
Diaptomus is a genus of copepods with a single eye spot. It is superficially similar in size and appearance to Cyclops. However it has characteristically very long first antennae that exceed the body length. In addition, the females carry the eggs in a single sac rather than the twin sacs seen in Cyclops. It is a copepod of larger freshwater ponds, lakes and still waters.
Arctodiaptomus is a genus of copepods in the family Diaptomidae.
Argyrodiaptomus neglectus is a species of crustacean in the family Diaptomidae. It is endemic to Brazil.
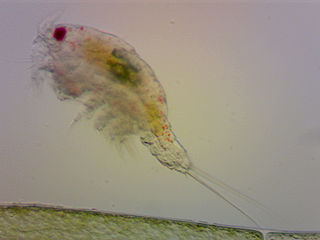
Attheyella is a genus of copepods in the family Canthocamptidae, containing the following species:
Boeckella is a genus of copepods in the family Centropagidae.
Elaphoidella is a genus of freshwater copepods in the family Canthocamptidae. It contains over 200 species, including three classified as vulnerable species by the IUCN – three endemic to Slovenia and one endemic to the United States. In total, the genus Elaphoidella contains the following species:
Eodiaptomus is a genus of copepods in the family Diaptomidae, containing the following species:

Eudiaptomus is a genus of freshwater crustaceans in the family Diaptomidae. It contains the following species:
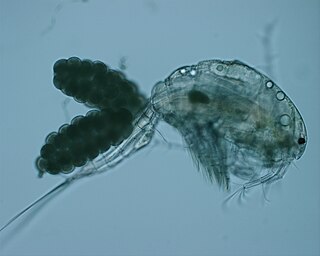
Mesocyclops is a genus of copepod crustaceans in the family Cyclopidae. Because the various species of Mesocyclops are known to prey on mosquito larvae, it is used as a nontoxic and inexpensive form of biological mosquito control.
Metacyclops is a genus of copepod crustaceans in the family Cyclopidae, containing 61 species, of which three are listed on the IUCN Red List – M. campestris from Brazil, M. gasparoi from Italy (vulnerable) and M. postojnae from Slovenia (vulnerable).
Notodiaptomus is a genus of copepods in the family Diaptomidae. It is the most widely distributed, most abundant and most species-rich genus of freshwater calanoid copepods in the Neotropics. The genus was erected in 1936 by Friedrich Kiefer for eleven species formerly placed in a wider Diaptomus. Notodiaptomus deitersi was chosen to be the type species by Raúl Adolfo Ringuelet in 1958.
Odontodiaptomus thomseni is a species of crustacean in the family Diaptomidae. It is found in Uruguay and Venezuela.
Odontodiaptomus is a genus of freshwater copepods in the family Diaptomidae. It includes the following species:

Thermocyclops is a genus of crustacean in family Cyclopidae. It was first described and later extensively researched by Friedrich Kiefer, who discovered some 20 species. The species and subspecies of the genus inhabit fresh and brackish waters alike all around the world, although most are from tropical areas.
Tropocyclops is a genus of copepod crustaceans in the family Cyclopidae. It contains the following species:
Tropodiaptomus is a genus of copepods in the family Diaptomidae. It includes the following species, many of which are narrow endemics and are included on the IUCN Red List :

Diaptomidae is a family of freshwater pelagic copepods. It includes around 50 genera:

The Cyclopidae are a family of copepods containing more than half of the 1,200 species in the order Cyclopoida in over 70 genera.
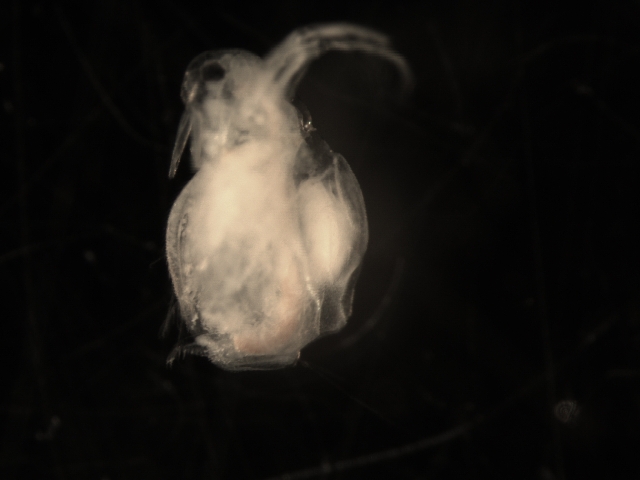
Moina is a genus of crustaceans within the family Moinidae. The genus was first described by W. Baird in 1850. They are referred to as water fleas, but are related to the much larger Daphnia magna and the larger Daphnia pulex. This genus demonstrates the ability to survive in waters containing low oxygen levels, high salinity, and other impurities, including salt pans, and commonly eutrophication. An example of such an extreme habitat is the highly saline Makgadikgadi Pans of Botswana, which supports prolific numbers of Moina belli.
Microcyclops is a genus of copepods, containing the following species:







