Related Research Articles
The Rhodospirillales are an order of Pseudomonadota.
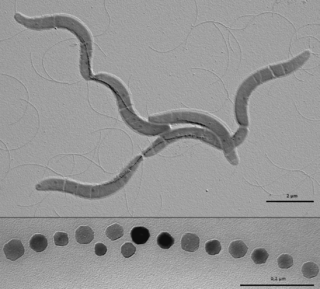
The Beijerinckiaceae are a family of Hyphomicrobiales named after the Dutch microbiologist Martinus Willem Beijerinck. Beijerinckia is a genus of free-living aerobic nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Acidotolerant Beijerinckiaceae has been shown to be the main bacterial methanol sink in a deciduous forest soil and highlights their importance for the conversion of methanol in forest soils.
Lentisphaerota is a phylum of bacteria closely related to Chlamydiota and Verrucomicrobiota.
Armatimonadota is a phylum of gram-negative bacteria.
Massilia dura is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacterium from the genus Massilia and family Oxalobacteraceae, which was isolated with Massilia albidiflava, Massilia plicata, and Massilia lutea from soil samples collected from southeast China. Colonies of M. dura are hard and compact and their color is pale white to yellow.
Comamonas zonglianii is a Gram-negative, aerobic, oxidase- and catalase-positive, nonmotile bacterium from the genus Comamonas and family Comamonadaceae, which was isolated from a phenol-contaminated soil. Colonies of C. zonglianii are pale yellow in color.
Thiomonas cuprina is an As(III)-oxidizing bacterium from the genus Thiomonas. It is proposed to be reclassified, along with Thiomonas arsenivorans, as strains of Thiomonas delicata.
Thiomonas delicata is an As(III)-oxidizing, nonmotile bacterium from the genus Thiomonas. Colonies of T. delicata are whitish-yellow in color.
Variovorax dokdonensis is a Gram-negative, motile bacterium from the genus Variovorax, which was isolated from soil in Dokdo in Korea. Colonies of V. dokdonensis are yellow in color.
Sutterella parvirubra is a Gram-negative, oxidase- and catalase-negative, anaerobic, non-spore-forming, nonmotile bacterium from the genus Sutterella in the family Sutterellaceae, which was isolated from human faeces.
Sutterella stercoricanis is a Gram-negative, oxidase- and catalase-negative, anaerobic and microaerophilic, non-spore-forming, rod-shaped bacterium from the genus Sutterella in the family of Sutterellaceae, which was isolated from dog faeces.
Azospirillum doebereinerae is a species of nitrogen-fixing bacteria associated with the roots of Miscanthus species. Its type strain is GSF71T.
Aeromonas fluvialis is a Gram-negative, oxidase- and catalase-positive, facultatively anaerobic, non-spore-forming bacterium of the genus Aeromonas isolated from water from the Muga River in Girona in northeastern Spain.
Beijerinckia is a free living nitrogen-fixing aerobic microbe. It has abundant of nitrogenase enzyme capable of nitrogen reduction.
Beijerinckia derxii is a nitrogen fixing strain of bacteria from the genus of Beijerinckia.
Beijerinckia mobilis is a nitrogen fixing bacteria from the genus of Beijerinckia.
Ancylobacter oerskovii is a Gram-negative, pleomorphic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria from the family of Xanthobacteraceae which has been isolated from soil from Muğla in Turkey. Ancylobacter oerskovii has the ability to utilize oxalic acid.
Azospirillum is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic, non-fermentative and nitrogen-fixing bacterial genus from the family of Rhodospirillaceae. Azospirillum bacteria can promote plant growth.
Nitriliruptor alkaliphilus is a non-spore-forming and non-motile bacterium from the genus Nitriliruptor which has been isolated from sediments from a soda lake in Siberia in Russia.
References
- ↑ LPSN lpsn.dsmz.de
- ↑ "Straininfo of Beijerinckia doebereinerae". Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2014-06-25.
- ↑ UniProt
- ↑ Oggerin, M.; Arahal, D. R.; Rubio, V.; Marin, I. (2009). "Identification of Beijerinckia fluminensis strains CIP 106281T and UQM 1685T as Rhizobium radiobacter strains, and proposal of Beijerinckia doebereinerae sp. nov. To accommodate Beijerinckia fluminensis LMG 2819". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 59 (9): 2323–8. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.006593-0 . PMID 19620377.