
Hippoboscoidea is a superfamily of the Calyptratae. The flies in this superfamily are blood-feeding obligate parasites of their hosts. Four families are often placed here:

A nest box, also spelled nestbox, is a man-made enclosure provided for animals to nest in. Nest boxes are most frequently utilized for birds, in which case they are also called birdhouses or a birdbox/bird box, but some mammals such as bats may also use them. Placing nestboxes or roosting boxes may also be used to help maintain populations of particular species in an area.

The common vampire bat is a small, leaf-nosed bat native to the Americas. It is one of three extant species of vampire bats, the other two being the hairy-legged and the white-winged vampire bats.

Nycteribiidae is a family of the true fly superfamily Hippoboscoidea. Together with their close relatives the Streblidae, they are known as "bat flies". As the latter do not seem to be a monophyletic group, it is conceivable that bat flies cannot be united into a single family.
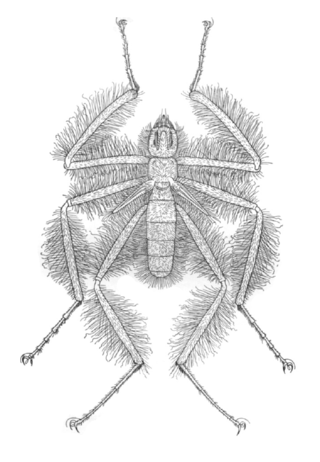
The family Mormotomyiidae contains only one known species, Mormotomyia hirsuta, commonly known as the frightful hairy fly or terrible hairy fly, which is found in Kenya. The fly was first described by English entomologist Ernest Edward Austen, and specimens have been collected from one location on a mountain in the Ukasi Hill, in a cleft where a bat roost is located; this may possibly be the most restricted geographic distribution for any fly family. The larvae have been collected from bat guano. Adult flies are believed to feed on bodily secretions of bats. The fly measures about 1 cm long, with hairy legs, and, due to its nonfunctional wings and tiny eyes, looks more like a spider than a fly. Specimens have been collected only three times, in 1933, 1948, and 2010. Tested members of the population showed higher levels of genetic variation than would be expected for such a restricted range, suggesting that additional undiscovered populations exist with gene flow occurring between them and the known population in Ukasi Hill.

The greater noctule bat is a rare carnivorous bat found in Europe, West Asia, and North Africa. It is the largest and least studied bat in Europe with a wingspan of up to 46 centimetres (18 in) and is one of the few bat species to feed on passerine birds. Greater noctule bats are the only bat species to hunt birds on the wing rather than when roosting. The greater noctule bat has wings adapted for open-air hunting and uses echolocation frequencies above the hearing range of birds.

The Hawaiian hoary bat, also known as ʻōpeʻapeʻa, is a species of bat endemic to the islands of Hawaiʻi. The Hawaiian hoary bat occupies the major Hawaiian islands, making it the only extant and native terrestrial mammal in the islands. Some studies report that the mainland hoary bat lives in sympatry on the Hawaiian Islands alongside the Hawaiian hoary bat, although this is disputed. The Hawaiian hoary bat was officially named the state land mammal of Hawaiʻi in 2015. It is a federally listed endangered taxon of the United States.
Dormer's bat or Dormer's pipistrelle is a species of vesper bat. It is the only species in its genus. It is found in Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, and Pakistan. Its natural habitats are subtropical and tropical dry forests, arable land, plantations, rural gardens, and urban areas.

The lesser bamboo bat or lesser flat-headed bat is one of the smallest species of vesper bat, and is native to Southeast Asia.

Townsend's big-eared bat is a species of vesper bat.
The dark-brown serotine is a species of vesper bat found in Central and West Africa.

White-nose syndrome (WNS) is a fungal disease in North American bats which has resulted in the dramatic decrease of the bat population in the United States and Canada, reportedly killing millions as of 2018. The condition is named for a distinctive fungal growth around the muzzles and on the wings of hibernating bats. It was first identified from a February 2006 photo taken in a cave located in Schoharie County, New York. The syndrome has rapidly spread since then. In early 2018, it was identified in 33 U.S. states and seven Canadian provinces; plus the fungus, albeit sans syndrome, had been found in three additional states. Most cases are in the eastern half of both countries, but in March 2016, it was confirmed in a little brown bat in Washington state. In 2019, evidence of the fungus was detected in California for the first time, although no affected bats were found.

Basilia is a genus of bat flies in the family Nycteribiidae.

The New Zealand bat fly is a small, wingless insect which lives in a commensal relationship with the New Zealand lesser short-tailed bat. It is a true fly, in the order Diptera, placed in its own genus, Mystacinobia, and its own family, Mystacinobiidae. Although many other species of bat fly exist throughout the world, the New Zealand bat fly is endemic to the islands of New Zealand. Unlike other similar looking bat flies, this species is not a parasite and is only phoretic, feeding on bat guano. It appears to be the only insect, parasitic or otherwise, which lives with these bats.

Campiglossa is a genus of fruit flies in the family Tephritidae. There are at least 190 described species in Campiglossa.
Figaro is a genus of shark, and part of the family Pentanchidae, the deepwater catsharks. Until 2008, Figaro was generally considered to be a subgenus of Galeus, the sawtail catsharks. The two known species are found off Australia, inhabiting deep, offshore waters on or near the bottom. Figaro contains small, slender, firm-bodied sharks that bear distinctive crests of enlarged, spiny dermal denticles along the dorsal and ventral edges of their short caudal fins. The caudal peduncle is relatively long, such as that the anal and caudal fins are some distance apart. In adult males, the inner margins of the pelvic fins are fused together to form a subtle "apron" over the claspers. F. boardmani is a predator of fishes, crustaceans, and cephalopods, and is oviparous; less is known about the F. striatus. Both are harmless and are of no economic importance.
Basilia fletcheri is parasitic bat fly in the genus Basilia, in the subgenus Basilia. It is found in India.

Enischnomyia is an extinct genus of bat fly in the family Streblidae. At the time of its description the new genus comprised a single species, Enischnomyia stegosoma, known from a single Miocene fossil found on Hispaniola. E. stegosoma was the first fossil streblid bat fly described from a fossil, and the only member of the subfamily Nycterophiliinae described from Hispaniola. The species is host for the plasmodiid Vetufebrus ovatus preserved in its salivary glands and midgut.
Livingstone's yellow bat or Livingstone's house bat is a species of bat found in Africa.













