
Oregano is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae. It was native to the Mediterranean region, but widely naturalised elsewhere in the temperate Northern Hemisphere.

Salvia rosmarinus, commonly known as rosemary, is a shrub with fragrant, evergreen, needle-like leaves and white, pink, purple, or blue flowers, native to the Mediterranean region. Until 2017, it was known by the scientific name Rosmarinus officinalis, now a synonym.

Begonia is a genus of perennial flowering plants in the family Begoniaceae. The genus contains more than 2,000 different plant species. The Begonias are native to moist subtropical and tropical climates. Some species are commonly grown indoors as ornamental houseplants in cooler climates. In cooler climates some species are cultivated outside in summertime for their bright colorful flowers, which have sepals but no petals.

Psilocybe cubensis, commonly known as the magic mushroom, shroom, golden halo, cube, or gold cap, is a species of psilocybin mushroom of moderate potency whose principal active compounds are psilocybin and psilocin. It belongs to the fungus family Hymenogastraceae and was previously known as Stropharia cubensis. It is the best-known psilocybin mushroom due to its wide distribution and ease of cultivation. This mushroom being optimal for home cultivation specifically, as was suggested in the 1970s, is primarily what led to P. cubensis being the psilocybin mushroom species most common on the black market as a street drug.

Guava is a common tropical fruit cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions. The common guava Psidium guajava is a small tree in the myrtle family (Myrtaceae), native to Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean and northern South America. The name guava is also given to some other species in the genus Psidium such as strawberry guava and to the pineapple guava, Feijoa sellowiana. In 2019, 55 million tonnes of guavas were produced worldwide, led by India with 45% of the total. Botanically, guavas are berries.

Ulex is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. The genus comprises about 20 species of thorny evergreen shrubs in the subfamily Faboideae of the pea family Fabaceae. The species are native to parts of western Europe and northwest Africa, with the majority of species in Iberia.
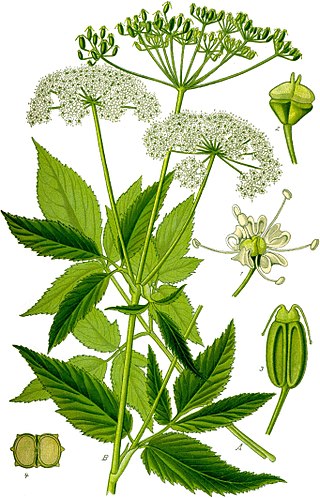
Aegopodium podagraria, commonly called ground elder, is a species of flowering plant in the carrot family Apiaceae that grows in shady places. The name "ground elder" comes from the superficial similarity of its leaves and flowers to those of elder (Sambucus), which is not closely related. Other common names include herb gerard, bishop's weed, goutweed, gout wort, snow-in-the-mountain, English masterwort and wild masterwort. It is the type species of the genus Aegopodium. It is native to Europe and Asia, but has been introduced around the world as an ornamental plant, where it occasionally poses an ecological threat as an invasive exotic plant.

Delonix regia is a species of flowering plant in the bean family Fabaceae, subfamily Caesalpinioideae native to Madagascar. It is noted for its fern-like leaves and flamboyant display of orange-red flowers over summer. In many tropical parts of the world it is grown as an ornamental tree and in English it is given the name royal poinciana, flamboyant, phoenix flower, flame of the forest, or flame tree.

Plumeria, also known as frangipani, is a genus of flowering plants in the subfamily Rauvolfioideae, of the family Apocynaceae. Most species are deciduous shrubs or small trees. The species variously are endemic to the Neotropical realm, but are often grown as cosmopolitan ornamentals in tropical regions, especially in Hawaii, as well as hot desert climates in the Arabian Peninsula with proper irrigation.

Sanguisorba minor, the salad burnet, garden burnet, small burnet, burnet, pimpernelle, Toper's plant, and burnet-bloodwort, is an edible perennial herbaceous plant in the family Rosaceae. It has ferny, toothed-leaf foliage; the unusual crimson, spherical flower clusters rise well above the leaves on thin stems. It generally grows to 25–55 cm tall. The large, long, taproots store water, making it drought-tolerant.

Caulophyllum is a small genus of perennial herbs belonging to the family Berberidaceae and closely related to the Eurasian genera Leontice and Gymnospermium. It is native to eastern Asia and eastern North America. These plants are distinctive spring wildflowers, which grow in moist, rich woodland, it is known for its large triple-compound leaf, and large blue, berry-like fruits. Unlike many spring wildflowers, it is not an ephemeral plant and persists throughout much of the summer. Common names for plants in this genus include blue cohosh, squaw root, and papoose root. As hinted at by its common names, this plant is well known as an alternative medicine for inducing childbirth and menstrual flow; it is also considered a poisonous plant.

Alternanthera sessilis is a flowering plant known by several common names, including sissoo spinach, Brazilian spinach, sessile joyweed, dwarf copperleaf. It is cultivated as a vegetable worldwide.

Prosopis velutina, commonly known as velvet mesquite, is a small to medium-sized tree. It is a legume adapted to a dry, desert climate. Though considered to be a noxious weed in states outside its natural range, it plays a vital role in the ecology of the Sonoran Desert.

Emilia sonchifolia, also known as lilac tasselflower or cupid's shaving brush, is a tropical flowering species of tasselflower in the sunflower family. It is widespread in tropical regions around the world, apparently native to Asia and naturalized in Africa, Australia, the Americas, and various oceanic islands.

Drimia maritima is a species of flowering plant in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae. This species is known by several common names, including squill, sea squill, sea onion, and maritime squill. It may also be called red squill, particularly a form which produces red-tinged flowers instead of white. It is native to southern Europe, western Asia, and northern Africa.

Hildegardia cubensis is a species of flowering plant in the family Malvaceae. The species is endemic to Cuba, and is threatened by habitat loss. In Cuba it is commonly known as Guana.

Hyssopus officinalis or hyssop is a shrub in the Lamiaceae or mint family native to Southern Europe, the Middle East, and the region surrounding the Caspian Sea. Due to its purported properties as an antiseptic, cough reliever, and expectorant, it has been used in traditional herbal medicine.

Bougainvillea spectabilis, also known as great bougainvillea, is a species of flowering plant. It is native to Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, and Argentina's Chubut Province.

Ceratotheca sesamoides is an annual flowering plant in the genus Ceratotheca. It is indigenous to Africa, and grows both as a wild and locally-cultivated species, and is colloquially referred to as false sesame owing to its marked similarities with common sesame. The plant is most commonly cultivated in the African savannah and other semi-arid areas on the continent, and is found across Africa in both tropical and sub-tropical latitudes, usually growing in sandier soils south of the Sahara. It can be identified by numerous hairs on the stem; its pinkish flowers, often showing brown and purple markings; and a sub-erect growth habit. The leaves and flowers are often consumed as a vegetable or used in sauces. The leaves are thought to have medicinal properties, while the seeds can be used to produce cooking oil. Despite its many uses and increasing domestication at a local level, the plant remains predominantly underused and undervalued.

Begonia cucullata, also known as clubbed begonia, is a species of the Begoniaceae that is native to South American countries of Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. A common garden plant and part of the section Begonia, it was described in 1805 by Carl Ludwig Willdenow (1765–1812). The specific epithet "cucullata" means "resembling a hood" or "hooded".




















