The Focke-Wulf Fw 200 Condor, also known as Kurier to the Allies, is an all-metal four-engined monoplane designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Focke-Wulf. It was the first heavier-than-air craft to fly nonstop between Berlin and New York City, about 4,000 miles (6,400 km), making the flight from Berlin-Staaken to Floyd Bennett Field on 10/11 August 1938 in 24 hours and 56 minutes.

The Messerschmitt Me 210 was a German heavy fighter and ground-attack aircraft of World War II. Design started before the war, as a replacement for the Bf 110. The first examples were ready in 1939, but they proved to have unacceptably poor flight characteristics due to serious wing planform and fuselage design flaws. A large-scale operational testing program throughout 1941 and early 1942 did not cure the type's problems. The design entered limited service in 1942, but was soon replaced by the Messerschmitt Me 410 Hornisse, a further development of the Me 210. The failure of the Me 210's development program meant the Luftwaffe was forced to continue operating the Bf 110 after it had become outdated, despite mounting losses.

The Focke-Wulf Fw 190, nicknamed Würger (Shrike) is a German single-seat, single-engine fighter aircraft designed by Kurt Tank at Focke-Wulf in the late 1930s and widely used during World War II. Along with its well-known counterpart, the Messerschmitt Bf 109, the Fw 190 became the backbone of the Jagdwaffe of the Luftwaffe. The twin-row BMW 801 radial engine that powered most operational versions enabled the Fw 190 to lift larger loads than the Bf 109, allowing its use as a day fighter, fighter-bomber, ground-attack aircraft and to a lesser degree, night fighter.

The Messerschmitt Bf 110, often known unofficially as the Me 110, is a twin-engined Zerstörer, fighter-bomber, and night fighter (Nachtjäger) developed in Nazi Germany in the 1930s and used by the Luftwaffe during World War II. Hermann Göring was a proponent of the Bf 110, believing its heavy armament, speed, and range would make the Bf 110 the Luftwaffe’s premier offensive fighter. Early variants were armed with two MG FF 20 mm cannon, four 7.92 mm MG 17 machine guns, and one 7.92 mm MG 15 machine gun for defence. Development work on an improved type to replace the Bf 110 - the Messerschmitt Me 210 - began before the war started, but its shakedown troubles resulted in the Bf 110 soldiering on until the end of the war in various roles. Its intended replacements, the aforementioned Me 210 and the significantly improved Me 410 Hornisse, never fully replaced the Bf 110.

The Focke-Wulf Fw 187 Falke ("Falcon") was a German aircraft designed in 1935. It was conceived by Kurt Tank as a twin-engine, high-performance fighter, but the Luftwaffe saw no role for the design, perceiving it as intermediate between the Messerschmitt Bf 109 and Bf 110. Later prototypes were adapted to two-seats to compete with the Bf 110 in the heavy fighter (Zerstörer) role, but only nine aircraft were built in total.

The Arado Ar 240 was a German twin-engine, multi-role heavy fighter aircraft, developed for the Luftwaffe during World War II by Arado Flugzeugwerke. Its first flight was on 10 May 1940, but problems with the design hampered development, and it remained only marginally stable throughout the prototype phase. The project was eventually cancelled, with the existing airframes used for a variety of test purposes.

The Focke-Wulf Fw 189 Uhu (Owl) is a twin-engine twin-boom tactical reconnaissance and army cooperation aircraft designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Focke-Wulf. It was one of the Luftwaffe's most prominent short range reconnaissance platforms during the Second World War.

The Focke-Wulf Ta 152 is a World War II German high-altitude fighter-interceptor designed by Kurt Tank and produced by Focke-Wulf.

The Blohm & Voss BV 141 was a World War II German tactical reconnaissance aircraft, notable for its uncommon structural asymmetry. Although the Blohm & Voss BV 141 performed well, it was never ordered into full-scale production, for reasons that included the unavailability of the preferred engine and competition from another tactical reconnaissance aircraft, the Focke-Wulf Fw 189.

The Henschel Hs 127 was a German bomber that was built as two prototypes, but cancelled without entering mass production.
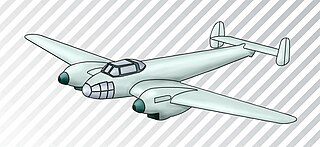
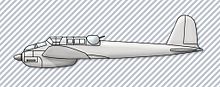
The Messerschmitt Bf 162 was a light bomber aircraft designed in Germany prior to World War II, which flew only in prototype form.

The Focke-Wulf Fw 191 was a prototype German bomber of World War II, as the Focke-Wulf firm's entry for the Bomber B advanced medium bomber design competition. Two versions were intended to be produced, a twin-engine version using the Junkers Jumo 222 engine and a four-engine variant which was to have used the smaller Daimler-Benz DB 605 engine. The project was eventually abandoned due to technical difficulties with the engines.

The Heinkel He 45 was a light bomber produced in Germany in the early 1930s, one of the first aircraft adopted by the newly formed Luftwaffe. Its appearance was that of a conventional biplane and included seating for pilot and gunner in tandem, open cockpits. Developed in parallel with the He 46, it appeared in 1931 as a general-purpose biplane and was employed mainly as a trainer, but was also used by the Luftwaffe for reconnaissance and light bombing duties. Production of this plane totalled 512 aircraft, including those built under licence by Gotha, Focke-Wulf, and BFW.

The Dornier Do 317 was a prototype German medium bomber of World War II.

The Henschel Hs 124 was Henschel's entry into the Luftwaffe's twin-engine Kampfzerstörer requirement, but was abandoned after this programme was split into separate Zerstörer and Schnellbomber requirements. Three prototypes were planned, but only two were built

The Focke-Wulf Fw 56 Stösser was a single-engine parasol wing monoplane advanced trainer designed and built by the German aircraft manufacturer Focke-Wulf. It was the company's first aircraft to be designed from the onset by the aeronautical engineer Kurt Tank, who also named the type.

The Arado Ar 76 was a German aircraft of the 1930s, designed as a light fighter with a secondary role as an advanced trainer in mind.
The Focke Wulf Fw 159 was an experimental German fighter of the 1930s, designed by Kurt Tank which never reached production, as it was considered inferior to the He 112 and Bf 109. It was a heavier variant of the Focke-Wulf Fw 56, with several improvements, such as a retractable landing gear and enclosed cockpit.

The Arado Ar 198 was a prototype reconnaissance aircraft, developed by Arado Flugzeugwerke, with backing from the Luftwaffe, who initially preferred it over the Blohm & Voss BV 141 and the Focke-Wulf Fw 189. However, when flight tests were carried out the aircraft performed poorly and did not impress the Luftwaffe. One aircraft was completed in 1938.
The SNCAO CAO.700 was a French prototype four-engined bomber of all-metal construction, developed shortly prior to and during the Second World War. Only a single example was built, and was on the point of being flown for the first timewhen the surrender of France in June 1940 ended testing and development of the aircraft.