
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus species in the genus Tobamovirus that infects a wide range of plants, especially tobacco and other members of the family Solanaceae. The infection causes characteristic patterns, such as "mosaic"-like mottling and discoloration on the leaves. TMV was the first virus to be discovered. Although it was known from the late 19th century that a non-bacterial infectious disease was damaging tobacco crops, it was not until 1930 that the infectious agent was determined to be a virus. It is the first pathogen identified as a virus.
Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) is a member of the genus Caulimovirus, one of the six genera in the family Caulimoviridae, which are pararetroviruses that infect plants. Pararetroviruses replicate through reverse transcription just like retroviruses, but the viral particles contain DNA instead of RNA.

Geminiviridae is a family of plant viruses that encode their genetic information on a circular genome of single-stranded (ss) DNA. There are currently 485 species in this family, divided among 9 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: bright yellow mosaic, yellow mosaic, yellow mottle, leaf curling, stunting, streaks, reduced yields. They have single-stranded circular DNA genomes encoding genes that diverge in both directions from a virion strand origin of replication. According to the Baltimore classification they are considered class II viruses. It is the largest known family of single stranded DNA viruses.

Potyvirus is a genus of viruses in the family Potyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 183 species in this genus including the type species Potato virus Y. The genus is named after the type virus. Potyviruses account for ~30% of the currently known plant viruses. Like begomoviruses, members of this genus may cause significant losses in agricultural, pastoral, horticultural and ornamental crops. More than 200 species of aphids spread potyviruses and most are from the subfamily Aphidinae.

Begomovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Geminiviridae. They are plant viruses that as a group have a very wide host range, infecting dicotyledonous plants. Worldwide they are responsible for a considerable amount of economic damage to many important crops such as tomatoes, beans, squash, cassava and cotton. There are currently 424 species in this genus including the type species Bean golden yellow mosaic virus.

Maize streak virus (MSV) is a virus primarily known for causing maize streak disease (MSD) in its major host, and which also infects over 80 wild and domesticated grasses. It is an insect-transmitted maize pathogen in the genus Mastrevirus of the family Geminiviridae that is endemic in sub-Saharan Africa and neighbouring Indian Ocean island territories such as Madagascar, Mauritius and La Reunion. The A-strain of MSV (MSV-A) causes sporadic maize streak disease epidemics throughout the maize growing regions of Africa. MSV was first described by the South African entomologist Claude Fuller who referred to it in a 1901 report as "mealie variegation".

Alfalfa mosaic virus (AMV), also known as Lucerne mosaic virus or Potato calico virus, is a worldwide distributed phytopathogen that can lead to necrosis and yellow mosaics on a large variety of plant species, including commercially important crops. It is the only Alfamovirus of the Bromoviridae family. In 1931 Weimer J.L. was the first to report AMV in alfalfa. Transmission of the virus occurs mainly by some aphids, by seeds or by pollen to the seed.
Cotton leaf curl viruses (CLCuV) are a number of plant pathogenic virus species of the family Geminiviridae.
Mungbean yellow mosaic virus (MYMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Geminiviridae. Of the various viral diseases inflicting legume crops, Mungbean Yellow Mosaic disease is one of the most destructive and widely distributed. The disease has been reported from various countries.
Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) is a DNA virus from the genus Begomovirus and the family Geminiviridae. TYLCV causes the most destructive disease of tomato, and it can be found in tropical and subtropical regions causing severe economic losses. This virus is transmitted by an insect vector from the family Aleyrodidae and order Hemiptera, the whitefly Bemisia tabaci, commonly known as the silverleaf whitefly or the sweet potato whitefly. The primary host for TYLCV is the tomato plant, and other plant hosts where TYLCV infection has been found include eggplants, potatoes, tobacco, beans, and peppers. Due to the rapid spread of TYLCV in the last few decades, there is an increased focus in research trying to understand and control this damaging pathogen. Some interesting findings include virus being sexually transmitted from infected males to non-infected females, and an evidence that TYLCV is transovarially transmitted to offspring for two generations.
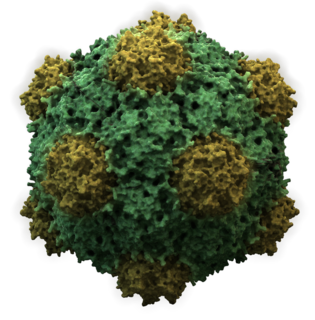
Secoviridae is a family of viruses in the order Picornavirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 86 species in this family, divided among 8 genera or not assigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of families Sequiviridae, now dissolved, and Comoviridae, now subfamily Comovirinae, along with the then unassigned genera Cheravirus, Sadwavirus, and Torradovirus.
Alphasatellites are single stranded satellite DNA that are dependent on a virus for transmission. The genome is a single circular single strand DNA molecule. The first alphasatellites were described in 1999 and were associated with cotton leaf curl disease and Ageratum yellow vein disease. As begomoviruses are being characterised at the molecular level an increasing number of alphasatellites are being described.

