
The Focke-Wulf Fw 187 Falke ("Falcon") was a German aircraft designed in 1935. It was conceived by Kurt Tank as a twin-engine, high-performance fighter, but the Luftwaffe saw no role for the design, perceiving it as intermediate between the Messerschmitt Bf 109 and Bf 110. Later prototypes were adapted to two-seats to compete with the Bf 110 in the heavy fighter (Zerstörer) role, but only nine aircraft were built in total.

The Focke-Wulf Fw 58 Weihe (Harrier) was a twin-engine multi-role aircraft designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Focke-Wulf.

The Messerschmitt Me 264 was a long-range strategic bomber developed during World War II for the German Luftwaffe as its main strategic bomber. The design was later selected as Messerschmitt's competitor in the Reichsluftfahrtministerium's Amerikabomber programme, for a strategic bomber capable of attacking New York City from bases in France or the Azores.

The Focke-Wulf Fw 191 was a prototype German bomber of World War II, as the Focke-Wulf firm's entry for the Bomber B advanced medium bomber design competition. Two versions were intended to be produced, a twin-engine version using the Junkers Jumo 222 engine and a four-engine variant which was to have used the smaller Daimler-Benz DB 605 engine. The project was eventually abandoned due to technical difficulties with the engines.

The Messerschmitt Me 309 was a prototype German fighter, designed in the early years of World War II to replace the Messerschmitt Bf 109. Although it had many advanced features, the Me 309's performance left much to be desired and it had so many problems that the project was cancelled with only four prototypes built. The Me 309 was one of two failed Messerschmitt projects intended to replace the Bf 109, the other being the 1943 Me 209 project.

The Focke-Wulf Ta 183 Huckebein was a design for a jet-powered fighter aircraft intended as the successor to the Messerschmitt Me 262 and other day fighters in Luftwaffe service during World War II. It had been developed only to the extent of wind tunnel models when the war ended, but the basic design was further developed postwar in Argentina as the FMA IAe 33 Pulqui II. The name Huckebein is a reference to a trouble-making raven from an illustrated story in 1867 by Wilhelm Busch.
The EF 132 was a planned jet bomber, under development for the Luftwaffe during World War II. It was the last aircraft project development undertaken by Junkers during the war, and was the culmination of the Ju 287 design started in 1942.

The Focke-Wulf Fw 57 was a prototype German heavy fighter and fighter-bomber. Prototypes were built in 1936 but never entered production.
The Focke-Wulf Ta 400 was a large six-engined heavy bomber design developed in Nazi Germany in 1943 by Focke-Wulf as a serious contender for the Amerikabomber project. One of the first aircraft to be developed from components from multiple countries, it was also one of the most advanced Focke-Wulf designs of World War II, though it never progressed beyond a wind tunnel model.
The Focke-Wulf Fw 300 was a proposed very-long-range civil airliner, transport, reconnaissance aircraft and anti-ship aircraft, designed by Focke-Wulf in 1941 and 1942. The design was intended to replace the Focke-Wulf Fw 200 Condor.

The Focke-Wulf Fw 56 Stösser was a single-engine parasol wing monoplane advanced trainer designed and built by the German aircraft manufacturer Focke-Wulf. It was the company's first aircraft to be designed from the onset by the aeronautical engineer Kurt Tank, who also named the type.
The Focke Wulf Fw 159 was an experimental German fighter of the 1930s, designed by Kurt Tank which never reached production, as it was considered inferior to the He 112 and Bf 109. It was a heavier variant of the Focke-Wulf Fw 56, with several improvements, such as a retractable landing gear and enclosed cockpit.

The Focke-Wulf Fw 62 was a reconnaissance floatplane, designed and built by Focke-Wulf for use by Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine. Only four were built.

The Focke-Wulf 1000x1000x1000, also known as Focke-Wulf Fw 239, was a twinjet bomber project for the Luftwaffe, designed by the Focke-Wulf aircraft manufacturing company during the last years of the Third Reich.

The Focke-Wulf Volksjäger, was a German emergency fighter project for the Luftwaffe. It was designed by Focke-Wulf towards the end of World War II as part of the defense effort against the devastating Allied bombing raids.
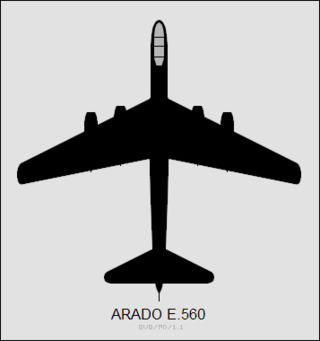
The Arado E.560 was a multi-engined Arado medium-range jet tactical bomber proposed during the Second World War.

The Blohm & Voss P 170 was a three-engined unarmed fast bomber and ground-attack aircraft project proposed by the aircraft manufacturer Blohm & Voss to the Luftwaffe during the Second World War.
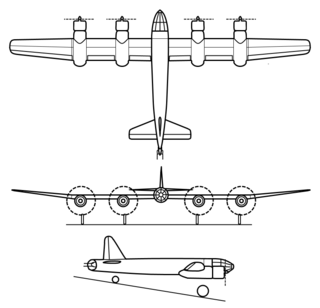
The Blohm & Voss P 184 was a German design for a long-range reconnaissance aircraft during World War II. Carrying a crew of five, it was of aerodynamically clean appearance and its wing had an unusually high aspect ratio.
The Focke-Wulf Nr. 238 Fernkampfflugzeug was a four-engine strategic bomber developed by the German aeronautical company Focke-Wulf-Flugzeugbau AG in the early 1940s and remained at the project stage. Designed to the same specifications issued by the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (RLM) which led to the Focke-Wulf Ta 400 and Junkers Ju 390, its development was cancelled by the RLM.














