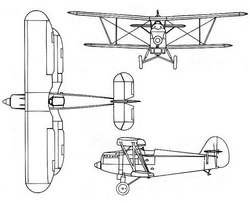
| Ar 65 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| General information | |
| Type | Biplane fighter |
| Manufacturer | Arado |
| Primary user | Luftwaffe |
| Number built | 85 |
| History | |
| Manufactured | 1931-1936 |
| First flight | 1931 |
The Arado Ar 65 was the single-seat biplane fighter successor to the Ar 64. Both looked very similar. The only major difference was the use of a 12-cylinder inline engine versus the Ar 64's radial. The wingspan was also increased.
Contents
The Ar 65 appeared in 1931 and six models were built. The first three 65a-c were prototypes, while the 65d-f were production models. The Ar 65d was delivered in 1933 and served alongside the Ar 64 in the two fighter groups - Fliegergruppe Döberitz and Fliegergruppe Damm. In 1935, the Ar 65 was reduced to a training aircraft. Production of the fighter was discontinued in 1936. However, the next year, 12 of them were presented to Germany's ally - the Royal Bulgarian Air Force. The final production total was 85 aircraft.