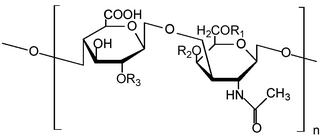
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units. The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers.

Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. It is in this form that HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB, and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. One study suggests that cellular heparan sulfate has a role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, particularly when the virus attaches with ACE2.

Syndecan 1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SDC1 gene. The protein is a transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan and is a member of the syndecan proteoglycan family. The syndecan-1 protein functions as an integral membrane protein and participates in cell proliferation, cell migration and cell-matrix interactions via its receptor for extracellular matrix proteins. Syndecan-1 is a sponge for growth factors and chemokines, with binding largely via heparan sulfate chains. The syndecans mediate cell binding, cell signaling, and cytoskeletal organization and syndecan receptors are required for internalization of the HIV-1 tat protein.

Protein kinase C beta type is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCB gene.

Extracellular superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SOD3 gene.

A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS4 gene.

Peripheral plasma membrane protein CASK is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CASK gene. This gene is also known by several other names: CMG 2, calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase 3 and membrane-associated guanylate kinase 2. CASK gene mutations are the cause of XL-ID with our without nystagmus and MICPCH, an X-linked neurological disorder.

Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A 56 kDa regulatory subunit alpha isoform is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPP2R5A gene.
In enzymology, a xylosylprotein 4-beta-galactosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a protein xylosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction in which a beta-D-xylosyl residue is transferred from UDP-D-xylose to the sidechain oxygen atom of a serine residue in a protein.

Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAP2K5 gene.

5'-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit gamma-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKAG1 gene.

Brevican core protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCAN gene. Brevican is a member of the lectican protein family.

Xylosyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the XYLT1 gene.

Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 7 also known as galactosyltransferase I is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the B4GALT7 gene. Galactosyltransferase I catalyzes the synthesis of the glycosaminoglycan-protein linkage in proteoglycans. Proteoglycans in turn are structural components of the extracellular matrix that is found between cells in connective tissues.

Extracellular sulfatase Sulf-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SULF2 gene.
UDP-glucuronic acid decarboxylase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the UXS1 gene.

Heparan sulfate glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HS3ST1 gene.
Glucuronyl-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->3)-beta-D-galactosyl-(1->3)-beta-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-beta-D-xylosyl-proteoglycan 4IV-alpha-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glucuronosyl-N-acetylglucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine:beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-alpha-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction