
A carbon sink is anything, natural or otherwise, that accumulates and stores some carbon-containing chemical compound for an indefinite period and thereby removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These sinks form an important part of the natural carbon cycle. An overarching term is carbon pool, which is all the places where carbon can be. A carbon sink is a type of carbon pool that has the capability to take up more carbon from the atmosphere than it releases.

In botany, an evergreen is a plant which has foliage that remains green and functional through more than one growing season. This contrasts with deciduous plants, which lose their foliage completely during the winter or dry season.

A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have special adaptations to take in extra oxygen and to remove salt, which allow them to tolerate conditions that would kill most plants. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in several plant families. They occur worldwide in the tropics and subtropics and even some temperate coastal areas, mainly between latitudes 30° N and 30° S, with the greatest mangrove area within 5° of the equator. Mangrove plant families first appeared during the Late Cretaceous to Paleocene epochs, and became widely distributed in part due to the movement of tectonic plates. The oldest known fossils of mangrove palm date to 75 million years ago.
Leaf mold is the compost produced by decomposition of shaded deciduous shrub and tree leaves, primarily by fungal breakdown in a slower, cooler manner as opposed to the bacterial degradation of leaves.
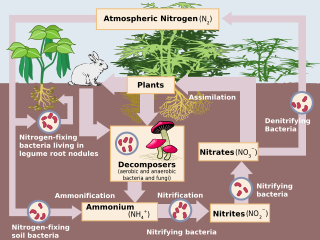
Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process where nitrate (NO3−) is reduced and ultimately produces molecular nitrogen (N2) through a series of intermediate gaseous nitrogen oxide products. Facultative anaerobic bacteria perform denitrification as a type of respiration that reduces oxidized forms of nitrogen in response to the oxidation of an electron donor such as organic matter. The preferred nitrogen electron acceptors in order of most to least thermodynamically favorable include nitrate (NO3−), nitrite (NO2−), nitric oxide (NO), nitrous oxide (N2O) finally resulting in the production of dinitrogen (N2) completing the nitrogen cycle. Denitrifying microbes require a very low oxygen concentration of less than 10%, as well as organic C for energy. Since denitrification can remove NO3−, reducing its leaching to groundwater, it can be strategically used to treat sewage or animal residues of high nitrogen content. Denitrification can leak N2O, which is an ozone-depleting substance and a greenhouse gas that can have a considerable influence on global warming.

Coarse woody debris (CWD) or coarse woody habitat (CWH) refers to fallen dead trees and the remains of large branches on the ground in forests and in rivers or wetlands. A dead standing tree – known as a snag – provides many of the same functions as coarse woody debris. The minimum size required for woody debris to be defined as "coarse" varies by author, ranging from 2.5–20 cm (1–8 in) in diameter.
Methanotrophs are prokaryotes that metabolize methane as their source of carbon and chemical energy. They are bacteria or archaea, can grow aerobically or anaerobically, and require single-carbon compounds to survive.
Methylotrophs are a diverse group of microorganisms that can use reduced one-carbon compounds, such as methanol or methane, as the carbon source for their growth; and multi-carbon compounds that contain no carbon-carbon bonds, such as dimethyl ether and dimethylamine. This group of microorganisms also includes those capable of assimilating reduced one-carbon compounds by way of carbon dioxide using the ribulose bisphosphate pathway. These organisms should not be confused with methanogens which on the contrary produce methane as a by-product from various one-carbon compounds such as carbon dioxide. Some methylotrophs can degrade the greenhouse gas methane, and in this case they are called methanotrophs. The abundance, purity, and low price of methanol compared to commonly used sugars make methylotrophs competent organisms for production of amino acids, vitamins, recombinant proteins, single-cell proteins, co-enzymes and cytochromes.
Microbial intelligence is the intelligence shown by microorganisms. The concept encompasses complex adaptive behavior shown by single cells, and altruistic or cooperative behavior in populations of like or unlike cells mediated by chemical signalling that induces physiological or behavioral changes in cells and influences colony structures.
Pink-Pigmented Facultative Methylotrophs, commonly abbreviated to PPFMs, are bacteria that are members of the genus Methylobacterium and are commonly found in soil, dust, various fresh water supplies and on plant surfaces. Although Gram negative, Methylobacteria often stain gram variable and are easily isolated using methanol-based mineral medium. Their pigmentation, which is frequently pink but may also be yellow or orange, is thought to provide protection from solar UV radiation which damages the DNA of bacteria at low doses because of their small cell size. This color is present due to the carotenoid pigments within the cell.

