Related Research Articles

Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically conducting phase between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte.

In electrochemistry, standard electrode potential, or , is a measure of the reducing power of any element or compound. The IUPAC "Gold Book" defines it as; "the value of the standard emf of a cell in which molecular hydrogen under standard pressure is oxidized to solvated protons at the left-hand electrode".

In electrochemistry, cyclic voltammetry (CV) is a type of voltammetric measurement where the potential of the working electrode is ramped linearly versus time. Unlike in linear sweep voltammetry, after the set potential is reached in a CV experiment, the working electrode's potential is ramped in the opposite direction to return to the initial potential. These cycles in potential are repeated until the voltammetric trace reaches a cyclic steady state. The current at the working electrode is plotted versus the voltage at the working electrode to yield the cyclic voltammogram. Cyclic voltammetry is generally used to study the electrochemical properties of an analyte in solution or of a molecule that is adsorbed onto the electrode.
In analytical electrochemistry, coulometry determines the amount of matter transformed during an electrolysis reaction by measuring the amount of electricity consumed or produced. It can be used for precision measurements of charge, and the amperes even used to have a coulometric definition. However, today coulometry is mainly used for analytical applications. It is named after Charles-Augustin de Coulomb.

A reference electrode is an electrode that has a stable and well-known electrode potential. The overall chemical reaction taking place in a cell is made up of two independent half-reactions, which describe chemical changes at the two electrodes. To focus on the reaction at the working electrode, the reference electrode is standardized with constant concentrations of each participant of the redox reaction.
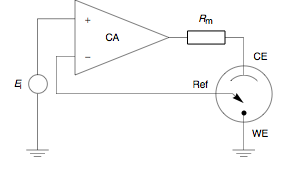
A potentiostat is the electronic hardware required to control a three electrode cell and run most electroanalytical experiments. A Bipotentiostat and polypotentiostat are potentiostats capable of controlling two working electrodes and more than two working electrodes, respectively.

Voltammetry is a category of electroanalytical methods used in analytical chemistry and various industrial processes. In voltammetry, information about an analyte is obtained by measuring the current as the potential is varied. The analytical data for a voltammetric experiment comes in the form of a voltammogram, which plots the current produced by the analyte versus the potential of the working electrode.
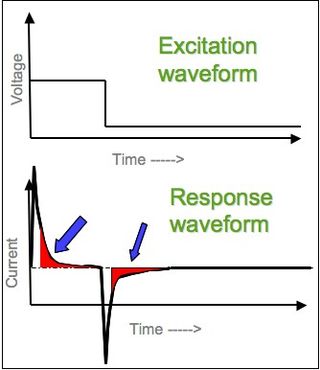
In electrochemistry, chronoamperometry is an analytical technique in which the electric potential of the working electrode is stepped and the resulting current from faradaic processes occurring at the electrode is monitored as a function of time. The functional relationship between current response and time is measured after applying single or double potential step to the working electrode of the electrochemical system. Limited information about the identity of the electrolyzed species can be obtained from the ratio of the peak oxidation current versus the peak reduction current. However, as with all pulsed techniques, chronoamperometry generates high charging currents, which decay exponentially with time as any RC circuit. The Faradaic current - which is due to electron transfer events and is most often the current component of interest - decays as described in the Cottrell equation. In most electrochemical cells, this decay is much slower than the charging decay-cells with no supporting electrolyte are notable exceptions. Most commonly a three-electrode system is used. Since the current is integrated over relatively longer time intervals, chronoamperometry gives a better signal-to-noise ratio in comparison to other amperometric techniques.
Polarography is a type of voltammetry where the working electrode is a dropping mercury electrode (DME) or a static mercury drop electrode (SMDE), which are useful for their wide cathodic ranges and renewable surfaces. It was invented in 1922 by Czechoslovak chemist Jaroslav Heyrovský, for which he won the Nobel prize in 1959. The main advantages of mercury as electrode material are as follows: 1) a large voltage window: ca. from +0.2 V to -1.8 V vs reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE). Hg electrode is particularly well-suited for studying electroreduction reactions. 2) very reproducible electrode surface, since mercury is liquid. 3) very easy cleaning of the electrode surface by making a new drop of mercury from a large Hg pool connected by a glass capillary.
In electrochemistry, overpotential is the potential difference (voltage) between a half-reaction's thermodynamically determined reduction potential and the potential at which the redox event is experimentally observed. The term is directly related to a cell's voltage efficiency. In an electrolytic cell the existence of overpotential implies that the cell requires more energy than thermodynamically expected to drive a reaction. In a galvanic cell the existence of overpotential means less energy is recovered than thermodynamics predicts. In each case the extra/missing energy is lost as heat. The quantity of overpotential is specific to each cell design and varies across cells and operational conditions, even for the same reaction. Overpotential is experimentally determined by measuring the potential at which a given current density is achieved.
Electroanalytical methods are a class of techniques in analytical chemistry which study an analyte by measuring the potential (volts) and/or current (amperes) in an electrochemical cell containing the analyte. These methods can be broken down into several categories depending on which aspects of the cell are controlled and which are measured. The three main categories are potentiometry, amperometry, coulometry.

