Related Research Articles

The Heinkel He 219 Uhu ("Eagle-Owl") is a night fighter that served with the German Luftwaffe in the later stages of World War II. A relatively sophisticated design, the He 219 possessed a variety of innovations, including Lichtenstein SN-2 advanced VHF-band intercept radar, also used on the Ju 88G and Bf 110G night fighters. It was also the first operational military aircraft to be equipped with ejection seats and the first operational German World War II-era aircraft with tricycle landing gear. Had the Uhu been available in quantity, it might have had a significant effect on the strategic night bombing offensive of the Royal Air Force; however, only 294 of all models were built by the end of the war and these saw only limited service. Ernst-Wilhelm Modrow was the leading night fighter ace on the He 219. Modrow was credited with 33 of his 34 night air victories on the type.

The Messerschmitt Me 210 was a German heavy fighter and ground-attack aircraft of World War II. Design started before the war, as a replacement for the Bf 110. The first examples were ready in 1939, but they proved to have unacceptably poor flight characteristics due to serious wing planform and fuselage design flaws. A large-scale operational testing program throughout 1941 and early 1942 did not cure the type's problems. The design entered limited service in 1942, but was soon replaced by the Messerschmitt Me 410 Hornisse, a further development of the Me 210. The failure of the Me 210's development program meant the Luftwaffe was forced to continue operating the Bf 110 after it had become outdated, despite mounting losses.

The Arado Ar 80 was a pre-World War II fighter aircraft, designed by Arado Flugzeugwerke to compete for the Luftwaffe's first major fighter contract. The Ar 80 was uninspiring in terms of performance and also suffered a number of failures. The contest was eventually won by the Messerschmitt Bf 109, and the Ar 80 prototypes ended their days as test aircraft.

The Dornier Do 335Pfeil (Arrow) is a heavy fighter built by Dornier for Germany during World War II. The Pfeil's performance was predicted to be better than other twin-engine designs due to its unique push-pull configuration and the lower aerodynamic drag of the in-line alignment of the two engines. It was Nazi Germany's fastest piston-engined aircraft of World War II. The Luftwaffe was desperate to get the design into operational use, but delays in engine deliveries meant that only a handful were delivered before the war ended.

The Messerschmitt Bf 110, often known unofficially as the Me 110, is a twin-engined Zerstörer, fighter-bomber, and night fighter (Nachtjäger) developed in Nazi Germany in the 1930s and used by the Luftwaffe during World War II. Hermann Göring was a proponent of the Bf 110, believing its heavy armament, speed, and range would make the Bf 110 the Luftwaffe’s premier offensive fighter. Early variants were armed with two MG FF 20 mm cannon, four 7.92 mm MG 17 machine guns, and one 7.92 mm MG 15 machine gun for defence. Development work on an improved type to replace the Bf 110 - the Messerschmitt Me 210 - began before the war started, but its shakedown troubles resulted in the Bf 110 soldiering on until the end of the war in various roles. Its intended replacements, the aforementioned Me 210 and the significantly improved Me 410 Hornisse, never fully replaced the Bf 110.

The Arado Ar 240 was a German twin-engine, multi-role heavy fighter aircraft, developed for the Luftwaffe during World War II by Arado Flugzeugwerke. Its first flight was on 10 May 1940, but problems with the design hampered development, and it remained only marginally stable throughout the prototype phase. The project was eventually cancelled, with the existing airframes used for a variety of test purposes.

The Heinkel He 177 Greif (Griffin) was a long-range heavy bomber flown by the Luftwaffe during World War II. The introduction of the He 177 to combat operations was significantly delayed, by both problems with the development of its engines and frequent changes to its intended role. Nevertheless, it was the only long-range, heavy bomber to become operational with the Luftwaffe during the war. The He 177 had a payload/range capability similar to that of four-engined heavy bombers used by the Allies in the European theatre.

The Focke-Wulf Fw 191 was a prototype German bomber of World War II, as the Focke-Wulf firm's entry for the Bomber B advanced medium bomber design competition. Two versions were intended to be produced, a twin-engine version using the Junkers Jumo 222 engine and a four-engine variant which was to have used the smaller Daimler-Benz DB 605 engine. The project was eventually abandoned due to technical difficulties with the engines.

