Carbon compounds are defined as chemical substances containing carbon. More compounds of carbon exist than any other chemical element except for hydrogen. Organic carbon compounds are far more numerous than inorganic carbon compounds. In general bonds of carbon with other elements are covalent bonds. Carbon is tetravalent but carbon free radicals and carbenes occur as short-lived intermediates. Ions of carbon are carbocations and carbanions are also short-lived. An important carbon property is catenation as the ability to form long carbon chains and rings.

In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)–. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula CH3C(O)CH3. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.
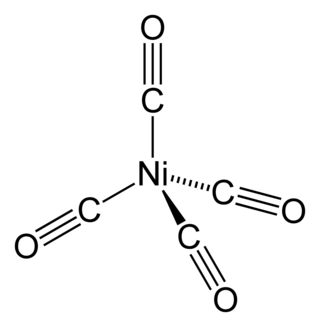
Nickel carbonyl (IUPAC name: tetracarbonylnickel) is a nickel(0) organometallic compound with the formula Ni(CO)4. This colorless liquid is the principal carbonyl of nickel. It is an intermediate in the Mond process for producing very high-purity nickel and a reagent in organometallic chemistry, although the Mond Process has fallen out of common usage due to the health hazards in working with the compound. Nickel carbonyl is one of the most dangerous substances yet encountered in nickel chemistry due to its very high toxicity, compounded with high volatility and rapid skin absorption.
Phosphorus trifluoride (formula PF3), is a colorless and odorless gas. It is highly toxic and reacts slowly with water. Its main use is as a ligand in metal complexes. As a ligand, it parallels carbon monoxide in metal carbonyls, and indeed its toxicity is due to its binding with the iron in blood hemoglobin in a similar way to carbon monoxide.

Iron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula Fe(CO)5. Under standard conditions Fe(CO)5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. Older samples appear darker. This compound is a common precursor to diverse iron compounds, including many that are useful in small scale organic synthesis.
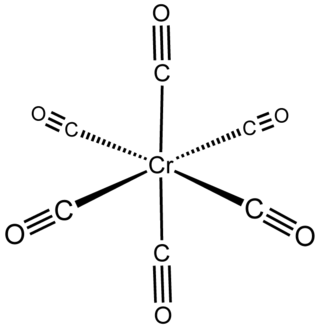
Chromium carbonyl, also known as chromium hexacarbonyl, is the chemical compound with the formula Cr(CO)6. At room temperature the solid is stable to air, although it does have a high vapor pressure and sublimes readily. Cr(CO)6 is zerovalent, meaning that Cr has an oxidation state of zero, and it is a homoleptic complex, which means that all the ligands are identical. The complex is octahedral with Cr–C and C–O distances of 1.91 and 1.14 Å, respectively.
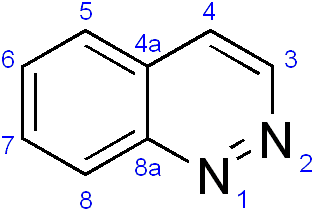
Cinnoline is an aromatic heterocyclic compound with the formula C8H6N2. It is isomeric with other naphthyridines including quinoxaline, phthalazine and quinazoline.

Metal carbonyls are coordination complexes of transition metals with carbon monoxide ligands. Metal carbonyls are useful in organic synthesis and as catalysts or catalyst precursors in homogeneous catalysis, such as hydroformylation and Reppe chemistry. In the Mond process, nickel tetracarbonyl is used to produce pure nickel. In organometallic chemistry, metal carbonyls serve as precursors for the preparation of other organometallic complexes.