In analytical chemistry, linear sweep voltammetry is a method of voltammetry where the current at a working electrode is measured while the potential between the working electrode and a reference electrode is swept linearly in time. Oxidation or reduction of species is registered as a peak or trough in the current signal at the potential at which the species begins to be oxidized or reduced.
In electrochemistry, the working electrode is the electrode in an electrochemical system on which the reaction of interest is occurring. The working electrode is often used in conjunction with an auxiliary electrode, and a reference electrode in a three-electrode system. Depending on whether the reaction on the electrode is a reduction or an oxidation, the working electrode is called cathodic or anodic, respectively. Common working electrodes can consist of materials ranging from inert metals such as gold or platinum, to inert carbon such as glassy carbon, boron-doped diamond or pyrolytic carbon, and mercury drop and film electrodes. Chemically modified electrodes are employed for the analysis of both organic and inorganic samples.
In analytical chemistry, hydrodynamic voltammetry is a form of voltammetry in which the analyte solution flows relative to a working electrode. In many voltammetry techniques, the solution is intentionally left still to allow diffusion-controlled mass transfer. When a solution is made to flow, through stirring or some other physical mechanism, it is very important to the technique to achieve a very controlled flux or mass transfer in order to obtain predictable results. These methods are types of electrochemical studies which use potentiostats to investigate reaction mechanisms related to redox chemistry among other chemical phenomenon.
Bulk electrolysis is also known as potentiostatic coulometry or controlled potential coulometry. The experiment is a form of coulometry which generally employs a three electrode system controlled by a potentiostat. In the experiment the working electrode is held at a constant potential (volts) and current (amps) is monitored over time (seconds). In a properly run experiment an analyte is quantitatively converted from its original oxidation state to a new oxidation state, either reduced or oxidized. As the substrate is consumed, the current also decreases, approaching zero when the conversion nears completion.
A liquid metal electrode is an electrode that uses a liquid metal, such as mercury, Galinstan, and NaK. They can be used in electrocapillarity, voltammetry, and impedance measurements.
Scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) is a technique within the broader class of scanning probe microscopy (SPM) that is used to measure the local electrochemical behavior of liquid/solid, liquid/gas and liquid/liquid interfaces. Initial characterization of the technique was credited to University of Texas electrochemist, Allen J. Bard, in 1989. Since then, the theoretical underpinnings have matured to allow widespread use of the technique in chemistry, biology and materials science. Spatially resolved electrochemical signals can be acquired by measuring the current at an ultramicroelectrode (UME) tip as a function of precise tip position over a substrate region of interest. Interpretation of the SECM signal is based on the concept of diffusion-limited current. Two-dimensional raster scan information can be compiled to generate images of surface reactivity and chemical kinetics.

Electrochemical stripping analysis is a set of analytical chemistry methods based on voltammetry or potentiometry that are used for quantitative determination of ions in solution. Stripping voltammetry have been employed for analysis of organic molecules as well as metal ions. Carbon paste, glassy carbon paste, and glassy carbon electrodes when modified are termed as chemically modified electrodes and have been employed for the analysis of organic and inorganic compounds.
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) absorption spectroelectrochemistry (SEC) is a multiresponse technique that analyzes the evolution of the absorption spectra in UV-Vis regions during an electrode process. This technique provides information from an electrochemical and spectroscopic point of view. In this way, it enables a better perception about the chemical system of interest. On one hand, molecular information related to the electronic levels of the molecules is obtained from the evolution of the spectra. On the other hand, kinetic and thermodynamic information of the processes is obtained from the electrochemical signal.

Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance (EQCM) is the combination of electrochemistry and quartz crystal microbalance, which was generated in the eighties. Typically, an EQCM device contains an electrochemical cells part and a QCM part. Two electrodes on both sides of the quartz crystal serve two purposes. Firstly, an alternating electric field is generated between the two electrodes for making up the oscillator. Secondly, the electrode contacting electrolyte is used as a working electrode (WE), together with a counter electrode (CE) and a reference electrode (RE), in the potentiostatic circuit constituting the electrochemistry cell. Thus, the working electrode of electrochemistry cell is the sensor of QCM.
References
- ↑ Kissinger, Peter; William R. Heineman (1996-01-23). Laboratory Techniques in Electroanalytical Chemistry, Second Edition, Revised and Expanded (2 ed.). CRC. ISBN 978-0-8247-9445-3.
- ↑ Bard, Allen J.; Larry R. Faulkner (2000-12-18). Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications (2 ed.). Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-04372-0.
- ↑ Zoski, Cynthia G. (2007-02-07). Handbook of Electrochemistry. Elsevier Science. ISBN 978-0-444-51958-0.