The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, commonly known as the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) or the United Nations Human Rights Office, is a department of the Secretariat of the United Nations that works to promote and protect human rights that are guaranteed under international law and stipulated in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights of 1948. The office was established by the United Nations General Assembly on 20 December 1993 in the wake of the 1993 World Conference on Human Rights.
The Council of the Baltic Sea States (CBSS) is a regional intergovernmental organisation working on three priority areas: Regional Identity, Safe & Secure Region and Sustainable & Prosperous Region. These three priority areas aim to address the themes of environment, economic development, entrepreneurship, education, culture, civil security, children's rights and trafficking in human beings.

A coast guard or coastguard is a maritime security organization of a particular country. The term embraces wide range of responsibilities in different countries, from being a heavily armed military force with customs and security duties to being a volunteer organization tasked with search and rescue without law enforcement authority. In most countries, a typical coast guard's functions are distinct from those of the navy and the transit police, while in certain countries has similarities to both.

The United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) is a United Nations (U.N.) body established in December 1991 by the General Assembly to strengthen the international response to complex emergencies and natural disasters. It is the successor to the Office of the United Nations Disaster Relief Coordinator (UNDRO).

The Military Staff of the European Union (EUMS) is the directorate-general of the European Union's (EU) External Action Service (EEAS) that contributes to the EU's Common Security and Defence Policy (CSDP) by providing strategic advice to the High Representative (HR/VP) and commanding operations through its Military Planning and Conduct Capability (MPCC) operational headquarters. From the end of 2020 the MPCC will also be capable of running executive operations of up to 2500 troops, i.e. the size of one battle group, as well as 3 non-executive missions.

The European Fisheries Control Agency (EFCA) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that co-ordinates the national operational activities in the area of fisheries, and assists the member states in their application of the Common Fisheries Policy (CFP). The agency is based in Vigo, Spain.
The Australian Intelligence Community (AIC) and the National Intelligence Community (NIC) or National Security Community of the Australian Government are the collectives of statutory intelligence agencies, policy departments, and other government agencies concerned with protecting and advancing the national security and national interests of the Commonwealth of Australia. The intelligence and security agencies of the Australian Government have evolved since the Second World War and the Cold War and saw transformation and expansion during the Global War on Terrorism with military deployments in Afghanistan, Iraq and against ISIS in Syria. Key international and national security issues for the Australian Intelligence Community include terrorism and violent extremism, cybersecurity, transnational crime, the rise of China, and Pacific regional security.
A Sector is a shore-based operational unit of the United States Coast Guard. Each Sector is responsible for the execution of all Coast Guard missions within its Area of Responsibility (AOR), with operational support from Coast Guard Cutters and Air Stations. Subordinate commands within a Sector typically include Stations and Aids-to-Navigation (ATON) Teams. Some Sector commands also have subordinate units such as Sector Field Offices and Marine Safety Units that are responsible for mission execution in parts of the Sector's AOR. There are 37 sectors within the Coast Guard.
The counter-terrorism page primarily deals with special police or military organizations that carry out arrest or direct combat with terrorists. This page deals with the other aspects of counter-terrorism:
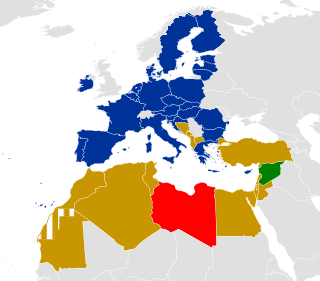
The Union for the Mediterranean is an intergovernmental organization of 42 member states from Europe and the Mediterranean Basin: the 27 EU member states and 15 Mediterranean partner countries from North Africa, Western Asia and Southern Europe. It was founded on 13 July 2008 at the Paris Summit for the Mediterranean, with an aim of reinforcing the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership (Euromed) that was set up in 1995 as the Barcelona Process. Its general secretariat is located in Barcelona, Spain.

The European Maritime Force is a non-standing, military force with the current participation of France, Italy, Portugal and Spain. The force may carry out naval, air and amphibious operations, with an activation time of 5 days after an order is received.
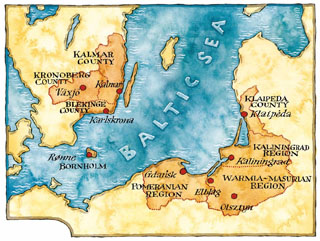
Euroregion Baltic(ERB) is an institutionalised form of cross-border cooperation in the south-east of the Baltic Sea Region, consisting of eight regions of Denmark, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, and Sweden.
The United Arab Emirates Federal Customs Authority is an Emirati governmental authority concerned with drawing customs policy in cooperation with customs administrations, preparing unified legislation to regulate customs work, and supervising implementation of it by customs administrations and related government authorities, and protecting the State from revenue fraud and smuggling operations in cooperation and coordination with competent authorities.

The Ministry of Public Safety and Security was an organization of the national government of South Korea with the responsibility of public safety and security. It was established on November 19, 2014 with a merger of the National Emergency Management Agency, Korea Coast Guard, a branch of Safety of Ministry of Security and Public Administration to prevent and efficiently respond to national disasters. It has its headquarters in the Seoul Government Complex.

The Bali Process is an official international forum, established in 2002, to facilitate discussion and information sharing about issues relating to people smuggling, human trafficking, and related transnational crime and appropriate responses to these issues.
The Secretariat for Multidimensional Security of the Organization of American States is a part of the General Secretariat, which is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States. The Secretariat for Multidimensional Security has a mandate to promote cooperation between Organization's Member States, Inter-American and international organizations, as well as with entities such as the United Nations and its subsidiaries, in order to analyze, prevent, confront and respond to security threats.

The Trilateral Cooperation Secretariat (TCS) is an international organization established with a vision to promote peace and common prosperity among China, Japan, and South Korea. Upon the agreement signed and ratified by each of the three governments, the TCS was officially inaugurated in Seoul, on 1 September 2011. On the basis of equal participation, each government shares 1/3 of the total operational budget.
The Department of Home Affairs is the Australian Government interior ministry with responsibilities for national security, law enforcement, emergency management, border control, immigration, refugees, citizenship, transport security and multicultural affairs. The portfolio also includes federal agencies such as the Australian Federal Police, Australian Border Force and the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation. The Home Affairs portfolio reports to the Minister for Home Affairs, Karen Andrews, and is led by the Secretary of the Department of Home Affairs, Mike Pezzullo.