
ATP synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). ATP synthase is a molecular machine. The overall reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase is:
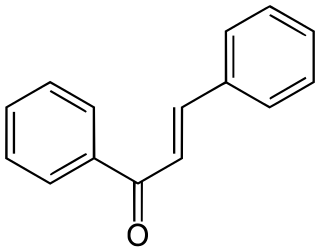
Chalcone is the organic compound C6H5C(O)CH=CHC6H5. It is an α,β-unsaturated ketone. A variety of important biological compounds are known collectively as chalcones or chalconoids. They are widely known bioactive substances, fluorescent materials, and chemical intermediates.
Glycogen synthase is a key enzyme in glycogenesis, the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase that catalyses the reaction of UDP-glucose and n to yield UDP and n+1.

Methionine synthase (MS, MeSe, MTR) is responsible for the regeneration of methionine from homocysteine. In humans it is encoded by the MTR gene (5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase). Methionine synthase forms part of the S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) biosynthesis and regeneration cycle, and is the enzyme responsible for linking the cycle to one-carbon metabolism via the folate cycle. There are two primary forms of this enzyme, the Vitamin B12 (cobalamin)-dependent (MetH) and independent (MetE) forms, although minimal core methionine synthases that do not fit cleanly into either category have also been described in some anaerobic bacteria. The two dominant forms of the enzymes appear to be evolutionary independent and rely on considerably different chemical mechanisms. Mammals and other higher eukaryotes express only the cobalamin-dependent form. In contrast, the distribution of the two forms in Archaeplastida (plants and algae) is more complex. Plants exclusively possess the cobalamin-independent form, while algae have either one of the two, depending on species. Many different microorganisms express both the cobalamin-dependent and cobalamin-independent forms.

Thromboxane A synthase 1 , also known as TBXAS1, is a cytochrome P450 enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the TBXAS1 gene.

Aldosterone synthase, also called steroid 18-hydroxylase, corticosterone 18-monooxygenase or P450C18, is a steroid hydroxylase cytochrome P450 enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone and other steroids. The enzyme catalyzes sequential hydroxylations of the steroid angular methyl group at C18 after initial 11β-hydroxylation. It is encoded by the CYP11B2 gene in humans.
Polyphenol oxidase, an enzyme involved in fruit browning, is a tetramer that contains four atoms of copper per molecule.

In molecular biology, Beta-ketoacyl-ACP synthase EC 2.3.1.41, is an enzyme involved in fatty acid synthesis. It typically uses malonyl-CoA as a carbon source to elongate ACP-bound acyl species, resulting in the formation of ACP-bound β-ketoacyl species such as acetoacetyl-ACP.
1,3-Beta-glucan synthase is a glucosyltransferase enzyme involved in the generation of beta-glucan in fungi. It serves as a pharmacological target for antifungal drugs such as caspofungin, anidulafungin, and micafungin, deemed 1,3-Beta-glucan synthase inhibitors. Under the CAZy classification system, fungi and plant members fall in the glycosyltransferase 48 family (GT48). Some members of the glycosyltransferase 2 family, such as the curdlan synthase CrdS, also has a similar activity.
Nitric oxide synthase 1 (neuronal), also known as NOS1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS1 gene.

Hyaluronan synthase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HAS3 gene.
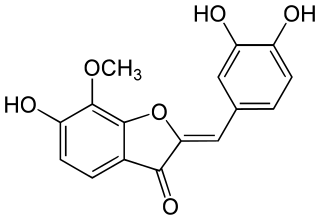
Leptosidin was the first aurone to be isolated in Coreopsis grandiflora by Geissman T.A. and Heaton C.D. in 1943. Leptosidin blocks the active residues of PRKACA.

An aurone is a heterocyclic chemical compound, which is a type of flavonoid. There are two isomers of the molecule, with (E)- and (Z)-configurations. The molecule contains a benzofuran element associated with a benzylidene linked in position 2. In aurone, a chalcone-like group is closed into a 5-membered ring instead of the 6-membered ring more typical of flavonoids.
Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is the thioester of coenzyme-A and coumaric acid. Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is a central intermediate in the biosynthesis of myriad natural products found in plants. These products include lignols, flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and other phenylpropanoids.

Chalconoids, also known as chalcones, are natural phenols derived from chalcone. They form the central core for a variety of important biological compounds.

Anthochlor pigments are a group of secondary plant metabolites and with carotenoids and some flavonoids produce yellow flower colour. Both, chalcones and aurones are known as anthochlor pigments. Anthochlor pigments serve as UV nectar guides in some plants. Important anthochlor pigments accumulating plants are from the genus Coreopsis, Snapdragon or Bidens ferulifolia.












