
In anatomy, the palatine bones are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species, located above the uvula in the throat. Together with the maxilla, they comprise the hard palate.

The North Santiam River is a 92-mile (148 km) tributary of the Santiam River in western Oregon in the United States. It drains 766 square miles (1,980 km2) of the Cascade Range on the eastern side of the Willamette Valley east of Salem.

The Siskiyou Mountains salamander, also called the Siskiyou Mountain salamander, exists only in isolated locations along the Klamath River in northern California and southern Oregon. It is a close relative of the Del Norte salamander, and some herpetologists believe it may be a subspecies of that animal.

The northwestern salamander is a species of mole salamander that inhabits the northwest Pacific coast of North America. These fairly large salamanders grow to 8.7 in (220 mm) in length. It is found from southeastern Alaska on May Island, through Washington and Oregon south to the mouth of the Gualala River, Sonoma County, California. It occurs from sea level to the timberline, but not east of the Cascade Divide. Its range includes Vancouver Island in British Columbia and The San Juan Islands, Cypress, Whidbey, Bainbridge, and Vashon Islands in Washington.

The genus Taricha consists of four species of highly toxic newts in the family Salamandridae. Their common name is Pacific newts, sometimes also western newts or roughskin newts. The four species within this genus are the California newt, the rough-skinned newt, the red-bellied newt, and the sierra newt, all of which are found on the Pacific coastal region from southern Alaska to southern California, with one species possibly ranging into northern Baja California, Mexico.

The rough-skinned newt or roughskin newt is a North American newt known for the strong toxin exuded from its skin.

The Mount Jefferson Wilderness is a wilderness area located on and around Mount Jefferson in the central Cascade Range of Oregon in the United States. The wilderness lies within the Willamette National Forest and Deschutes National Forest. The wilderness area covers 111,177 acres (449.92 km2), with more than 150 lakes. It also has 190 miles (310 km) of trails, including 40 miles (64 km) of the Pacific Crest National Scenic Trail. Three Fingered Jack and Mount Jefferson are both prominent features of the wilderness area. Mount Jefferson Wilderness is the second most visited Oregon wilderness area after the Three Sisters Wilderness.

The Sierra newt is a newt found west of the Sierra Nevada, from Shasta county to Tulare County, in California, Western North America.
The Tulameen River is a tributary of the Similkameen River in the Canadian province of British Columbia. The Tulameen River is part of the Columbia River drainage basin, being a tributary of the Similkameen River, which flows into the Okanagan River, which flows into the Columbia River.
The Crater Lake newt or Mazama newt, Taricha granulosa mazamae, is a subspecies of the rough-skinned newt. Its type locality is Crater Lake, Oregon. Similar newts have been found in Alaska, but their identity is unclear.

A nuptial pad is a secondary sex characteristic present on some mature male frogs and salamanders. Triggered by androgen hormones, this breeding gland appears as a spiked epithelial swelling on the forearm and prepollex that aids with grip, which is used primarily by males to grasp females during amplexus. They can also be used in male–male combat in some species.
Megalobatrachonema is a nematode genus. Species of this genus are parasites of a number of amphibians including the rough-skinned newt.
Karotomorpha is a genus of parasites with a flagellum structure. This organism can infect a variety of higher life forms including a number of amphibians. For example, this genus is known to be a parasite of the rough-skinned newt, a widespread newt in the western USA.
Cephalouterina is a genus of trematodes within the family Lecithodendriidae under the order Plagiorchiida. Individuals of this genus are known to use amphibian hosts.
Cephalouterina decamptodoni is a species of trematodes within the family Lecithodendriidae under the order Plagiorchiida. This species is sometimes known to use amphibian hosts.
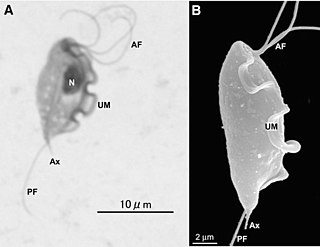
Tritrichomonas is a genus of single celled flagellated parasitic excavates, some of whose species are known to be pathogens of the bovine reproductive tract as well as the intestinal tract of felines.

Marion Lake is a subalpine lake located in Linn County of the U.S. state of Oregon. The lake is in central Oregon's Cascades within the Mount Jefferson Wilderness. The lake is approximately 300 acres (1.2 km2), at an elevation of 4,134 feet (1,260 m).
Perennibranchiate, in zoology, is the condition of an organism retaining branchae, or gills, through life. This condition is generally said of certain amphibia, such as the mudpuppy. The term is opposed to caducibranchiate. In some cases only a small proportion of a given amphibian population is perennibranchiate, but in other instances a preponderance of the individuals have an adult gill retention. For example, in the case of the Rough-skinned Newt in the Cascade Mountains populations, approximately ninety percent of the adult population is perennibranchiate.

The Ecology of the North Cascades is heavily influenced by the high elevation and rain shadow effects of the mountain range. The North Cascades is a section of the Cascade Range from the South Fork of the Snoqualmie River in Washington, United States, to the confluence of the Thompson and Fraser Rivers in British Columbia, Canada, where the range is officially called the Cascade Mountains but is usually referred to as the Canadian Cascades. The North Cascades Ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion in the Commission for Environmental Cooperation's classification system.

There are 14 species of amphibians and 5 species of reptiles known to occur in Mount Rainier National Park.














