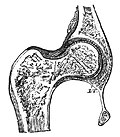
| Ball and socket joint | |
|---|---|
 1: Ball and socket joint; 2: Condyloid joint (Ellipsoid); 3: Saddle joint; 4 Hinge joint; 5: Pivot joint | |
 Capsule of shoulder-joint (distended). Anterior aspect. | |
| Identifiers | |
| TA98 | A03.0.00.050 |
| TA2 | 1562 |
| FMA | 75301 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The ball-and-socket joint (or spheroid joint) is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of axes, which have one common center. This enables the joint to move in many directions.
Contents
An enarthrosis is a special kind of spheroidal joint in which the socket covers the sphere beyond its equator. [1]