Triiron dodecarbonyl is the organoiron compound with the formula Fe3(CO)12. It is a dark green solid that sublimes under vacuum. It is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents to give intensely green solutions. Most low-nuclearity clusters are pale yellow or orange. Hot solutions of Fe3(CO)12 decompose to an iron mirror, which can be pyrophoric in air.The solid decomposes slowly in air, and thus samples are typically stored cold under an inert atmosphere. It is a more reactive source of iron(0) than iron pentacarbonyl.
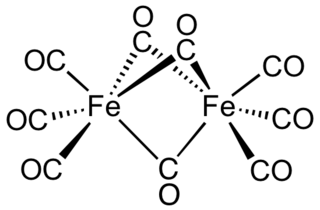
Diiron nonacarbonyl is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe2(CO)9. This metal carbonyl is an important reagent in organometallic chemistry and of occasional use in organic synthesis. It is a more reactive source of Fe(0) than Fe(CO)5. This micaceous orange solid is virtually insoluble in all common solvents.
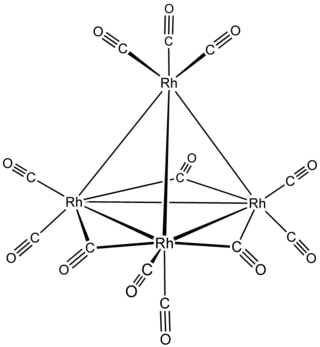
Tetrarhodium dodecacarbonyl is the chemical compound with the formula Rh4(CO)12. This dark-red crystalline solid is the smallest binary rhodium carbonyl that can be handled as a solid under ambient conditions. It is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis.
Carbonylation refers to reactions that introduce carbon monoxide into organic and inorganic substrates. Carbon monoxide is abundantly available and conveniently reactive, so it is widely used as a reactant in industrial chemistry. The term carbonylation also refers to oxidation of protein side chains.

Hexadecacarbonylhexarhodium is a metal carbonyl cluster with the formula Rh6(CO)16. It exists as purple-brown crystals that are slightly soluble in dichloromethane and chloroform. It is the principal binary carbonyl of rhodium.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. While iron adopts oxidation states from Fe(−II) through to Fe(VII), Fe(IV) is the highest established oxidation state for organoiron species. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.

Iron tetracarbonyl dihydride is the organometallic compound with the formula H2Fe(CO)4. This compound was the first transition metal hydride discovered. The complex is stable at low temperatures but decomposes rapidly at temperatures above –20 °C.
Boron monofluoride or fluoroborylene is a chemical compound with formula BF, one atom of boron and one of fluorine. It was discovered as an unstable gas and only in 2009 found to be a stable ligand combining with transition metals, in the same way as carbon monoxide. It is a subhalide, containing fewer than the normal number of fluorine atoms, compared with boron trifluoride. It can also be called a borylene, as it contains boron with two unshared electrons. BF is isoelectronic with carbon monoxide and dinitrogen; each molecule has 14 electrons.
A metallacarboxylic acid is a metal complex with the ligand CO2H. These compounds are intermediates in reactions that involve carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, these species are intermediates in the water gas shift reaction. Metallacarboxylic acids are also called hydroxycarbonyls.
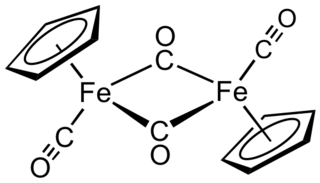
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula [(η5-C5H5)Fe(CO)2]2, often abbreviated to Cp2Fe2(CO)4, [CpFe(CO)2]2 or even Fp2, with the colloquial name "fip dimer". It is a dark reddish-purple crystalline solid, which is readily soluble in moderately polar organic solvents such as chloroform and pyridine, but less soluble in carbon tetrachloride and carbon disulfide. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is insoluble in but stable toward water. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is reasonably stable to storage under air and serves as a convenient starting material for accessing other Fp (CpFe(CO)2) derivatives (described below).

In chemistry, a metal carbonyl cluster is a compound that contains two or more metals linked in part by metal-metal bonds and containing carbon monoxide (CO) as the exclusive or predominant ligand. The area is a subfield of metal carbonyl chemistry, and many metal carbonyl clusters are in fact prepared from simple metal carbonyls. Simple examples include Fe2(CO)9, Fe3(CO)12, Mn2(CO)10. High nuclearity clusters include [Rh13(CO)24H3]2− and the stacked Pt3 triangules [Pt3n(CO)6n]2− (n = 2–6).
Nickel compounds are chemical compounds containing the element nickel which is a member of the group 10 of the periodic table. Most compounds in the group have an oxidation state of +2. Nickel is classified as a transition metal with nickel(II) having much chemical behaviour in common with iron(II) and cobalt(II). Many salts of nickel(II) are isomorphous with salts of magnesium due to the ionic radii of the cations being almost the same. Nickel forms many coordination complexes. Nickel tetracarbonyl was the first pure metal carbonyl produced, and is unusual in its volatility. Metalloproteins containing nickel are found in biological systems.













