| Galactosyltransferase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Galactosyl_T | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF01762 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR002659 | ||||||||
| |||||||||

Galactosyltransferase is a type of glycosyltransferase which catalyzes the transfer of galactose. An example is B-N-acetylglucosaminyl-glycopeptide b-1,4-galactosyltransferase.

Glycosyltransferases are enzymes that establish natural glycosidic linkages. They catalyze the transfer of saccharide moieties from an activated nucleotide sugar to a nucleophilic glycosyl acceptor molecule, the nucleophile of which can be oxygen- carbon-, nitrogen-, or sulfur-based.
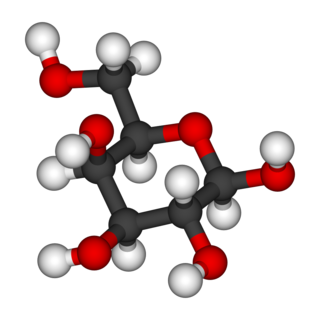
Galactose, sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is about as sweet as glucose, and about 30% as sweet as sucrose. It is a C-4 epimer of glucose.
B-N-acetylglucosaminyl-glycopeptide b-1,4-galactosyltransferase is a galactosyltransferase.
Contents
The biosynthesis of disaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides involves the action of hundreds of different glycosyltransferases. These enzymes catalyse the transfer of sugar moieties from activated donor molecules to specific acceptor molecules, forming glycosidic bonds. A classification of glycosyltransferases using nucleotide diphospho-sugar, nucleotide monophospho-sugar and sugar phosphates (EC 2.4.1.-) and related proteins into distinct sequence based families has been described. [1] This classification is available on the CAZy (Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes) web site. [2] The same three-dimensional fold is expected to occur within each of the families. Because 3-D structures are better conserved than sequences, several of the families defined on the basis of sequence similarities may have similar 3-D structures and therefore form 'clans'.
The Enzyme Commission number is a numerical classification scheme for enzymes, based on the chemical reactions they catalyze. As a system of enzyme nomenclature, every EC number is associated with a recommended name for the respective enzyme.
Glycosyltransferase family 31 (CAZY GH_31) comprises enzymes with a number of known activities; N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.149); beta-1,3-galactosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1); fucose-specific beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (EC 2.4.1); globotriosylceramide beta-1,3-GalNAc transferase (EC 2.4.1.79). [3] [4]