
The Irrawaddy dolphin is a euryhaline species of oceanic dolphin found in scattered subpopulations near sea coasts and in estuaries and rivers in parts of the Bay of Bengal and Southeast Asia. It closely resembles the Australian snubfin dolphin, which was not described as a separate species until 2005. It has a slate blue to a slate gray color. Although found in much of the riverine and marine zones of South and Southeast Asia, the only concentrated lagoon populations are found in Chilika Lake in Odisha, India and Songkhla Lake in southern Thailand.
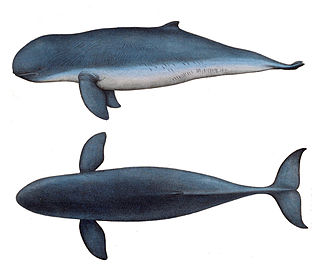
The snubfin dolphins (Orcaella) are a genus of cetaceans containing two members: the Irrawaddy dolphin and the Australian snubfin dolphin. The genus was long believed to be monotypic with the only species being the Irrawaddy dolphin; however, in 2005, supposed Irrawaddy dolphin populations inhabiting the Australian/New Guinean regions were found to be significantly different and were declared a separate new species named the Australian snubfin dolphin.

The lemon shark is a species of shark from the family Carcharhinidae, known for its yellowish color, which inspires its common name. It is classified as a Vulnerable species by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature. Lemon sharks can grow to 3.4 metres (11 ft) in length. They are often found in shallow subtropical waters and are known to inhabit and return to specific nursery sites for breeding. Often feeding at night, these sharks use electroreceptors to find their main source of prey, fish. Lemon sharks enjoy the many benefits of group living such as enhanced communication, courtship, predatory behavior, and protection. This species of shark gives birth to live young, and the females are polyandrous and have a biennial reproductive cycle. Lemon sharks are not thought to be a large threat to humans; there have been 10 recorded bites, none of which were life-threatening. The lemon shark's life span is unknown, but the average shark is 25 to 30 years old. The oldest recorded lemon shark in captivity died in 2023 at the age of 40 years.

The shortnose sucker , also known as the koptu by the Klamath Tribes, is a rare species of fish in the family Catostomidae, the suckers. It is native to southern Oregon and northern California in the United States. This species and related ones were a major food source for local tribes, and are still considered to be sacred animals. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.

Negaprion is a genus of requiem sharks in the family Carcharhinidae. It contains the two extant species of lemon sharks: the lemon shark of the Americas, and the sicklefin lemon shark of the Indo-Pacific. Both species are large, slow-moving, bulky sharks inhabiting shallow coastal waters, and can be identified by their short, blunt snouts, two dorsal fins of nearly equal size, and uniform yellowish brown or gray coloration.
Tylognathus is an invalid genus of ray-finned fishes in the family Cyprinidae. It was established by Heckel in 1843 without a type species. Varicorhinus diplostomus, described by Heckel in 1838 and erroneously redescribed by the same author in 1844 as T. valenciennesii, was later designated the type species. Today this fish is placed in the genus Bangana.

Naso brevirostris, also known as the short-nosed unicornfish, spotted unicornfish, brown unicornfish, lined unicornfish, longnose surgeonfish, palefin unicornfish, paletail unicornfish, shorthorned unicornfish or shortsnouted unicornfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Acanthuridae, the surgeonfishes, unicornfishes and tangs. It occurs in the Indian and western Pacific Oceans.
Chromis brevirostris, or colloquially known as the shortsnout chromis, is a type of damselfish that was described in 2008 by R. Pyle, J. Earle, and B. Greene in the western Pacific Ocean. This species comes from the genus Chromis which contains eighty species and counting, including C. abyssus, C. circumaurea, C. degruyi, and C. earina. Chromis brevirostris can be found in the Pacific Ocean, located as far north as the Marshall Islands to as far south as Fiji and Vanuatu, and spanning from Palau to Paluwat of the Caroline Islands. The species’ name, Chromis brevirostris, derives from Latin origin; brevis and rostrum mean “short” and “snout” respectively. It is generally abundant in its environment, living at depths of 90–120 metres (300–390 ft), tending to live in groups ranging in size from six to several dozen.
Bangana gedrosicus is a species of cyprinid fish endemic to Pakistan and Iran where it is only found in the Mashkel River drainage in Baluchistan.

Bangana is a genus of fish in the family Cyprinidae, the carps and minnows. It is distributed across much of southern and eastern Asia. Species live mainly in the flowing waters of tropical and subtropical rivers.
Sinilabeo is a genus of cyprinid freshwater fish found in China and Vietnam.

Leiognathus brevirostris, commonly known as the shortnose ponyfish, is a ray-finned fish of brackish and marine waters found from Indo-West Pacific to the Indian coasts and off Sri Lanka to China and south of Australia. Like its relatives, the fish is an amphidromous, demersal species which feeds on diatoms, copepods, Lucifer, nematodes and polychaetes. The fish has eight dorsal spines, sixteen dorsal soft rays, three anal spines and fourteen anal soft rays. Fresh specimens possess a golden gleam which fades with dryness.
Bangana almorae is a species of cyprinid fish endemic the Ganges basin in India.

Incisilabeo behri is a species of cyprinid fish endemic the Mekong basin in Cambodia, Thailand, Laos, and China. It was formerly categorized in the genus Bangana.

The kalabans is a species of cyprinid fish found in streams in the Himalayan foothills in India, Nepal, and China. It is also found in Bangladesh.
Bangana devdevi is a species of cyprinid fish found in India, Myanmar, and Thailand.

Bangana diplostoma is a species of cyprinid fish found in India and Pakistan.
Speolabeo musaei is a species of cyprinid cavefish endemic to the Xe Bang Fai River in Laos. It is the only species in the genus Speolabeo, but it was formerly included in Bangana.

Malacanthus brevirostris, the quakerfish, flagtail blanquillo, false whiting or stripetail tilefish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a tilefish belonging to the family Malacanthidae. It has a wide Indo-Pacific distribution.
Bangana nukta is a species of cyprinid fish, also known as nukta. It inhabits Krishna and Kaveri river systems in the states of Maharashta, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu. It is found in large streams and rivers with sand and boulder bed. It grows to 30 cm (12 in) total length.









