
Palmaria palmata, also called dulse, dillisk or dilsk, red dulse, sea lettuce flakes, or creathnach, is a red alga (Rhodophyta) previously referred to as Rhodymenia palmata. It grows on the northern coasts of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It is a well-known snack food. In Iceland, where it is known as söl[ˈsœːl̥], it has been an important source of dietary fiber throughout the centuries.

The Fucales (fucoids) are an order in the brown algae. The list of families in the Fucales, as well as additional taxonomic information on algae, is publicly accessible at Algaebase.

Valonia is a genus of green algae in the Valoniaceae family. The genus Ventricaria is now regarded as a synonym of Valonia.

Bacteriastrum is a genus of diatoms in family Chaetocerotaceae. There are more than 30 described species in genus Bacteriastrum, but many of these are not currently accepted, and new species are still added to the genus. The type species for the genus is Bacteriastrum furcatum Shadbolt.
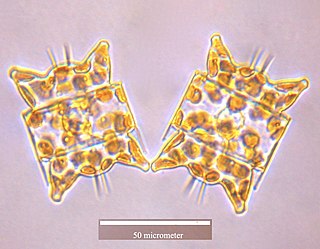
Odontella aurita is a diatom and the type species of genus Odontella. The easiest way to identify this species is by recognizing the very distinct shape of the cells belonging to this genus. Odontella aurita is cultivated industrially for human consumption due to its ability to produce up to 28% of its total lipids as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), a long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA). PUFAs such as EPA are known to provide a variety of health benefits in humans, and are commonly obtained by fish oil. However, with the increasing concern of over-exploited fisheries, microalgae are a promising source of PUFAs as they can be grown year-round and their fatty acid profile and content are easily manipulated by growth conditions.

Corallina is a genus of red seaweeds with hard, abrasive calcareous skeletons in the family Corallinaceae. They are stiff, branched plants with articulations.

Wrangeliaceae is a red alga family in the order Ceramiales. It was published by J.Agardh in 1851 in his book Species, genera et ordines algarum : seu descriptiones succinctae specierum.

Laminaria pallida, the split-fan kelp, is a species of large brown seaweed of the class Phaeophyceae found from Danger Point on the south coast of South Africa to Port Nolloth, Tristan da Cunha and Gough islands in the Atlantic and Île Saint-Paul in the Indian Ocean.

Prasiola crispa is a small terrestrial green alga.

Prasiola stipitata is a small green alga.

Diatoms belong to a large group called the heterokonts, which include both autotrophs such as golden algae and kelp; and heterotrophs such as water moulds. The classification of heterokonts is still unsettled: they may be designated a division, phylum, kingdom, or something intermediate to those. Consequently, diatoms are ranked anywhere from a class, usually called Diatomophyceae or Bacillariophyceae, to a division (=phylum), usually called Bacillariophyta, with corresponding changes in the ranks of their subgroups.
Asterionellopsidaceae is a family of diatoms belonging to the order Rhaphoneidales.
Asteroplanus is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Fragilariaceae.
Cavinula is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Cavinulaceae.










