
The Blohm & Voss BV 155 is a German high-altitude interceptor aircraft intended to be used by the Luftwaffe against raids by USAAF Boeing B-29 Superfortresses. Work started on the design as the Messerschmitt Me 155 in 1942, but the project went through a protracted development period and change of ownership, and prototypes were still under test and development when World War II ended.

The Hawker Tempest is a British fighter aircraft that was primarily used by the Royal Air Force (RAF) in the Second World War. The Tempest, originally known as the Typhoon II, was an improved derivative of the Hawker Typhoon, intended to address the Typhoon's unexpected deterioration in performance at high altitude by replacing its wing with a thinner laminar flow design. Since it had diverged considerably from the Typhoon, it was renamed Tempest. The Tempest emerged as one of the most powerful fighters of World War II and at low altitude was the fastest single-engine propeller-driven aircraft of the war.

The Mikoyan-Gurevich I-250, aka MiG-13, was a Soviet fighter aircraft developed as part of a crash program in 1944 to develop a high-performance fighter to counter German turbojet-powered aircraft such as the Messerschmitt Me 262. The Mikoyan-Gurevich design bureau decided to focus on a design that used something more mature than the jet engine, which was still at an experimental stage in the Soviet Union, and chose a mixed-power solution with the VRDK motorjet powered by the Klimov VK-107 V12 engine. While quite successful when it worked, with a maximum speed of 820 km/h (510 mph) being reached during trials, production problems with the VRDK fatally delayed the program and it was canceled in 1948 as obsolete.

Alexander Lippisch's Delta IV was a continuation of his work on delta wing designs pioneered in his Delta I, Delta II and Delta III aircraft.

The Fieseler Fi 167 was a 1930s German biplane torpedo and reconnaissance bomber designed for use from the Graf Zeppelin class aircraft carriers under construction from 1936 to 1942.

The Gotha WD.27 was a long-range maritime patrol floatplane developed during World War I by Gothaer Waggonfabrik (Gotha) for the Imperial German Navy's Naval Air Service. It was a large, four-engine aircraft with the same general layout as the WD.22; a conventional floatplane with engines grouped in tractor-pusher pairs on the lower wings. Three aircraft were ordered in early 1918, but the first prototype was not completed until after the end of the war in November. It may not have flown before it was ordered to be destroyed by the victorious Allies.

The Dornier Do Y was a trimotor German monoplane bomber of the early 1930s designed by Dornier Flugzeugwerke to an order by the Royal Yugoslav Air Force (RYAF). The Yugoslavs originally intended to use war reparations to pay for them, but ultimately had to use their own funds. Only a pair of aircraft were initially ordered to give the Yugoslavs experience with multi-engine bombers and Dornier failed to sell any more Do Y's. Two improved versions were subsequently built on speculation, but failed to find purchasers until the RYAF bought them in 1935.
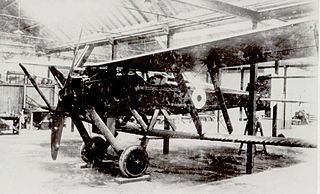
The Parnall Scout, unofficially nicknamed the Zeppelin Chaser, was a British fighter prototype of the 1910s. It was the first fighter design from Parnall.

The Zeppelin-Lindau Rs.I was a large three-engined biplane flying boat designed by Claudius Dornier and built during 1914–15 on the German side of Lake Constance. It was destroyed in a storm.

The Zeppelin-Lindau Rs.II was a biplane flying boat, designed by Claudius Dornier as a follow-on to his Zeppelin-Lindau Rs.I and built during 1914–1915 on the German side of Lake Constance. Initially this aircraft was powered by three engines mounted inside the hull driving three pusher propellers via gearboxes and shafts. The later version was powered by four engines in two push-pull nacelles mounted between the wings.

The Zeppelin-Lindau Rs.III was a large four-engined monoplane flying boat designed by Claudius Dornier and built during 1917 on the German side of Lake Constance at the Zeppelin-Lindau works.

The Aeromarine AM-1 was a biplane built to pursue a US Air Mail Service requirement for a nighttime transport.

The LFG Roland D.XV was a World War I German single-seat fighter aircraft ordered as a test bed for engine comparisons. It was distinguished from earlier Roland biplane designs by the elimination of flying wires. Two later aircraft, also called LFG Roland D.XV, were completely different designs with slab-sided fuselages.

The Zeppelin D.I, or Zeppelin-Lindau D.I or Zeppelin D.I (Do), as named in German documents, also sometimes referred to postwar as the Dornier D.I or Dornier-Zeppelin D.I, for the designer, was a single-seat all-metal stressed skin monocoque cantilever-wing biplane fighter, developed by Claude Dornier while working for Luftschiffbau Zeppelin at their Lindau facility. It was too late to see operational service with the German Air Force (Luftstreitkräfte) during World War I.

The Zeppelin-Lindau Rs.IV was a Riesenflugzeug monoplane all metal flying boat with a stressed skin hull and fuselage developed for the Imperial German Navy to perform long range patrols over the North Sea. It had been developed by Claudius Dornier while working for Zeppelin in the town of Lindau.

The Zeppelin-Lindau CS.I was a German single-engined reconnaissance seaplane with a low-wing monoplane layout.

The Zeppelin-Lindau Gs.I, often known post-WWI as the Dornier Gs.I after its designer Claude Dornier, was a civil flying boat developed immediate post-war from a military prototype. Its passenger cabin seated six. Only one was completed, and that was eventually scuttled to keep it out of Allied hands. Another of the military prototypes was intended to have a bigger, nine seat cabin and other refinements but the Gs.II was incomplete when discovered by Allied inspectors.

The Zeppelin-Lindau V I was a metal-framed, pusher configuration, German sesquiplane, designed by Claude Dornier. It flew on 13 November 1916 and crashed on the first flight.

The Zeppelin-Staaken L was an experimental long-range maritime patrol floatplane developed during World War I by Zeppelin-Staaken for the Imperial German Navy's Naval Air Service. Derived from the Zeppelin-Staaken R.VI heavy bomber, it was a large, four-engine aircraft with a crew of seven men. Its engines were grouped in tractor-pusher pairs between the wings. A single aircraft was ordered for evaluation purposes in 1917. It was destroyed in a crash in June 1918 with the death of everyone aboard.



