The microbial loop describes a trophic pathway where, in aquatic systems, dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is returned to higher trophic levels via its incorporation into bacterial biomass, and then coupled with the classic food chain formed by phytoplankton-zooplankton-nekton. In soil systems, the microbial loop refers to soil carbon. The term microbial loop was coined by Farooq Azam, Tom Fenchel et al. in 1983 to include the role played by bacteria in the carbon and nutrient cycles of the marine environment.

Gammaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota. It contains about 250 genera, which makes it the most genus-rich taxon of the Prokaryotes. Several medically, ecologically, and scientifically important groups of bacteria belong to this class. It is composed by all Gram-negative microbes and is the most phylogenetically and physiologically diverse class of Proteobacteria.

Temperate deciduous or temperate broad-leaf forests are a variety of temperate forest 'dominated' by deciduous trees that lose their leaves each winter. They represent one of Earth's major biomes, making up 9.69% of global land area. These forests are found in areas with distinct seasonal variation that cycle through warm, moist summers, cold winters, and moderate fall and spring seasons. They are most commonly found in the Northern Hemisphere, with particularly large regions in eastern North America, East Asia, and a large portion of Europe, though smaller regions of temperate deciduous forests are also located in South America. Examples of trees typically growing in the Northern Hemisphere's deciduous forests include oak, maple, basswood, beech and elm, while in the Southern Hemisphere, trees of the genus Nothofagus dominate this type of forest. Temperate deciduous forests provide several unique ecosystem services, including habitats for diverse wildlife, and they face a set of natural and human-induced disturbances that regularly alter their structure.
Methylorubrum extorquens is a Gram-negative bacterium. Methylorubrum species often appear pink, and are classified as pink-pigmented facultative methylotrophs, or PPFMs. The wild type has been known to use both methane and multiple carbon compounds as energy sources. Specifically, M. extorquens has been observed to use primarily methanol and C1 compounds as substrates in their energy cycles. It has been also observed that use lanthanides as a cofactor to increase its methanol dehydrogenase activity

Phospholipid-derived fatty acids (PLFAs) are widely used in microbial ecology as chemotaxonomic markers of bacteria and other organisms. Phospholipids are the primary lipids composing cellular membranes. Phospholipids can be saponified, which releases the fatty acids contained in their diglyceride tail. Once the phospholipids of an unknown sample are saponified, the composition of the resulting PLFA can be compared to the PLFA of known organisms to determine the identity of the sample organism. PLFA analysis may be combined with other techniques, such as stable isotope probing to determine which microbes are metabolically active in a sample. PLFA analysis was pioneered by D.C. White at the University of Tennessee, in the early to mid 1980s.
The Xanthobacteraceae are a family of bacteria that includes Azorhizobium, a genus of rhizobia. Xanthobacteraceae bacteria are diverse and Gram-negative, rod-shaped, and may be motile or non-motile depending on the specific bacteria. Their cells range in size from 0.4–1.0 × 0.8–6 µm, but when grown in the presence of alcohol as the sole carbon source, they can reach up to 10 µm in length. These bacteria do not form spores and have opaque, slimy colonies that appear slightly yellow due to the presence of zeaxanthin dirhamnoside.

Greenhouse gas emissions from wetlands of concern consist primarily of methane and nitrous oxide emissions. Wetlands are the largest natural source of atmospheric methane in the world, and are therefore a major area of concern with respect to climate change. Wetlands account for approximately 20 - 30% of atmospheric methane through emissions from soils and plants, and contribute an approximate average of 161 Tg of methane to the atmosphere per year.
Methylocella silvestris is a bacterium from the genus Methylocella spp which are found in many acidic soils and wetlands. Historically, Methylocella silvestris was originally isolated from acidic forest soils in Germany, and it is described as Gram-negative, aerobic, non-pigmented, non-motile, rod-shaped and methane-oxidizing facultative methanotroph. As an aerobic methanotrophic bacteria, Methylocella spp use methane (CH4), and methanol as their main carbon and energy source, as well as multi compounds acetate, pyruvate, succinate, malate, and ethanol. They were known to survive in the cold temperature from 4° to 30° degree of Celsius with the optimum at around 15° to 25 °C, but no more than 36 °C. They grow better in the pH scale between 4.5 to 7.0. It lacks intracytoplasmic membranes common to all methane-oxidizing bacteria except Methylocella, but contain a vesicular membrane system connected to the cytoplasmic membrane. BL2T (=DSM 15510T=NCIMB 13906T) is the type strain.
Methylocapsa is a genus of bacteria from the family of Beijerinckiaceae. M. gorgona has been shown to metabolize significant amounts of atmospheric methane.
Caballeronia is a genus of bacteria from the family of Burkholderiaceae which has been reported to perform biological nitrogen fixation and promote plant growth









