
Yanachaga–Chemillén National Park is a protected area located in the region of Pasco, Peru. It preserves part of the rainforests and cloud forests of central Peru.

An IUCN Red List Critically Endangered species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. As of 2021, of the 120,372 species currently tracked by the IUCN, there are 8,404 species that are considered to be Critically Endangered.
Barbatula namiri is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Balitoridae. It is found in Lebanon, Syria, and Turkey. Its natural habitat is rivers. It is found in the Orontes River watershed and coastal rivers of Lebanon and Syria north of southern Nahr al-Kabir al-Janoubi. It is threatened by habitat loss by water extraction and dams and pollution in Turkey; threats in Lebanon and Syria are unknown. The population is unknown but is considered stable in Turkey.
Barbatula samantica is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Balitoridae. It is found only in Turkey. Its natural habitat is rivers. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The stone loach is a European species of fresh water ray-finned fish in the family Nemacheilidae. It is one of nineteen species in the genus Barbatula. Stone loaches live amongst the gravel and stones of fast flowing water where they can search for food. The most distinctive feature of this small fish is the presence of barbels around the bottom jaw, which they use to detect their invertebrate prey. The body is a mixture of brown, green and yellow.

The Somali hedgehog is a species of mammal in the family Erinaceidae. It is endemic to Somalia and Somaliland. The Somali hedgehog is nocturnal.
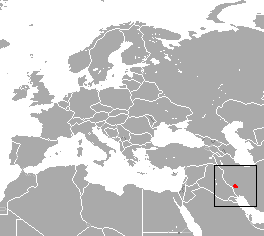
The Iranian shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to Iran. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Pearson's long-clawed shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is the only species within the genus Solisorex. It is endemic to Sri Lanka. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests and lowland grasslands. It is threatened by habitat loss. It is named after Joseph Pearson FRSE, Director of the Columbo Museum 1910-1933 who found it on 1 January 1924.

Day's shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to India. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The Mount Cameroon forest shrew or arrogant shrew, is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae endemic to Cameroon. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist montane forests.
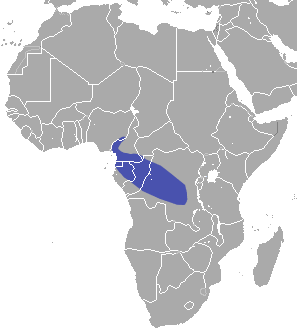
The greater forest shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae found in Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and Nigeria. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest.
Barbatula altayensis is one of seventeen species of ray-finned fish in the genus Barbatula. It is found in Mongolia and Xinjiang Province in China.
Oxynoemacheilus araxensis is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Oxynoemacheilus. It was described from specimens taken at a single locality near Kandili, the type locality, the upper drainage of the Euphrates in eastern Turkey. It has never been recorded anywhere else although there are many populations of superficially similar loaches in the Euphrates drainage which have not yet been identified; these may prove to be of this species or of Oxynoemacheilus kaynaki. Its habitat appears to be moderately fast flowing streams with a gravel bottom.
Oxynoemacheilus cinicus is a species of Cypriniformes fish in the genus Oxynoemacheilus. It is little known and is most likely from western Anatolia and the Büyük Menderes River.
Oxynoemacheilus argyrogramma, the two-spot loach is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Oxynoemacheilus. This species is found in the drainage of the Queiq River in Syria and Turkey, and the upper Euphrates drainage in Turkey and possibly in this drainage in Syria and Iraq. It has almost been extirpated from the Queiq as this river has virtually dried out but it remains abundant in the Euphrates. This species can be found in a wide range of habitats as long as there is a moderately fast current from small upland streams to banks of large rivers. It can also occur in stagnant water bodies such as reservoirs. It is threatened by water abstraction, lowering rainfall due to climate change and the construction of dams. The economic development of the area where this species occurs exacerbates these threats. Freyhof and Özuluǧ published a paper in 2017 that argued that Oxynoemacheilus euphraticus was a valid species and not a synonym of O. argyrogramma.
Oxynoemacheilus germencicus, the Carian loach, is a species of Cypriniformes fish in the genus Oxynoemacheilus. It is known only from the Büyük Menderes River and lower Gediz River in western Anatolia, it probably also occurred in the Kücük Menderes, a river which sits between the Büyük Menderes and Gediz, and has been extirpated from that river by pollution and abstraction. It remains widespread and locally abundant in the other two rivers but the populations have declined and the species is threatened by climate change reducing rainfall in the area and human activities such as damming and water abstraction as well as pollution>
Oxynoemacheilus kosswigi, the Paphlagonian loach, is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Oxynoemacheilus. This species is found in the Kizilirmak and Yeşilırmak drainages in northern Anatolia, Turkey. It lives in waters which vary from those with a moderately fast flow to almost still waters and prefers muddy or gravel substrates, It remains abundant and widespread within the two drainage systems in which it occurs but it is suspected that a number f populations may have declined or been made locally extinct by the increasing construction of small hydro-electric dams.

Barbatula quignardi, the Languedoc stone loach, is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Barbatula.
Barbatula zetensis, also known as the Zeta stone loach, is a species of Cypriniformes fish in the genus Barbatula it is found in the drainage of the River Morača in the Lake Skadar basin in Montenegro. It is common in streams and rivers with stone bottom.
Ctenophryne barbatula is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Peru and only known from the Yanachaga–Chemillén National Park, its type locality in the Pasco Region. The specific name barbatula is the diminutive of the Latin barbatus, meaning "bearded". It refers to the beard-like spines under the lower jaw of males.










