
Listeria is a genus of bacteria that acts as an intracellular parasite in mammals. Until 1992, 10 species were known, each containing two subspecies. By 2024, 28 species had been identified. The genus is named in honour of the British pioneer of sterile surgery Joseph Lister. Listeria species are Gram-positive, rod-shaped, and facultatively anaerobic, and do not produce endospores. The major human pathogen in the genus Listeria is L. monocytogenes. It is usually the causative agent of the relatively rare bacterial disease listeriosis, an infection caused by eating food contaminated with the bacteria. Listeriosis can cause serious illness in pregnant women, newborns, adults with weakened immune systems and the elderly, and may cause gastroenteritis in others who have been severely infected.
The Aurantimonadaceae are a small family of marine bacteria.
Aurantimonas is a genus of bacteria from the family of Aurantimonadaceae.
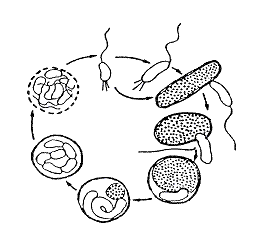
The Bdellovibrionaceae are a family of Pseudomonadota. They include genera, such as Bdellovibrio and Vampirovibrio, which are unusual parasites that enter other bacteria.
Thiothrix is a genus of filamentous sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, related to the genera Beggiatoa and Thioploca. They are usually Gram-negative and rod-shaped. They form ensheathed multicellular filaments that are attached at the base, and form gonidia at their free end. The apical gonidia have gliding motility. Rosettes of the filaments are not always formed but are typical. Sulfur is deposited in invaginations within the cell membrane.
Caldococcus is a genus of Archaea in the order Desulfurococcales.
Limnobacter litoralis is a Gram-negative, oxidase- and catalase-positive, non-spore-forming, thiosulfate-oxidizing, anaerobic bacterium of the genus Limnobacter and family Burkholderiaceae, isolated from a 22-year-old volcanic deposit on the island of Miyake-jima in Japan.
Roseobacter litoralis is a species of aerobic pink-pigmented bacteria. It contains Bacteriochlorophyll a. It contains spheroidenone, does not synthesize bacteriochlorophyll anaerobically, but shows aerobic phototrophic activity. It is also considered a photosynthetic marine bacterium. Cells are ovoid or rod-shaped and motile by subpolar flagella. R. litoralis does not reduce nitrate, while R. dentrificans does. R. litoralis can be found in marine seaweed.
Roseobacter denitrificans is a species of aerobic pink-pigmented bacteria. It contains Bacteriochlorophyll a. It contains spheroidenone, does not synthesize bacteriochlorophyll anaerobically, but shows aerobic phototrophic activity. Cells are ovoid or rod-shaped and motile by subpolar flagella. R. litoralis does not reduce nitrate, while R. denitrificans does.
Halobacillus litoralis is a species of bacteria. It is halophilic, gram-positive, heterotrophic and its type strain is DSM 10405T.
Aurantimonas coralicida is a gram-negative bacterium, and a causative agent of white plague in Caribbean corals. It is rod-shaped, with polar flagella.
Erythrobacter litoralis is a species of bacterium. E. litoralis strain HTCC2594 was first sequenced in 2009. Erythrobacter litoralis strain DSM 8509 was developed as a comparative genetic model system to investigate the role of visible light in regulation of the general stress response in Alphaproteobacteria. The complete genome sequence of E. litoralis DSM 8509 has been published.
Aureimonas altamirensis is a Gram-negative, catalase- and oxidase-positive, non-motile bacteria from the genus Aurantimonas which was isolated from Altamira Cave in Cantabria in Spain. Aurantimonas altamirensis was reclassified to Aureimonas altamirensis.
Aurantimonas manganoxydans is a Gram-negative, catalase- and oxidase-positive, non-spore-forming, motile bacteria from the genus of Aurantimonas which has the ability to oxidize Manganese. Aurantimonas manganoxydans was isolated from coastal water from Oregon in the United States.
Aureimonas frigidaquae is a Gram-negative, catalase- and oxidase-positive, facultatively anaerobic bacteria from the genus of Aurantimonas which was isolated from a water-cooling system in Gwangyang in the Republic of Korea. Aurantimonas frigidaquae was reclassified to Aureimonas frigidaquae.
Aureimonas jatrophae is a bacterium from the genus of Aurantimonas which was isolated from the plant Jatropha curcas Linnaeus in the Agrotechnology Experimental Station of Lim Chu Kang in Singapore.
Aureimonas phyllosphaerae is a bacterium from the genus of Aurantimonas which was isolated from the plant Jatropha curcas Linnaeus from an agrotechnology experimental station in Lim Chu Kang in Singapore.
Aliiglaciecola lipolytica is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, rod-shaped and motile from the genus of Aliiglaciecola with a single polar flagellum which has been isolated from seawater in China.
Aliiglaciecola litoralis is a gram-negative, aerobic, non-pigmented, catalase- and oxidase-positive, rod-shaped motile bacterium from the genus of Aliiglaciecola which was isolated from a marine sandy sample of the Sea of Japan. Aestuariibacter litoralis has been reclassified to Aliiglaciecola litoralis.
Aurantimonas endophytica is a short-rod-shaped, aerobic and motile bacteria from the genus of Aurantimonas which has been isolated from the roots of the plant Anabasis elatior in Urumqi in China.

