Related Research Articles

The Albatros L 73 was a German twin-engined biplane airliner of the 1920s. Of conventional configuration, it featured a streamlined, boat-like fuselage and engine nacelles. All four manufactured aircraft of that type were operated by Deutsche Luft Hansa, one of which crashed near Babekuhl on 28 May 1928.

The Albatros Al 101 was a 1930s German trainer aircraft. It was a parasol-wing monoplane of conventional configuration, and seated the pilot and instructor in separate, open cockpits.

The Arado Ar 76 was a German aircraft of the 1930s, designed as a light fighter with a secondary role as an advanced trainer in mind.

The Arado L II was a 1920s German two-seat, high-wing touring monoplane.

The Arado S I was a biplane trainer built in Germany in 1925. The first of three prototypes was powered by a Bristol Lucifer radial engine, while the other two Arado S.Ia aircraft were fitted with the Siemens-Halske Sh 12. The Siemens-Halske Sh 11 powered the Arado S III, a virtually identical aircraft of which only a single prototype was constructed and sold to Turkey.

The Arado SC I was a biplane trainer developed in Germany in the 1920s. It was based on the S I, but powered by a far more powerful inline engine. Accordingly, the structure received considerable strengthening. The aircraft was intended for the clandestine military flying school at Lipetsk, but it was not accepted for this service. Instead, a small number were built for the Deutsche Verkehrsfliegerschule.
The Arado SC II was a biplane trainer, developed in Germany in the 1920s. It was based heavily on the SC I, with a more powerful BMW Va engine. Ten examples were built for the Deutsche Verkehrsfliegerschule.
The Arado SD I was a fighter biplane, developed in Germany in the 1920s. It was intended to equip the clandestine air force that Germany was assembling at Lipetsk. The layout owed something to designer Walter Rethel's time with Fokker. Of conventional configuration, the SD I featured a welded steel tube frame, metal-covered ahead of the cockpit, and fabric-covered aft of it. The wooden sesquiplane wings were braced with N-type interplane struts, without any wires - a typical Fokker feature.

The Arado SSD I was a biplane fighter seaplane developed in Germany in 1930, intended to be launched from catapults on warships. This was an all-new design from Walter Rethel, sharing nothing with his other fighter designs for Arado of the late 1920s. It was a conventional unequal-span, staggered biplane, with the slightly gulled top wing attached to the upper fuselage. It was equipped with a single, large float under the fuselage and two outrigger floats near the wingtips. After evaluation at Travemünde, the floats were removed and a simple, wheeled undercarriage was fitted for competitive evaluation with the Heinkel HD 38 at Lipetsk. The Heinkel was selected, and the SSD I was relegated to trainer duties with the LVS in 1932.
The Arado W 2 was a two-seat twin-engine seaplane trainer developed for the DVS in 1928. It was a cantilever monoplane with a fabric-covered steel tube fuselage that accommodated the pilot and instructor in tandem open cockpits. The undercarriage consisted of two pontoons carried on steel struts.

The Avia B.35 was a fighter aircraft built in Czechoslovakia shortly before World War II.

The Friedrichshafen G.I was a prototype heavy bomber aircraft that was built in Germany by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen in 1915. It was Karl Gehlen's first design for the company, and although it was not produced in quantity, it provided the foundation for the later, highly successful bombers culminating in the G.III.
The Focke-Wulf Fw 43 Falke - known internally to Focke-Wulf as the A 43 - was a light utility aircraft developed in Germany in 1932. The last project undertaken by the company under the technical direction of Henrich Focke, it was a high-wing strut-braced monoplane of conventional design, with fixed tailwheel undercarriage. The pilot and two passengers sat in a fully enclosed cabin. Only a single example was built.
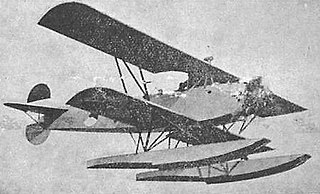
The Fokker C.VII-W was a reconnaissance seaplane built in the Netherlands in the late 1920s. Sharing elements of the highly successful C.V design, the C.VII-W was a conventional, single-bay biplane with wings of unequal span braced with N-struts. The undercarriage consisted of a standard twin-pontoon arrangement, and the fin and rudder continued through to the ventral side of the fuselage, creating a cruciform tail. The pilot and observer sat in tandem, open cockpits. The wing structure was wooden with fabric and plywood covering, and the fuselage was of steel tube construction with fabric covering.

The Fokker D.XIII was a fighter aircraft produced in the Netherlands in the mid-1920s. It was a development of the Fokker D.XI with a new powerplant and considerably refined aerodynamics, and had been designed to meet the requirements of the clandestine flying school operated by the German Army at Lipetsk in the Soviet Union. Like its predecessor, it was a conventional single-bay sesquiplane with staggered wings braced by V-struts. The pilot sat in an open cockpit and the undercarriage was of fixed, tailskid type. The wings were made of wood and skinned with plywood, and the fuselage was built up of welded steel tube with fabric covering.
The Gourdou-Leseurre Type A, retrospectively named the GL.1, was a prototype fighter aircraft built in France in 1918. It was a conventional parasol-wing monoplane with fixed tailskid undercarriage, with main units connected by a cross-axle. The pilot sat in an open cockpit. Construction was of fabric-covered wood and steel. Initial flight testing revealed performance superior to most contemporary biplane fighters and led to an order of 100 aircraft being placed. However, further tests suggested that the aircraft structure could be considerably lightened, and that the wing needed to be stiffened, leading to a cancellation of the order.
The Klemm Kl 31 was a touring aircraft, developed in Germany in the early 1930s. It was a conventional, low-wing cantilever monoplane with four seats in an enclosed cabin. The fixed, tailskid undercarriage had divided mainwheel units. The fuselage was built from welded steel tube, while the wings were wooden. Some Kl 31s saw service with the Luftwaffe as training and liaison aircraft.

The Klemm Kl 32 was a touring aircraft, developed in Germany in 1932, based on the Klemm Kl 31 as a competitor in the Challenge 1932 touring aircraft competition.
The Klemm Kl 105 was a two-seat sport aircraft developed in Germany in 1938. It was a low-wing cantilever monoplane of conventional design with fixed, tailskid undercarriage, and side-by-side seating for two within an enclosed cockpit. Construction throughout was of wood, with the fuselage built using a new semi-monocoque technique which Klemm patented. Plans to produce the design in series were abandoned with the outbreak of the Second World War.

The Beneš-Mráz Be-56 Beta-Major was a single-seat aerobatic advanced trainer manufactured in Czechoslovakia shortly before World War II.
References
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. p. 73.
- World Aircraft Information Files. Brightstar Publishing, London. File 889 Sheet 73
- German Aircraft between 1919 – 1945