 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate | |
| Other names Phenyldiazonium tetrafluoroborate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5BF4N2 | |
| Molar mass | 191.92 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless crystals |
| Density | 1.565 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | decomposes |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
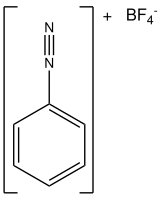
Benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate is an organic compound with the formula [C6H5N2]BF4. It is a salt of a diazonium cation and tetrafluoroborate. It exists as a colourless solid that is soluble in polar solvents. It is the parent member of the aryldiazonium compounds, [1] which are widely used in organic chemistry.