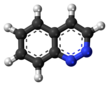
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom (=N−). It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide.

Hydroxylamine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NH2OH. The compound is in a form of a white hygroscopic crystals. Hydroxylamine is almost always provided and used as an aqueous solution. It is consumed almost exclusively to produce Nylon-6. The oxidation of NH3 to hydroxylamine is a step in biological nitrification.
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions. Both proceed by electrophilic aromatic substitution.
The aldol reaction is a reaction in organic chemistry that combines two carbonyl compounds to form a new β-hydroxy carbonyl compound. Its simplest form might involve the nucleophilic addition of an enolized ketone to another:

In organic chemistry, an imine is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions.

In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base. An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternative name is muriate, derived from hydrochloric acid's ancient name: muriatic acid.
Dimethylformamide, DMF is an organic compound with the chemical formula HCON(CH3)2. Its structure is HC(=O)−N(−CH3)2. Commonly abbreviated as DMF, this colourless liquid is miscible with water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions. Dimethylformamide is odorless, but technical-grade or degraded samples often have a fishy smell due to impurity of dimethylamine. Dimethylamine degradation impurities can be removed by sparging samples with an inert gas such as argon or by sonicating the samples under reduced pressure. As its name indicates, it is structurally related to formamide, having two methyl groups in the place of the two hydrogens. DMF is a polar (hydrophilic) aprotic solvent with a high boiling point. It facilitates reactions that follow polar mechanisms, such as SN2 reactions.

In organic chemistry, sulfonic acid refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula R−S(=O)2−OH, where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the S(=O)2(OH) group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is known as a sulfo group. A sulfonic acid can be thought of as sulfuric acid with one hydroxyl group replaced by an organic substituent. The parent compound is the parent sulfonic acid, HS(=O)2(OH), a tautomer of sulfurous acid, S(=O)(OH)2. Salts or esters of sulfonic acids are called sulfonates.
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. Like triethanolamine and tetraethylammonium, it is often abbreviated TEA. It is a colourless volatile liquid with a strong fishy odor reminiscent of ammonia. Like diisopropylethylamine (Hünig's base), triethylamine is commonly employed in organic synthesis, usually as a base.

Triazines are a class of nitrogen-containing heterocycles. The parent molecules' molecular formula is C3H3N3. They exist in three isomeric forms, 1,3,5-triazines being common.

Cyanuric chloride is an organic compound with the formula (NCCl)3. This white solid is the chlorinated derivative of 1,3,5-triazine. It is the trimer of cyanogen chloride. Cyanuric chloride is the main precursor to the popular but controversial herbicide atrazine.

Cyanamide is an organic compound with the formula CN2H2. This white solid is widely used in agriculture and the production of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. It is also used as an alcohol-deterrent drug. The molecule features a nitrile group attached to an amino group. Derivatives of this compound are also referred to as cyanamides, the most common being calcium cyanamide (CaCN2).
1,3,5-Triazine, also called s-triazine, is an organic chemical compound with the formula (HCN)3. It is a six-membered heterocyclic aromatic ring, one of several isomeric triazines. s-Triazine —the "symmetric" isomer—and its derivatives are useful in a variety of applications.

Phthalazine, also called benzo-orthodiazine or benzopyridazine, is a heterocyclic organic compound with the molecular formula C8H6N2. It is isomeric with other naphthyridines including quinoxaline, cinnoline and quinazoline.
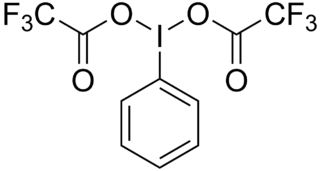
(Bis iodo)benzene, C
6H
5I(OCOCF
3)
2, is a hypervalent iodine compound used as a reagent in organic chemistry. It can be used to carry out the Hofmann rearrangement under acidic conditions.
Pyrylium is a cation with formula C5H5O+, consisting of a six-membered ring of five carbon atoms, each with one hydrogen atom, and one positively charged oxygen atom. The bonds in the ring are conjugated as in benzene, giving it an aromatic character. In particular, because of the positive charge, the oxygen atom is trivalent. Pyrilium is a mono-cyclic and heterocyclic compound, one of the oxonium ions.

Trichloroacetonitrile is an organic compound with the formula CCl3CN. It is a colourless liquid, although commercial samples often are brownish. It is used commercially as a precursor to the fungicide etridiazole. It is prepared by dehydration of trichloroacetamide. As a bifunctional compound, trichloroacetonitrile can react at both the trichloromethyl and the nitrile group. The electron-withdrawing effect of the trichloromethyl group activates the nitrile group for nucleophilic additions. The high reactivity makes trichloroacetonitrile a versatile reagent, but also causes its susceptibility towards hydrolysis.

Tetramethylurea is the organic compound with the formula (Me2N)2CO. It is a substituted urea. This colorless liquid is used as an aprotic-polar solvent, especially for aromatic compounds and is used e. g. for Grignard reagents. Tetramethylurea is a colorless liquid with mild aromatic odor. Unusual for an urea is the liquid state of tetramethylurea in a range of > 170 °C.

Trifluoroperacetic acid is an organofluorine compound, the peroxy acid analog of trifluoroacetic acid, with the condensed structural formula CF
3COOOH. It is a strong oxidizing agent for organic oxidation reactions, such as in Baeyer–Villiger oxidations of ketones. It is the most reactive of the organic peroxy acids, allowing it to successfully oxidise relatively unreactive alkenes to epoxides where other peroxy acids are ineffective. It can also oxidise the chalcogens in some functional groups, such as by transforming selenoethers to selones. It is a potentially explosive material and is not commercially available, but it can be quickly prepared as needed. Its use as a laboratory reagent was pioneered and developed by William D. Emmons.

Acetamidine hydrochloride is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(NH)NH2·HCl, used in the synthesis of many nitrogen-bearing compounds. It is the hydrochloride of acetamidine, one of the simplest amidines.