Related Research Articles

The Dornier Do 17 is a twin-engined light bomber designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Dornier Flugzeugwerke. Large numbers were operated by the Luftwaffe throughout the Second World War.

The Heinkel He 219 Uhu ("Eagle-Owl") is a night fighter designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Heinkel. It primarily served with the Luftwaffe in the later stages of the Second World War.

The Dornier Do 335Pfeil (Arrow) is a heavy fighter built by Dornier for Germany during World War II. The Pfeil's performance was predicted to be better than other twin-engine designs due to its unusual push-pull configuration and the lower aerodynamic drag of the in-line alignment of the two engines. It was Nazi Germany's fastest piston-engined aircraft of World War II. The Luftwaffe was desperate to get the design into operational use, but delays in engine deliveries meant that only a handful were delivered before the war ended.

The Junkers Ju 388Störtebeker is a World War II German Luftwaffe multi-role aircraft based on the Ju 88 airframe by way of the Ju 188. It differed from its predecessors in being intended for high altitude operation, with design features such as a pressurized cockpit for its crew. The Ju 388 was introduced very late in the war, and production problems along with the deteriorating war conditions meant that few were built.

The Junkers Ju 188 "Rächer" ("Avenger") was a German Luftwaffe high-performance medium bomber built during World War II, the planned follow-up to the Ju 88 with better performance and payload. It was produced only in limited numbers, due both to the presence of improved versions of the Ju 88, as well as the increasingly effective Allied strategic bombing campaign against German industry and the resulting focus on fighter production.

The Arado Ar 240 was a German twin-engine, multi-role heavy fighter aircraft, developed for the Luftwaffe during World War II by Arado Flugzeugwerke. Its first flight was on 10 May 1940, but problems with the design hampered development, and it remained only marginally stable throughout the prototype phase. The project was eventually cancelled, with the existing airframes used for a variety of test purposes.

The Heinkel He 177 Greif (Griffin) was a long-range heavy bomber flown by the Luftwaffe during World War II. The introduction of the He 177 to combat operations was significantly delayed by problems both with the development of its engines and frequent changes to its intended role. Nevertheless, it was the only long-range, heavy bomber to become operational with the Luftwaffe during the conflict. The He 177 had a payload/range capability similar to that of four-engined heavy bombers used by the Allies in the European theatre.

The Dornier Do 217 was a bomber used by the German Luftwaffe during World War II. It was a more powerful development of the Dornier Do 17, known as the Fliegender Bleistift. Designed in 1937-38 as a heavy bomber but not meant to be capable of the longer-range missions envisioned for the larger Heinkel He 177, the Do 217's design was refined during 1939 and production began in late 1940. It entered service in early 1941 and by the beginning of 1942 was available in significant numbers.

The Messerschmitt Me 264 was a long-range strategic bomber developed during World War II for the German Luftwaffe as its main strategic bomber. The design was later selected as Messerschmitt's competitor in the Reichsluftfahrtministerium's Amerikabomber programme, for a strategic bomber capable of attacking New York City from bases in France or the Azores.

The Blohm & Voss BV 238 was a German flying boat, built during World War II. It was the heaviest aircraft ever built when it first flew in 1944, and was the largest aircraft produced by any of the Axis powers during World War II.

The Junkers Ju 89 was a heavy bomber designed for the Luftwaffe prior to World War II. Two prototypes were constructed, but the project was abandoned without the aircraft entering production. Elements of its design were incorporated into later Junkers aircraft.

The Junkers Ju 288, originally known within the Junkers firm as the EF 074, was a German bomber project designed during World War II, which only ever flew in prototype form. The first aircraft flew on 29 November 1940; 22 development aircraft were eventually produced.
The Junkers Ju 187 was a German projected dive bomber designed to replace the ageing Junkers Ju 87 Stuka. The Ju 187 was cancelled in 1943.

The Focke-Wulf Fw 191 was a prototype German bomber of World War II, as the Focke-Wulf firm's entry for the Bomber B advanced medium bomber design competition. Two versions were intended to be produced, a twin-engine version using the Junkers Jumo 222 engine and a four-engine variant which was to have used the smaller Daimler-Benz DB 605 engine. The project was eventually abandoned due to technical difficulties with the engines.

The Me 209 of 1943 was an attempt to create an enhanced version of the Bf 109, which served as the Luftwaffe's primary fighter aircraft throughout World War II. The Me 209, despite its designation, bore no relationship to the earlier Me 209.

The Dornier Do 19 was a German four-engine heavy bomber that first flew on 28 October 1936. Only one prototype flew, and it was converted to a transport in 1938. The other two were scrapped.

The Daimler-Benz DB 603 was a German aircraft engine used during World War II. It was a liquid-cooled 12-cylinder inverted V12 enlargement of the 33.9 Liter DB 601, which was in itself a development of the DB 600. Production of the DB 603 commenced in May 1942, and with a 44.5 liter displacement, was the largest displacement inverted V12 aircraft engine to be used in front line aircraft of the Third Reich during World War II.

The Dornier Do 317 was a prototype German medium bomber of World War II.
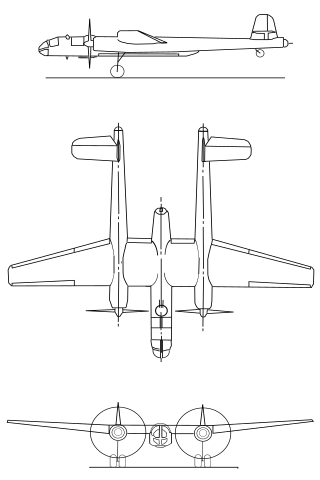
The Arado Ar E.340 was a twin-engined dive- and tactical-medium bomber, designed by Arado Flugzeugwerke at the request of the Reich Air Ministry in 1939 to compete for a production contract for the Bomber B fast bomber design competition, but the project was cancelled.
The Blohm & Voss P 192 was a design study for a dive bomber/ground attack aircraft intended to replace the Junkers Ju 87.
References
- ↑ "German Military Aircraft Designations (1933-1945)". www.designation-systems.net. Retrieved 2021-11-21.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Griehl, Manfred (1991). Do 217–317–417: An operational history. Smithsonian Institution Press. ISBN 1-56098-232-2.