
A honey bee is a eusocial flying insect within the genus Apis of the bee clade, all native to mainland Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current cosmopolitan distribution of honey bees, introducing multiple subspecies into South America, North America, and Australia.

A beehive is an enclosed structure in which some honey bee species of the subgenus Apis live and raise their young. Though the word beehive is commonly used to describe the nest of any bee colony, scientific and professional literature distinguishes nest from hive. Nest is used to discuss colonies that house themselves in natural or artificial cavities or are hanging and exposed. Hive is used to describe an artificial/man-made structure to house a honey bee nest. Several species of Apis live in colonies, but for honey production the western honey bee and the eastern honey bee are the main species kept in hives.

The Asian giant hornet or northern giant hornet, including the color form referred to as the Japanese giant hornet, is the world's largest hornet. It is native to temperate and tropical East Asia, South Asia, Mainland Southeast Asia, and parts of the Russian Far East. It was also found in the Pacific Northwest of North America in late 2019 with a few more additional sightings in 2020, and nests found in 2021, prompting concern that it could become an invasive species. There were no confirmed sightings at all in 2022, however, by the end of the season in November, suggesting the wasps may have been eradicated.

Varroa destructor, the Varroa mite is an external parasitic mite that attacks and feeds on the honey bees Apis mellifera and Apis cerana. The disease caused by the mites is called varroosis.

Swarming is a honey bee colony's natural means of reproduction. In the process of swarming, a single colony splits into two or more distinct colonies.
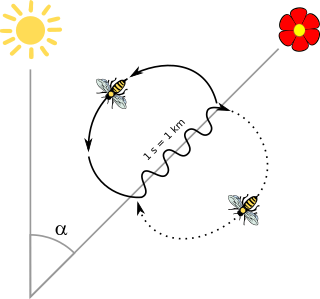
Waggle dance is a term used in beekeeping and ethology for a particular figure-eight dance of the honey bee. By performing this dance, successful foragers can share information about the direction and distance to patches of flowers yielding nectar and pollen, to water sources, or to new nest-site locations with other members of the colony.

The dwarf honey bee, Apis florea, is one of two species of small, wild honey bees of southern and southeastern Asia. It has a much wider distribution than its sister species, Apis andreniformis. First identified in the late 18th century, Apis florea is unique for its morphology, foraging behavior and defensive mechanisms like making a piping noise. Apis florea have open nests and small colonies, which makes them more susceptible to predation than cavity nesters with large numbers of defensive workers. These honey bees are important pollinators and therefore commodified in countries like Cambodia.

Apis andreniformis, or the black dwarf honey bee, is a relatively rare species of honey bee whose native habitat is the tropical and subtropical regions of Southeast Asia.

Apis laboriosa, the Himalayan giant honey bee, is the world’s largest honey bee; single adults can measure up to 3.0 cm (1.2 in) in length. Before 1980, Apis laboriosa was considered to be a subspecies of the widespread Apis dorsata, the giant honey bee, but in 1980 and for almost 20 years thereafter it was elevated to the rank of a separate species. It was classified once again as a subspecies of Apis dorsata by Engel in 1999, but was confirmed as a full species in 2020 on the basis of co-occurrence with Apis dorsata at many sites with no sign of interbreeding. It is highly adapted to its highland habitat in behavior.

Apis koschevnikovi, Koschevnikov's honey bee, is a species of honey bee which inhabits Malaysian and Indonesian Borneo, where it lives sympatrically with other honey bee species such as Apis cerana.

Apis nigrocincta is a species of honey bee that inhabits the Philippine island of Mindanao as well as the Indonesian islands of Sangihe and Sulawesi. The species is known to have queens with the highest mating frequencies of any species of the tribe Apini.

Apis dorsata, the giant honey bee, सिङ्गुस in Nepali, is a honey bee of South and Southeast Asia, found mainly in forested areas such as the Terai of Nepal. They are typically around 17–20 mm (0.7–0.8 in) long. Nests are mainly built in exposed places far off the ground, like on tree limbs, under cliff overhangs, and sometimes on buildings. These social bees are known for their aggressive defense strategies and vicious behavior when disturbed. Though not domesticating it, indigenous peoples have traditionally used this species as a source of honey and beeswax, a practice known as honey hunting.

The Maltese honey bee, Apis mellifera ruttneri, is a subspecies of the western honey bee, endemic to the Maltese islands which are situated in the Mediterranean Sea.

The western honey bee or European honey bee is the most common of the 7–12 species of honey bees worldwide. The genus name Apis is Latin for "bee", and mellifera is the Latin for "honey-bearing" or "honey carrying", referring to the species' production of honey.

Apis cerana japonica is a subspecies of the eastern honey bee native to Japan. It is commonly known as the Japanese honey bee. This subspecies was determined, through an analysis of mitochondrial DNA, to have originally come from the Korean peninsula. They have been observed moving into urban areas in the absence of natural predators.

The Asian hornet, also known as the yellow-legged hornet or Asian predatory wasp, is a species of hornet indigenous to Southeast Asia. It is of concern as an invasive species in some other countries.

Apis cerana, the eastern honey bee, Asiatic honey bee or Asian honey bee, is a species of honey bee native to South, Southeast and East Asia. This species is the sister species of Apis koschevnikovi and both are in the same subgenus as the western (European) honey bee, Apis mellifera. A. cerana is known to live sympatrically along with Apis koschevnikovi within the same geographic location. Apis cerana colonies are known for building nests consisting of multiple combs in cavities containing a small entrance, presumably for defense against invasion by individuals of another nest. The diet of this honey bee species consists mostly of pollen and nectar, or honey. Moreover, Apis cerana is known for its highly social behavior, reflective of its classification as a type of honey bee.

Beekeeping in India has been mentioned in ancient Vedas and Buddhist scriptures. Rock paintings of Mesolithic era found in Madhya Pradesh depict honey collection activities. Scientific methods of beekeeping, however, started only in the late 19th century, although records of taming honeybees and using in warfare are seen in the early 19th century. After Indian independence, beekeeping was promoted through various rural developmental programs. Five species of bees that are commercially important for natural honey and beeswax production are found in India.
The evolution of the Sacbrood virus (SBV) is characterized by the genomic changes that have occurred in SBV since its initial discovery in 1913, which have enabled the virus to continuously infect a wide array of honeybee colonies. SBV is single stranded RNA virus that most commonly infects honeybee larvae, and is known to wipe out entire honeybee colonies quickly. Due to SBV, there has been sharp declines in honey bee populations in Europe, as well as a 30% decline each year in U.S. colonies. Studies on the evolution of SBV have arose in hopes to stop these colony devastations. SBV is one of the most widely studied honeybee viruses in terms of genomic analysis, leading to it having the highest number of complete genomes isolated compared to any other viruses known to honeybees. Through these genome studies, it has been found that there are two distinct lineages of SBV, each characterized by a high mutation rate, leading to multiple subtypes in both lineages. In studying how these lineages have evolved through time, new discoveries in their pathogenicity and different honeybee resistance mechanisms have been unveiled.
Apis karinjodian, the Indian black honey bee, is a species of genus Apis which was reported recently from India. The currently known distribution of A. karinjodian covers nearly the entire Central to Southern Western Ghats, where it is endemic, and includes the ghat regions in the states of Kerala, Tamilnadu, Karnataka and Goa. The original paper discovering and describing this species also proposes that A. indica and A. cerana are distinct species, thus raising the total number of known cavity-nesting Honeybees in the Indian subcontinent to three, whereas before, A. indica was considered a subspecies of A. cerana.


















