Bernd Heine | |
|---|---|
| Born | 25 May 1939 |
| Nationality | German |
| Occupation | Linguist |
| Academic background | |
| Alma mater | University of Cologne |
| Academic work | |
| Institutions | University of Cologne |
| Main interests | Languages of Africa |
Bernd Heine (born 25 May 1939) is a German linguist and specialist in African studies.
From 1978 to 2004 Heine held the chair for African Studies at the University of Cologne,Germany,now being a Professor Emeritus. His main focal points in research and teaching are African linguistics,sociolinguistics,grammaticalization theory and language contact and discourse grammar. The grammaticalisation theory,which deals with the changes in grammar,and to which he contributed 7 books and numerous articles,is his main focal point. Jointly with Tania Kuteva and Gunther Kaltenböck,Heine is the founder of the framework of discourse grammar.
Heine was born in Mohrungen,East Prussia (now Morąg,Poland). During the Second World War,in 1944 his parents fled to Austria and later took up residence in Bavaria,before settling in Leverkusen in 1948. From 1949 to 1959 Heine attended the Landrat-Lucas-Gymnasium in Opladen. Afterwards,he studied at the University of Cologne and University of Hamburg. In 1967 he was awarded a PhD in Cologne. In 1972 he received his postdoctoral lecture qualification for African studies.
From 1968 to 1969 he was an assistant at the Department for African Studies of the University of Cologne,from 1969 to 1972 he was a lecturer and from 1975 to 1978 visiting professor at the University of Nairobi. In 1978 he took over the chair of African Studies at the University of Cologne.
He carried out 25 field research trips to Ghana,Togo,Kenya,Tanzania,Uganda and Namibia as well as lecturing trips to Australia,Austria,Brasil,England,Estonia,Ethiopia,Finland,France,Italy,Japan,Kenya,Mexico,Namibia,The Netherlands,Poland,Spain,South Africa,South Korea,Sweden,Tanzania and United States of America.
Guest professorships brought him to La Trobe University,Melbourne in 1994/1995 and from 1999 to 2000 to the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences in Stanford,United States,in 2002 to the Dartmouth College,US,in 2005 to the University of Graz and from 2005 to 2006 to the Netherlands Institute for Advanced Study in Wassenaar,the Netherlands,in 2006 to the University of Hamburg,in 2007 to the Ecole des Hautes Etudes (Centre de Recherches Linguistiques sur l'Asie Orientale "CRLAO"),Paris,in 2007 to the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro,2008 through 2009 to the Tokyo University of Foreign Studies,Japan,and in 2009 to the Chonnam National University,Korea. He was a visiting professor at the University of Cape Town in 2012 and 2015,and in 2014 he was appointed Yunshan Chair Professor at Guangdong University of Foreign Studies,China (2014 - 2016).
Bernd Heine has served as a keynote speaker or invited speaker of over 100 international conferences. His publications include more than 40 books on African linguistics,sociolinguistics,historical linguistics,grammaticalization theory,and discourse grammar. He is co-editor and/or member of the advisory boards of 17 journals or series of books. Since 2014 his main interest has been,jointly with Gunther Kaltenböck and Tania Kuteva,the analysis of linguistic discourse. In the framework of discourse grammar developed by these authors,two components of discourse planning are distinguished,where one,Sentence Grammar,is centrally concerned with the construction of sentences while the other,Thetical Grammar,is dedicated to the relationship between speaker,hearer,and the text.
His awards include a membership with the Executive Council,International African Institute,London. In 1986 he became Hans Wolff Memorial Lecturer at the Indiana University,US,in 1990 Raymond Dart Memorial Lecturer at the University of Johannesburg,South Africa. In 1990 he received the Kenya Kiswahili Association Award in Nairobi,in 1994 he was Fellow of the Australian Research Council,in 1995 he received an award from the National Kiswahili Council of the Republic of Tanzania. In 1995 he became August Klingenheben Memorial Lecturer at the University of Leipzig and in 1996 a Fellow of the British Academy. From 1997 to 2000 he was president of the Committee for World Congresses of African Linguistics and in 1999 he became a full member of the North Rhine-Westphalia Academy of Sciences. In 2008,the Ministry of Education,Science,and Technology,South Korea,appointed him a Distinguished World-Class Scholar,and in 2009 he received the Lifetime Achievement Award of the Evolutionary Linguistics Association,Brussels. He was made a member of the Academia Europaea (MAE) in 2015 and of the European Science Foundation in 2016. In 2012,he became an Honorary Member of the Linguistic Society of America,and in 2020 of the Philological Society of London.
Evolutionary linguistics or Darwinian linguistics is a sociobiological approach to the study of language. Evolutionary linguists consider linguistics as a subfield of sociobiology and evolutionary psychology. The approach is also closely linked with evolutionary anthropology, cognitive linguistics and biolinguistics. Studying languages as the products of nature, it is interested in the biological origin and development of language. Evolutionary linguistics is contrasted with humanistic approaches, especially structural linguistics.
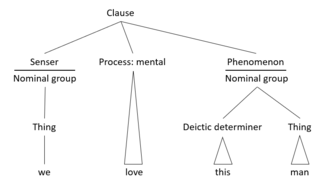
Functional linguistics is an approach to the study of language characterized by taking systematically into account the speaker's and the hearer's side, and the communicative needs of the speaker and of the given language community. Linguistic functionalism spawned in the 1920s to 1930s from Ferdinand de Saussure's systematic structuralist approach to language (1916).
