
The Acantharea (Acantharia) are a group of radiolarian protozoa, distinguished mainly by their strontium sulfate skeletons. Acantharians are heterotrophic marine microplankton that range in size from about 200 microns in diameter up to several millimeters. Some acantharians have photosynthetic endosymbionts and hence are considered mixotrophs.
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community, having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequently, they drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers.

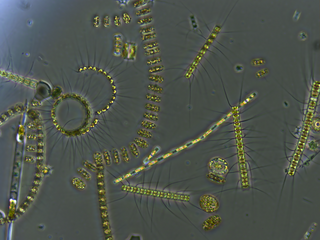
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are protozoa of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elaborate mineral skeleton is usually made of silica. They are found as zooplankton throughout the global ocean. As zooplankton, radiolarians are primarily heterotrophic, but many have photosynthetic endosymbionts and are, therefore, considered mixotrophs. The skeletal remains of some types of radiolarians make up a large part of the cover of the ocean floor as siliceous ooze. Due to their rapid change as species and intricate skeletons, radiolarians represent an important diagnostic fossil found from the Cambrian onwards.

Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes, is a family of ray-finned fishes, part of the suborder Notothenioidei which is traditionally placed within the order Perciformes. They are largely found in the Southern Ocean.

Foraminifera are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment, while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths, which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA.

Cercozoa is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead united by molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or polyubiquitin. They were the first major eukaryotic group to be recognized mainly through molecular phylogenies. They are the natural predators of many species of bacteria. They are closely related to the phylum Retaria, comprising amoeboids that usually have complex shells, and together form a supergroup called Rhizaria.
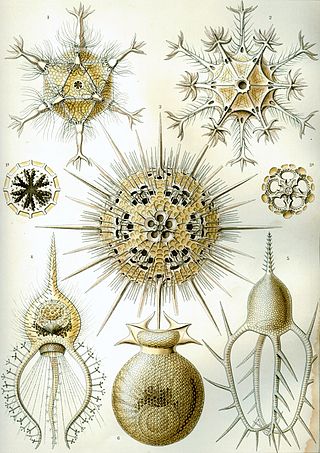
Phaeodarea or Phaeodaria is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They are distinguished by the structure of their central capsule and by the presence of a phaeodium, an aggregate of waste particles within the cell.
The Komokiacea are a small group of amoeboid protozoa, considered to be foraminifera, though there have been suggestions that they are a separate group, closely related to foraminifera. Komokiacea are rather large organisms, often exceeding 300 micrometers in maximum dimensions. Along with Xenophyophores they dominate the macro- and megabenthic fauna in the deep sea and are commonly referred to as "giants protists".

Biogenic silica (bSi), also referred to as opal, biogenic opal, or amorphous opaline silica, forms one of the most widespread biogenic minerals. For example, microscopic particles of silica called phytoliths can be found in grasses and other plants.

Aulosphaera is a genus of Cercozoa. The genus contains bioluminescent species. It one of two known bioluminescent phaeodarean genera, the other being Tuscaridium. The described bioluminescent species is Aulosphaera triodon Haeckel, 1887.

The family Cavoliniidae is a taxonomic group of small floating sea snails, pelagic marine opisthobranch gastropod mollusks.

Marine microorganisms are defined by their habitat as microorganisms living in a marine environment, that is, in the saltwater of a sea or ocean or the brackish water of a coastal estuary. A microorganism is any microscopic living organism or virus, which is invisibly small to the unaided human eye without magnification. Microorganisms are very diverse. They can be single-celled or multicellular and include bacteria, archaea, viruses, and most protozoa, as well as some fungi, algae, and animals, such as rotifers and copepods. Many macroscopic animals and plants have microscopic juvenile stages. Some microbiologists also classify viruses as microorganisms, but others consider these as non-living.

Picozoa, Picobiliphyta, Picobiliphytes, or Biliphytes are protists of a phylum of marine unicellular heterotrophic eukaryotes with a size of less than about 3 micrometers. They were formerly treated as eukaryotic algae and the smallest member of photosynthetic picoplankton before it was discovered they do not perform photosynthesis. The first species identified therein is Picomonas judraskeda. They probably belong in the Archaeplastida as sister of the Rhodophyta.
Sthenoteuthis pteropus, also known as the orangeback flying squid or orangeback squid, is a species of cephalopod in the family Ommastrephidae. It is native to tropical parts of the Atlantic Ocean where it is found to depths of about 200 m (656 ft).
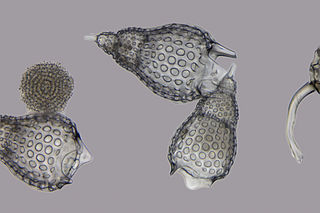
Nassellaria is an order of Rhizaria belonging to the class Radiolaria. The organisms of this order are characterized by a skeleton cross link with a cone or ring.
The genus Stylodictya belongs to a group of organisms called the Radiolaria. Radiolarians are amoeboid protists found as zooplankton in oceans around the world and are typically identified by their ornate skeletons.
Tuscaridium is a genus of phaeodarian,. The genus contains bioluminescent species. It one of two known bioluminescent phaeodarean genera, the other being Aulosphaera.

Marine protists are defined by their habitat as protists that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. Life originated as marine single-celled prokaryotes and later evolved into more complex eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are the more developed life forms known as plants, animals, fungi and protists. Protists are the eukaryotes that cannot be classified as plants, fungi or animals. They are mostly single-celled and microscopic. The term protist came into use historically as a term of convenience for eukaryotes that cannot be strictly classified as plants, animals or fungi. They are not a part of modern cladistics because they are paraphyletic.
Vitalia Viktorovna Reshetnyak (Решетняк) (1925–2015) was a Soviet protozoologist and marine biologist, specialising in Radiolaria, Phaeodorea and Acantharea.
Orcadia riedeli is a planktonic marine foraminifera. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Orcadia. It was originally classified in the genus Hastigerinella. It is found in the surface water of oceans and has a cosmopolitan distribution. The phylogenetic position of this genus remains enigmatic; it was originally assigned to the family Hastigerinidae, but was later moved to Globigerinellidae, in the order Globigerinida.