Emaravirus is a genus of plant viruses and the sole genus in the family Fimoviridae. The genus has 11 species. The type species European mountain ash ringspot-associated emaravirus is associated with a leaf mottling and ringspot disease of European mountain ash Sorbus aucuparia. It can be transmitted by grafting and possibly mites.

Pepper leaf curl virus(PepLCV) is a DNA virus from the genus Begomovirus and the family Geminiviridae. PepLCV causes severe disease especially in pepper. It can be found in tropical and subtropical regions such as Thailand and India, but has also been detected in countries such as the United States and Nigeria. This virus is transmitted by an insect vector from the family Aleyrodidae and order Hemiptera, the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. The primary host for PepLCV are several Capsicum spp.. PepLCV has been responsible for several epidemics and causes severe economic losses. It is the focus of research trying to understand the genetic basis of resistance. Currently, a source of resistance to the virus has been identified in the Bhut Jolokia pepper.
Chilli leaf curl virus(ChiLCV) is a DNA virus from the genus Begomovirus and the family Geminiviridae. ChiLCV causes severe disease especially in pepper, but also affects other crops such as tomato. It can be found in tropical and subtropical regions primarily in India, but has also been detected in countries such as Indonesia and Sri Lanka. This virus is transmitted by an insect vector from the family Aleyrodidae and order Hemiptera, the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. The primary host for ChiLCV are several Capsicum spp., but host species also include tomato and amaranth. ChiLCV has been responsible for several epidemics and causes severe economic losses. It is the focus of research trying to understand the genetic basis of resistance. Currently, a few sources of resistance have been discovered and used to breed resistant varieties.
Papaya leaf curl virus(PaLCuV) is a DNA virus from the genus Begomovirus and the family Geminiviridae. PaLCuV causes severe disease in papaya, but can sometimes infect other crops such as tobacco or tomato. It can be found in tropical and subtropical regions primarily in India, but closely related species have also been detected in countries such as China, Malaysia, Nigeria and South Korea. This virus is transmitted by an insect vector from the family Aleyrodidae and order Hemiptera, the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. PaLCuV has been responsible for several epidemics and causes severe economic losses. Because of the broad diversity of these viruses, their characterization and control remains difficult.
Riboviria is a realm of viruses that includes all viruses that use a homologous RNA-dependent polymerase for replication. It includes RNA viruses that encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; and, it includes reverse-transcribing viruses that encode an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called RNA replicase, produces RNA from RNA. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (RdDp), also called reverse transcriptase (RT), produces DNA from RNA. These enzymes are essential for replicating the viral genome and transcribing viral genes into messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation of viral proteins.
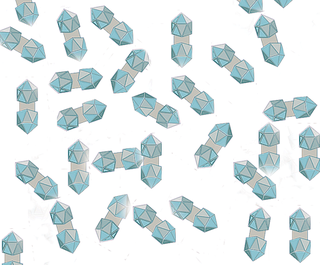
Sweet potato leaf curl virus is commonly abbreviated SPLCV. Select isolates are referred to as SPLCV followed by an abbreviation of where they were isolated. For example, the Brazilian isolate is referred to as SPLCV-Br.
Tomato yellow leaf curl China virus (TYLCCNV) is a virus which contains 25 isolates. It infects plants as different as tobacco and tomato, as well as genetically modified plants. Petunias can be infected, but show no symptoms. The microbiology of the virus has been studied in the Chinese province of Yunnan. Tomato yellow leaf curl China virus belongs to the genus Begomovirus, which also contains the tomato leaf curl China virus.








