
Dornier Flugzeugwerke was a German aircraft manufacturer founded in Friedrichshafen in 1914 by Claude Dornier. Over the course of its long lifespan, the company produced many designs for both the civil and military markets.
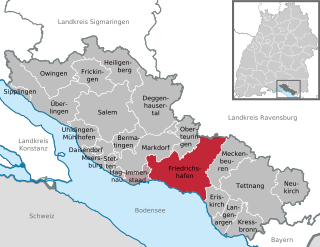
Friedrichshafen is a city on the northern shoreline of Lake Constance in Southern Germany, near the borders of both Switzerland and Austria. It is the district capital (Kreisstadt) of the Bodensee district in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg. Friedrichshafen has a population of about 58,000.
Luftschiffbau Zeppelin GmbH is a German aircraft manufacturing company. It is perhaps best known for its leading role in the design and manufacture of rigid airships, commonly referred to as Zeppelins due to the company's prominence. The name 'Luftschiffbau' is a German word meaning building of airships.
Theodor Kober was a twentieth-century German aviation engineer who contributed to the building of the first Zeppelin.

The Friedrichshafen G.III was a heavy bomber designed and manufactured by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen. They were used by the German Imperial Air Service during World War I for tactical and limited strategic bombing operations. After the end of the war a number of Friedrichshafen bombers were converted into transport aircraft while a small number also saw service as dedicated airliners.

Friedrichshafen FF.33 was a German single-engined reconnaissance three-bay wing structure biplane, using twin floats, designed by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen in 1914 for the Marine-Fliegerabteilung aviation forces of the Kaiserliche Marine.

The Friedrichshafen FF.41a was a large, German-built, three-seat, twin-engine floatplane reconnaissance aircraft designed by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen in 1917.

The Friedrichshafen G.II was a heavy bomber aircraft that was designed and manufactured in Germany during World War I by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen. The plane was used by the Luftstreitkräfte for tactical and limited strategic bombing operations.

The Friedrichshafen G.IV and G.V respectively were heavy bombers that were designed and manufactured in Germany during World War I by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen. The G.IV saw limited use by the Luftstreitkräfte for tactical and limited strategic bombing operations, while the G.V and a follow-on design, the FF.62 did not fly until after the Armistice.

The Friedrichshafen FF.29 was an unarmed maritime reconnaissance floatplane built for the Imperial German Navy's Naval Air Service that was produced by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen during World War I. The aircraft entered service in November 1914, mostly conducting maritime patrols over the North Sea and the English Channel, and played a small role in the Raid on Cuxhaven the following month. A FF.29 became the first aircraft to be transported by a submarine when it was used in experiments in January 1915. In May an emergency landing by a FF.29 was the cause of the action off Noordhinder Bank when German forces were searching for the floatplane when they encountered a superior British force. The aircraft was also involved in developing methods of controlling artillery fire from the air.

The Friedrichshafen FF.31 was a two-seat prototype German maritime reconnaissance floatplane built by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen during the First World War. Although primarily intended for reconnaissance duties, the aircraft was provided with a machine gun to engage other aircraft. Although it was satisfactory for its intended mission, it lacked the performance necessary for use as a fighter. A pair of aircraft were built in 1915 and it was not accepted for production by the Imperial German Navy's Naval Air Service.

The Friedrichshafen FF.34 was a German biplane floatplane of the 1910s produced by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen.

The Friedrichshafen FF.40 was a German three-seat floatplane of the 1910s produced by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen.

The Friedrichshafen FF.64 was a German two-seat biplane floatplane of the 1910s produced by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen.

The Friedrichshafen FF.53 was a German torpedo-carrying biplane floatplane of the 1910s produced by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen.

The Friedrichshafen FF.60 was a German experimental floatplane produced by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen.

The Friedrichshafen FF.35 was a German three-seat floatplane torpedo bomber built during World War I by Friedrichshafen Flugzeugbau built for the Imperial German Navy's Naval Air Service. Only one prototype was constructed in 1916 and it saw limited operational use during the war in Courland.

The Friedrichshafen D.I was a German single-seat fighter plane developed by the Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen during the First World War. Two prototypes were flown in 1917, but it was judged inferior to the Albatros D.III then in production and no further production ensued.

The Friedrichshafen FF.1 was a German experimental floatplane built in 1912. It was the first aircraft designed and built by the newly established Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen. Only one prototype was constructed and it set a German national record for endurance in 1913 before crashing in early 1914.

The Friedrichshafen FF.19 was an unarmed maritime reconnaissance floatplane built for the Imperial German Navy's Naval Air Service that was produced by Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen. Built in small numbers, the aircraft first flew in 1914 and saw service during the early months of World War I, mostly conducting maritime patrols over the North Sea, although they did attack British ships participating in the Raid on Cuxhaven at the end of the year.

