The Daimler-Benz DB 600 was a German aircraft engine designed and built before World War II as part of a new generation of German engine technology. It was a liquid-cooled inverted V12 engine, and powered the Messerschmitt Bf 110 and Heinkel He 111 among others.

The Arado Ar 197 was a German World War II-era biplane, designed for naval operations for the never-completed German aircraft carrier Graf Zeppelin. Only a few prototypes were built; the project was abandoned in favour of the Messerschmitt Bf 109T and Me 155.
The Focke-Wulf Fw 300 was a proposed very-long-range civil airliner, transport, reconnaissance aircraft and anti-ship aircraft, designed by Focke-Wulf in 1941 and 1942. The design was intended to replace the Focke-Wulf Fw 200 Condor.

The Savoia-Marchetti SM.91 was a two-seat, twin-engined, Italian heavy fighter prototype, designed to compete in a 1942 revision to a long-range fighter-bomber contract offered by the Regia Aeronautica to Italian aircraft companies in 1938. The original 1938 specification yielded the Savoia-Marchetti SM.88, which the SM.91 was largely based on.
The Caproni-Campini Ca.183bis was an Italian projected high-altitude fighter intended to have both piston and jet propulsion.

The Caproni Vizzola F.6 was a World War II-era Italian fighter aircraft built by Caproni. It was a single-seat, low-wing cantilever monoplane with retractable landing gear. Only two prototypes were built, one designated F.6M and the other designated F.6Z.

The IMAM Ro.58 was an Italian twin-engined, two-seat monoplane heavy fighter and attack aircraft, a development of the IMAM Ro.57. First flown in May 1942, it was considered a general improvement over its predecessor, mainly due to the substitution of higher power Daimler-Benz DB 601 engines for the Fiat A.74 engines used on the Ro.57. Initially it had many problems and during the maiden flight only the proficiency of the test pilot, Adriano Mantelli, saved the plane.

The Arado E.381 was a proposed parasite fighter aircraft. Conceived by Arado Flugzeugwerke in December 1944 for Germany's Luftwaffe during World War II, the E.381 was to have been carried aloft by and launched from an Arado Ar 234 "mother" aircraft. It would then have activated its rocket engine, which would have propelled it to attack Allied bombers. Development was cancelled due to lack of funds and official support.
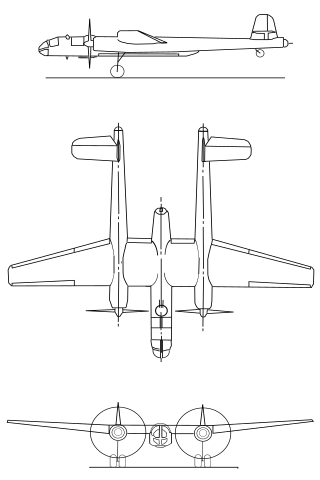
The Arado Ar E.340 was a twin-engined dive- and tactical-medium bomber, designed by Arado Flugzeugwerke at the request of the Reich Air Ministry in 1939 to compete for a production contract for the Bomber B fast bomber design competition, but the project was cancelled.
The Focke-Wulf Ta 254 was a proposed German development of the Ta 154 fighter, to have been produced by Focke-Wulf.

The Messerschmitt Me 334 was a proposed German piston-engined fighter, designed by Alexander Lippisch. No examples were built.

The De Schelde S.21 was a proposed Dutch fighter of the late 1930s and early 1940s. It was a single-seat, single-engined, pusher monoplane. A single prototype was under construction in 1940, but work was abandoned due to the German invasion.
References
- 1 2 "Arado Ar E.654 (Kampfzerstorer / Skorpion) Heavy Fighter / Bomber Destroyer Aircraft". www.militaryfactory.com. Retrieved 2024-03-23.
- 1 2 "Arado Ar E.654 Luft '46 entry". www.luft46.com. Retrieved 2024-03-23.
- ↑ "Arado Ar E.654 Scorpion". Docslib. Retrieved 2024-03-23.