
The Arado Ar 231 was a lightweight floatplane, developed during World War II in Nazi Germany as a scout plane for submarines by Arado. The need to be stored inside the submarine necessitated compromises in design that made this single-seat seaplane of little practical use.

The Arado Ar 64 was a single-seat biplane fighter designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Arado. It was among the first fighters produced when Germany abandoned the restrictions of the Treaty of Versailles and began rearming.

The Arado Ar 65 was the single-seat biplane fighter successor to the Ar 64. Both looked very similar. The only major difference was the use of a 12-cylinder inline engine versus the Ar 64's radial. The wingspan was also increased.

The Arado Ar 197 was a German World War II-era biplane, designed for naval operations for the never-completed German aircraft carrier Graf Zeppelin. Only a few prototypes were built; the project was abandoned in favour of the Messerschmitt Bf 109T and Me 155.

The Arado Ar 195 was a single-engine prototype carrier-based torpedo bomber, built by the German firm Arado for service on the German aircraft carrier Graf Zeppelin, during World War II.

The Arado Ar 76 was a German aircraft of the 1930s, designed as a light fighter with a secondary role as an advanced trainer in mind.
The Arado L I was a two-seat parasol-wing sport monoplane built in Germany in 1929, in order to compete in the Europa Rundflug that year. During the fuel consumption trials, the L 1 made a forced landing and was disqualified from the contest. Bringing the aircraft back to Paris, designer Hermann Hofmann performed some aerobatics over the airfield and was killed when it crashed.

The Arado L II was a 1920s German two-seat, high-wing touring monoplane.

The Arado S I was a biplane trainer built in Germany in 1925. The first of three prototypes was powered by a Bristol Lucifer radial engine, while the other two Arado S.Ia aircraft were fitted with the Siemens-Halske Sh 12. The Siemens-Halske Sh 11 powered the Arado S III, a virtually identical aircraft of which only a single prototype was constructed and sold to Turkey.

The Arado SC I was a biplane trainer developed in Germany in the 1920s. It was based on the S I, but powered by a far more powerful inline engine. Accordingly, the structure received considerable strengthening. The aircraft was intended for the clandestine military flying school at Lipetsk, but it was not accepted for this service. Instead, a small number were built for the Deutsche Verkehrsfliegerschule.
The Arado SC II was a biplane trainer designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Arado.

The Arado SD I was a fighter biplane, developed in Germany in the 1920s. It was intended to equip the clandestine air force that Germany was assembling at Lipetsk. The layout owed something to designer Walter Rethel's time with Fokker. Of conventional configuration, the SD I featured a welded steel tube frame, metal-covered ahead of the cockpit, and fabric-covered aft of it. The wooden sesquiplane wings were braced with N-type interplane struts, without any wires - a typical Fokker feature.

The Arado SSD I was a biplane fighter seaplane developed in Germany in 1930, intended to be launched from catapults on warships. This was an all-new design from Walter Rethel, sharing nothing with his other fighter designs for Arado of the late 1920s. It was a conventional unequal-span, staggered biplane, with the slightly gulled top wing attached to the upper fuselage. It was equipped with a single, large float under the fuselage and two outrigger floats near the wingtips. After evaluation at Travemünde, the floats were removed and a simple, wheeled undercarriage was fitted for competitive evaluation with the Heinkel HD 38 at Lipetsk. The Heinkel was selected, and the SSD I was relegated to trainer duties with the LVS in 1932.
The Arado V.1 was a prototype airliner, built in Germany in 1927. It was a single-engine, high-wing braced monoplane with tailwheel undercarriage. It made several long-distance flights, including carrying mail to South America, before being exhibited in Berlin in 1929, when it was bought by Deutsche Luft Hansa.
The Arado W 2 was a two-seat twin-engine seaplane trainer developed for the DVS in 1928. It was a cantilever monoplane with a fabric-covered steel tube fuselage that accommodated the pilot and instructor in tandem open cockpits. The undercarriage consisted of two pontoons carried on steel struts.

The Blume Bl.500, Bl.502, and Bl.503 were a family of four-seat light aircraft designed in West Germany by Dr Walter Blume in the late 1950s.

The Arado Ar 79 was an aerobatic two-seat trainer and touring aircraft designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Arado. It was the final civilian aircraft developed by the company.

The Arado Ar 199 was a floatplane aircraft, built by Arado Flugzeugwerke. It was a low-wing monoplane, designed in 1938 to be launched from a catapult and operated over water. The enclosed cockpit had two side-by-side seats for instructor and student, and a third, rear seat, for a trainee-navigator or radio operator.
The Arado Ar 69 was a two-seat German beginner's school and sport biplane with an open cockpit, developed in 1933 by Arado Flugzeugwerke.
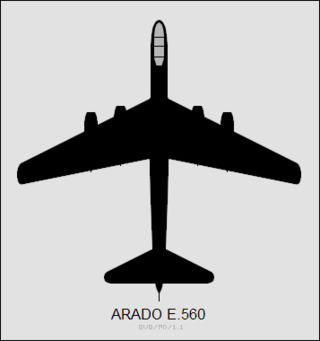
The Arado E.560 was a multi-engined Arado medium-range jet tactical bomber proposed during the Second World War.















