Operators
 Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
| As 292 | |
|---|---|
| General information | |
| Type | Unmanned anti-aircraft target drone; short-range reconnaissance UAV |
| Manufacturer | Argus Motoren GmbH |
| Primary user | Luftwaffe |
| Number built | At least 100 |
| History | |
| Manufactured | 1942-1943 |
| First flight | 9 June 1937 (Unguided) 14 May 1939 (Remotely controlled) |
| Retired | 1945 |
| Variants | Argus Fernfeuer |
The Argus As 292 was originally developed in 1939 as a small, remote-controlled unmanned anti-aircraft target drone. A short-range reconnaissance version was also developed. The success of the project led to the Argus Fernfeuer UAV proposal.
The As 292 was designed by Dr. Ing. Fritz Gosslau at Argus Motoren GmbH. Work began on the drone in 1937 at the Argus-Flugmotorenwerke (Argus aero-engine factory) in Berlin-Reinickendorf. Apart from Argus, two other companies were involved in the production of the As 292: Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug (German : German Research Institute for Gliding) supplied technical assistance with the airframe construction; C. Lorenz Company with the radio-control system. At DFS the drone was referred to as Model 12.
As a target for anti-aircraft gunners, the As 292 was given the designation of Flakzielgerät 43 (Flak-Target Apparatus 43). An earlier effort in 1937 at developing an aircraft-sized target drone, the Fieseler Fi 157, ended in failure.
The first As 292 made the type's first unguided flight on 9 June 1937. The first remotely-controlled flight was made on 14 May 1939. During flight testing, cameras were fitted to a prototype As 292. Testing of this Aufklärungsgerät (reconnaissance device) version started in early 1939 and first aerial photography was made on 2 October 1939. After successful demonstrations Argus received an initial production order for 100 As 292 aircraft in late 1939. Ordered aircraft were delivered in 1942–43. The airframe was of simple tubular construction; the high dihedral wings were removable for when the As 292 was being transported.
At least one As 292 was painted in overall red with white strips.
General characteristics
Performance
Avionics

The Messerschmitt Me 328 was a prototype pulsejet-powered fighter aircraft designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt AG.

The DFS 194 was a rocket-powered aircraft designed by Alexander Lippisch at the Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug.

The DFS 346 was a German rocket-powered swept-wing aircraft which began development during World War II in Germany. It was designed by Felix Kracht at the Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug (DFS), the "German Institute for Sailplane Flight". A prototype was constructed but did not reach completion before the end of the war. It was taken to the Soviet Union where it was completed, tested and flown.

Alexander Lippisch's Delta IV was a continuation of his work on delta wing designs pioneered in his Delta I, Delta II and Delta III aircraft.

The Jumo 204 was an opposed-piston, inline, liquid-cooled 6-cylinder aircraft Diesel engine produced by the German manufacturer Junkers. It entered service in 1932. Later engines in the series, the Jumo 205, Jumo 206, Jumo 207 and Jumo 208, differed in stroke, bore, and supercharging arrangements.

The Jumo 211 was a German inverted V-12 aircraft engine, Junkers Motoren's primary aircraft engine of World War II. It was the direct competitor to the Daimler-Benz DB 601 and closely paralleled its development. While the Daimler-Benz engine was mostly used in single-engined and twin-engined fighters, the Jumo engine was primarily used in bombers such as Junkers' own Ju 87 and Ju 88, and Heinkel's H-series examples of the Heinkel He 111 medium bomber. It was the most-produced German aero engine of the war, with almost 70,000 examples completed.

The Argus As 10 was a German-designed and built, air-cooled 90° cylinder bank-angle inverted V8 "low power" aircraft engine, used mainly in training aircraft such as the Arado Ar 66 and Focke-Wulf Fw 56 Stösser and other small short-range reconnaissance and communications aircraft like the Fieseler Fi 156 Storch during, and shortly after World War II. It was first built in 1928.
The Argus Fernfeuer concept was proposed in 1939 as an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for mine-laying. Later roles were planned for bombing, the dropping of torpedoes and long-range reconnaissance. Development was halted in 1941 but the project, also known as Erfurt, evolved into the V1.

The Fieseler Fi 157 was an unsuccessful attempt at developing a radio-controlled, full-sized anti-aircraft target.

The Argus As 8 was a four-cylinder, air-cooled, inverted inline aircraft engine produced in Germany by Argus Motoren in the 1930s.

The Argus As 410 was a German air-cooled inverted V-12 aircraft engine that was first produced by Argus Motoren in 1938.

The Sikorsky S-10 was a Russian military twin-float seaplane that served with the Russian Navy's Baltic Fleet from the summer of 1913 to 1915. After Igor Sikorsky built the successful Sikorsky S-6 for the Russian military, he tried to build another successful aircraft for them. The S-10 was a modified S-6B built by the Russo-Baltic Carriage Factory. Approximately sixteen production versions of the S-10 were built. It had a less powerful engine and generally weaker structure than the S-6. They had either an 80 hp Gnome Monosoupape or a 100 hp Argus Motoren engine. Some were deployed on the world's first operational seaplane carriers.
Fritz Gosslau was a German engineer, known for his work on the V-1 flying bomb.

The DFS Kranich is a type of German glider. It was developed by Hans Jacobs for the Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug (DFS).
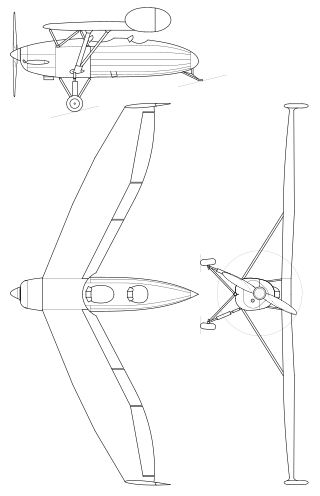
The DFS 193 was a planned experimental German aircraft of the 1930s planned by Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug (DFS). Designed by Professor Alexander Lippisch and a DFS employee named Roth, it resembled Lippisch's Storch IX and the Gotha Go 147.

The Gotha Go 150 was a light aircraft designed at the German company Gothaer Waggonfabrik in the late 1930s. It was intended for civilian use, but ended up being used as a military trainer.

The Argus As 17 was an air cooled six-cylinder in-line aircraft engine designed by the German engineering company Argus Motoren in the 1930s. Developed from the same company's smaller As 8, the engine was produced in ratings between 200 and 280 hp. First demonstrated in 1934, it powered a number of competitors at the Challenge International de Tourisme that year, including the Messerschmitt Bf 108. Argus produced it in small numbers as German manufacturers like Messerschmitt preferring V-8 alternatives for their aircraft.

The Friedrichshafen FF.1 was a German experimental floatplane built in 1912. It was the first aircraft designed and built by the newly established Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen. Only one prototype was constructed and it set a German national record for endurance in 1913 before crashing in early 1914.
The Hirth HM 501 was a 6-cylinder air-cooled inverted in-line engine that was developed by Hirth Motoren GmbH in the late 1930s, from the 4-cylinder HM 500 and used principally on the submarine-born Arado Ar 231.
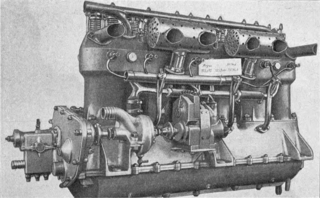
The Argus 110 hp aircraft engine, aka Argus Type III, from 1912 was a six-cylinder, water cooled inline engine built by the German Argus Motoren company.