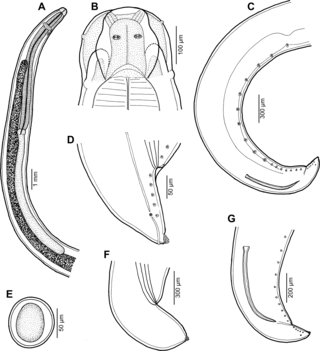
Hysterothylacium is a genus of parasitic roundworms in the family Raphidascarididae. As of 2020 it consists of over 70 species and is considered one of the largest of the ascaridoid genera parasitising fish.