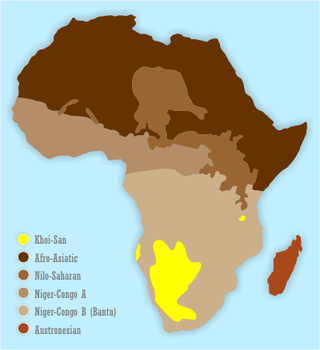
The Khoisan languages are a number of African languages once classified together, originally by Joseph Greenberg. Khoisan is defined as those languages that have click consonants and do not belong to other African language families. For much of the 20th century, they were thought to be genealogically related to each other, but this is no longer accepted. They are now held to comprise three distinct language families and two language isolates.
Principles and parameters is a framework within generative linguistics in which the syntax of a natural language is described in accordance with general principles and specific parameters that for particular languages are either turned on or off. For example, the position of heads in phrases is determined by a parameter. Whether a language is head-initial or head-final is regarded as a parameter which is either on or off for particular languages. Principles and parameters was largely formulated by the linguists Noam Chomsky and Howard Lasnik. Many linguists have worked within this framework, and for a period of time it was considered the dominant form of mainstream generative linguistics.
Robert Malcolm Ward "Bob" Dixon is a Professor of Linguistics in the College of Arts, Society, and Education and The Cairns Institute, James Cook University, Queensland. He is also Deputy Director of The Language and Culture Research Centre at JCU. Doctor of Letters, he was awarded an Honorary Doctor of Letters Honoris Causa by JCU in 2018. Fellow of British Academy; Fellow of the Australian Academy of the Humanities, and Honorary member of the Linguistic Society of America, he is one of three living linguists to be specifically mentioned in The Concise Oxford Dictionary of Linguistics by Peter Matthews (2014).
In historical linguistics, grammaticalization is a process of language change by which words representing objects and actions become grammatical markers. Thus it creates new function words from content words, rather than deriving them from existing bound, inflectional constructions. For example, the Old English verb willan 'to want', 'to wish' has become the Modern English auxiliary verb will, which expresses intention or simply futurity. Some concepts are often grammaticalized, while others, such as evidentiality, are not so much.
A discourse marker is a word or a phrase that plays a role in managing the flow and structure of discourse. Since their main function is at the level of discourse rather than at the level of utterances or sentences, discourse markers are relatively syntax-independent and usually do not change the truth conditional meaning of the sentence. They can also indicate what a speaker is doing on a variety of different planes. Examples of discourse markers include the particles oh, well, now, then, you know, and I mean, and the discourse connectives so, because, and, but, and or. The term discourse marker was popularized by Deborah Schiffrin in her 1987 book Discourse Markers.
Peter W. Culicover is Professor of Linguistics at Ohio State University. He works in the areas of syntactic theory, language learnability and computational modelling of language acquisition and language change.
Jeffrey Heath is Professor of Historical Linguistics, Morphology, Arabic and Linguistic Anthropology at the University of Michigan, US. He is known particularly for his work in historical linguistics and for his extensive fieldwork.
A genderless language is a natural or constructed language that has no distinctions of grammatical gender—that is, no categories requiring morphological agreement for gender between nouns and associated pronouns, adjectives, articles, or verbs.
The Ethiopian language area is a hypothesized linguistic area that was first proposed by Charles A. Ferguson, who posited a number of phonological and morphosyntactic features that were found widely across Ethiopia and Eritrea, including the Ethio-Semitic, Cushitic and Omotic languages but not the Nilo-Saharan languages.
Paul Newman is an American linguist active in the study of African languages. He writes on the Hausa language of Nigeria and on the Chadic language family. He wrote the Modern Hausa-English Dictionary (1977), co-authored with his wife, Roxana Ma Newman, and The Hausa Language: An Encyclopedic Reference Grammar (2000). He is the founder of the Journal of African Languages and Linguistics, a journal in the field of African-language studies.
Edward Keith Brown is a Scottish linguist, professor at the University of Cambridge, and the editor-in-chief of the Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics.
Elizabeth Closs Traugott is an American linguist and Professor Emerita of Linguistics and English, Stanford University. She is best known for her work on grammaticalization, subjectification, and constructionalization.
Discourse Grammar (DG) is a grammatical framework that grew out of the analysis of spoken and written linguistic discourse on the one hand, and of work on parenthetical expressions, including Simon C. Dik's study of extra-clausal constituents, on the other. Initiated by Gunther Kaltenböck, Bernd Heine and Tania Kuteva, the framework is based on the distinction between two organizing principles of grammar where one concerns the structure of sentences and the other the linguistic organization beyond the sentence.
Thetical grammar forms one of the two domains of discourse grammar, the other domain being sentence grammar. The building blocks of thetical grammar are theticals, that is, linguistic expressions which are interpolated in, or juxtaposed to, clauses or sentences but syntactically, semantically and, typically, prosodically independent from these structures. The two domains are associated with contrasting principles of designing texts: Whereas sentence grammar is essentially restricted to the structure of sentences in a propositional format, thetical grammar concerns the overall contours of discourse beyond the sentence, thereby being responsible for a higher level of discourse production.
Cooptation is a cognitive-communicative operation whereby a piece of text, such as a clause, a phrase, a word, or any other unit, is inserted in a sentence. In the framework of Discourse Grammar, cooptation is understood as leading to the transfer of linguistic material from the domain of Sentence Grammar to that of Thetical Grammar.
Alice Marie-Claude Caffarel-Cayron is a French-Australian linguist. She is an Honorary Senior Lecturer in Linguistics at the University of Sydney. Caffarel is recognized for the development of a Systemic Functional Grammar of French which has been applied in the teaching of the French language, Discourse analysis and Stylistics at the University of Sydney. Caffarel is recognised as an expert in the field of French Systemic Functional Linguistics (SFL).
Tania Kuteva is a historical linguist specializing in grammaticalization, language contact and discourse grammar.