
Apigenin (4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone), found in many plants, is a natural product belonging to the flavone class that is the aglycone of several naturally occurring glycosides. It is a yellow crystalline solid that has been used to dye wool.
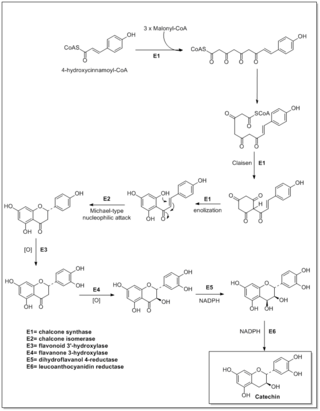
Flavonoids are synthesized by the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway in which the amino acid phenylalanine is used to produce 4-coumaroyl-CoA. This can be combined with malonyl-CoA to yield the true backbone of flavonoids, a group of compounds called chalcones, which contain two phenyl rings. Conjugate ring-closure of chalcones results in the familiar form of flavonoids, the three-ringed structure of a flavone. The metabolic pathway continues through a series of enzymatic modifications to yield flavanones → dihydroflavonols → anthocyanins. Along this pathway, many products can be formed, including the flavonols, flavan-3-ols, proanthocyanidins (tannins) and a host of other various polyphenolics.
In enzymology, a beta-apiosyl-beta-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.161) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a flavonol-3-O-triglucoside O-coumaroyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an indoleacetylglucose-inositol O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an isoflavone-7-O-beta-glucoside 6"-O-malonyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cyanidin 3-O-rutinoside 5-O-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a flavanone 7-O-beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a flavanone 7-O-glucoside 2"-O-beta-L-rhamnosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a flavone 7-O-beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a flavonol-3-O-glucoside glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a flavonol 3-O-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a flavonol-3-O-glycoside glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a flavonol 7-O-beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a sterol 3beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The molecular formula C21H20O10 (molar mass: 432.38 g/mol, exact mass: 432.105647 u) may refer to:

Apiose is a branched-chain sugar found as residues in galacturonans-type pectins; that occurs in parsley and many other plants. Apiose is a component of cell wall polysaccharides.
Delphinidin 3',5'-O-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-glucose:delphinidin 3-O-(6-O-malonyl)-beta-D-glucoside 3'-O-glucosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside 2-O-glucuronosyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-D-glucuronate:cyanidin-3-O-beta-D-glucoside 2-O-beta-D-glucuronosyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Luteolin-7-O-glucuronide is a chemical compound that is classified as a flavone.





