Dilationand curettage (D&C) refers to the dilation of the cervix and surgical removal of sections and or layers of the lining of the uterus and or contents of the uterus such as an unwanted fetus, remains of a non viable fetus, retained placenta after birth or abortion as well as any abnormal tissue which may be in the uterus causing abnormal cycles by scraping and scooping (curettage). It is a gynecologic procedure used for treatment and removal as well as diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, and is the most commonly used method for first trimester abortion or miscarriage.

The uterus or womb is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains glands in its lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment.

Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these symptoms. The pain may be described as sharp, dull, or crampy. Pain may also spread to the shoulder if bleeding into the abdomen has occurred. Severe bleeding may result in a fast heart rate, fainting, or shock. With very rare exceptions, the fetus is unable to survive.

Obstetric ultrasonography, or prenatal ultrasound, is the use of medical ultrasonography in pregnancy, in which sound waves are used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in the uterus (womb). The procedure is a standard part of prenatal care in many countries, as it can provide a variety of information about the health of the mother, the timing and progress of the pregnancy, and the health and development of the embryo or fetus.

Asherman's syndrome (AS) is an acquired uterine condition that occurs when scar tissue (adhesions) forms inside the uterus and/or the cervix. It is characterized by variable scarring inside the uterine cavity, where in many cases the front and back walls of the uterus stick to one another. AS can be the cause of menstrual disturbances, infertility, and placental abnormalities. Although the first case of intrauterine adhesion was published in 1894 by Heinrich Fritsch, it was only after 54 years that a full description of Asherman syndrome was carried out by Joseph Asherman. A number of other terms have been used to describe the condition and related conditions including: uterine/cervical atresia, traumatic uterine atrophy, sclerotic endometrium, and endometrial sclerosis.

Adenomyosis is a medical condition characterized by the growth of cells that proliferate on the inside of the uterus (endometrium) atypically located among the cells of the uterine wall (myometrium), as a result, thickening of the uterus occurs. As well as being misplaced in patients with this condition, endometrial tissue is completely functional. The tissue thickens, sheds and bleeds during every menstrual cycle.

Vaginal bleeding is any expulsion of blood from the vagina. This bleeding may originate from the uterus, vaginal wall, or cervix. Generally, it is either part of a normal menstrual cycle or is caused by hormonal or other problems of the reproductive system, such as abnormal uterine bleeding.

Hysteroscopy is the inspection of the uterine cavity by endoscopy with access through the cervix. It allows for the diagnosis of intrauterine pathology and serves as a method for surgical intervention.
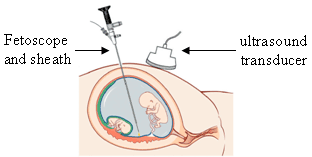
Fetoscopy is an endoscopic procedure during pregnancy to allow surgical access to the fetus, the amniotic cavity, the umbilical cord, and the fetal side of the placenta. A small (3–4 mm) incision is made in the abdomen, and an endoscope is inserted through the abdominal wall and uterus into the amniotic cavity. Fetoscopy allows for medical interventions such as a biopsy or a laser occlusion of abnormal blood vessels or the treatment of spina bifida.

Gynecologic ultrasonography or gynecologic sonography refers to the application of medical ultrasonography to the female pelvic organs as well as the bladder, the adnexa, and the recto-uterine pouch. The procedure may lead to other medically relevant findings in the pelvis.This technique is useful to detect myomas or mullerian malformations.

A uterine malformation is a type of female genital malformation resulting from an abnormal development of the Müllerian duct(s) during embryogenesis. Symptoms range from amenorrhea, infertility, recurrent pregnancy loss, and pain, to normal functioning depending on the nature of the defect.

Myomectomy, sometimes also called fibroidectomy, refers to the surgical removal of uterine leiomyomas, also known as fibroids. In contrast to a hysterectomy, the uterus remains preserved and the woman retains her reproductive potential. It still may impact hormonal regulation and the menstrual cycle.

A unicornuate uterus represents a uterine malformation where the uterus is formed from one only of the paired Müllerian ducts while the other Müllerian duct does not develop or only in a rudimentary fashion. The sometimes called hemi-uterus has a single horn linked to the ipsilateral fallopian tube that faces its ovary.

A bicornuate uterus or bicornate uterus, is a type of müllerian anomaly in the human uterus, where there is a deep indentation at the fundus (top) of the uterus.
A uterine septum is a congenital uterine malformation where the uterine cavity is partitioned by a longitudinal septum; the outside of the uterus has a normal typical shape. The wedge-like partition may involve only the superior part of the cavity resulting in an incomplete septum or a subseptate uterus, or less frequently the total length of the cavity and the cervix resulting in a double cervix. The septation may also continue caudally into the vagina resulting in a "double vagina".

Uterus didelphys represents a uterine malformation where the uterus is present as a paired organ when the embryogenetic fusion of the Müllerian ducts fails to occur. As a result, there is a double uterus with two separate cervices, and possibly a double vagina as well. Each uterus has a single horn linked to the ipsilateral fallopian tube that faces its ovary.

An interstitial pregnancy is a uterine but ectopic pregnancy; the pregnancy is located outside the uterine cavity in that part of the fallopian tube that penetrates the muscular layer of the uterus. The term cornual pregnancy is sometimes used as a synonym, but remains ambiguous as it is also applied to indicate the presence of a pregnancy located within the cavity in one of the two upper "horns" of a bicornuate uterus. Interstitial pregnancies have a higher mortality than ectopics in general.

A cervical pregnancy is an ectopic pregnancy that has implanted in the uterine endocervix. Such a pregnancy typically aborts within the first trimester, however, if it is implanted closer to the uterine cavity – a so-called cervico-isthmic pregnancy – it may continue longer. Placental removal in a cervical pregnancy may result in major hemorrhage.
Müllerian duct anomalies are those structural anomalies caused by errors in Müllerian duct development as an embryo forms. Factors contributing to them include genetics and maternal exposure to substances that interfere with fetal development.
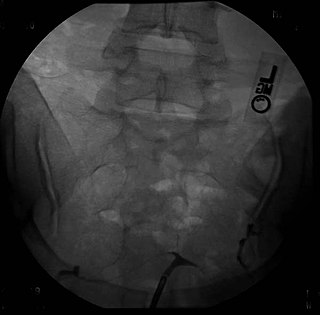
A t-shaped uterus is a type of uterine malformation wherein the uterus is shaped resembling the letter T. This is typically observed in DES-exposed women. It is recognised in the ESHRE/ESGE classification, and is associated with failed implantation, increased risk of ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage and preterm delivery. There is a surgical procedure to correct the malformation.


















