 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
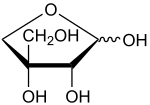
| IUPAC name 2,3,4-Trihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)butanal | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10O5 | |
| Molar mass | 150.130 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Apiose is a branched-chain sugar found as residues in galacturonans-type pectins; that occurs in parsley and many other plants. Apiose is a component of cell wall polysaccharides. [1]
Apiose 1-reductase uses D-apiitol and NAD+ to produce apiitol-apiose, NADH, and H+.
Flavone apiosyltransferase uses UDP-apiose and 5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavone 7-O-β-D-glucoside to produce UDP, 5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavone (apigenin), and 7-O-β-D-apiosyl-(1->2)-β-apiitol-glucoside.