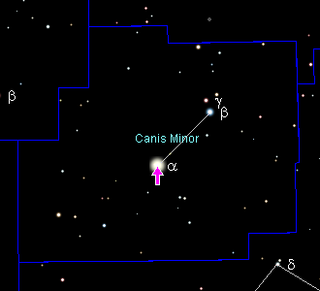
Procyon is the brightest star in the constellation of Canis Minor and usually the eighth-brightest star in the night sky, with an apparent visual magnitude of 0.34. It has the Bayer designation α Canis Minoris, which is Latinized to Alpha Canis Minoris, and abbreviated α CMi or Alpha CMi, respectively. As determined by the European Space Agency Hipparcos astrometry satellite, this system lies at a distance of just 11.46 light-years, and is therefore one of Earth's nearest stellar neighbors.
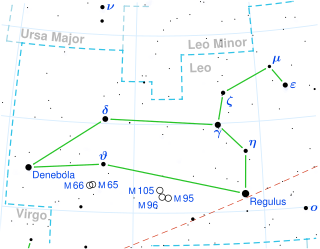
Denebola is the second-brightest individual star in the zodiac constellation of Leo. It is the easternmost of the bright stars of Leo. It has the Bayer designation Beta Leonis or β Leonis, which are abbreviated Beta Leo or β Leo. Denebola is an A-type main sequence star with 75% more mass than the Sun and 15 times the Sun's luminosity. Based on parallax measurements from the Hipparcos astrometry satellite, the star is at a distance of 36 light-years from the Sun. Its apparent visual magnitude is 2.14, making it readily visible to the naked eye. Denebola is a Delta Scuti type variable star, meaning its luminosity varies very slightly over a period of a few hours.

Alpha Persei, formally named Mirfak, is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Perseus, outshining the constellation's best-known star, Algol. Alpha Persei has an apparent visual magnitude of 1.8, and is a circumpolar star when viewed from mid-northern latitudes.

Beta Canis Majoris, also named Mirzam, is a star in the southern constellation of Canis Major, the "Great Dog", located at a distance of about 500 light-years (150 parsecs) from the Sun. In the modern constellation it lies at the position of the dog's front leg.

Gamma Pegasi is a star in the constellation of Pegasus, located at the southeast corner of the asterism known as the Great Square. It has the formal name Algenib ; the Bayer designation Gamma Pegasi is Latinized from γ Pegasi and abbreviated Gamma Peg or γ Peg. The average apparent visual magnitude of +2.84 makes this the fourth-brightest star in the constellation. The distance to this star has been measured using the parallax technique, yielding a value of roughly 470 light-years.
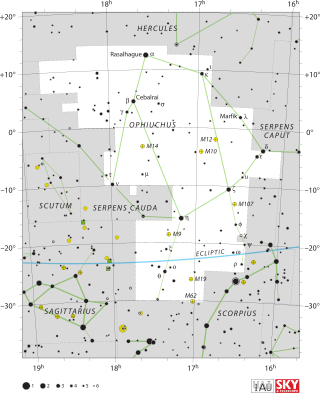
Beta Ophiuchi or β Ophiuchi, also named Cebalrai, is a star in the equatorial constellation of Ophiuchus. The apparent visual magnitude of this star is 2.7, which is readily visible to the naked eye even from urban skies. The distance to this star can be estimated using parallax measurements, yielding a value of 83.4 light-years from the Sun.

Gamma Ursae Minoris, also named Pherkad, is a star in the northern constellation of Ursa Minor. Together with Beta Ursae Minoris (Kochab), it forms the end of the dipper pan of the "Little Dipper", which is an asterism forming the tail of the bear. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 487 light-years from the Sun.

Beta Cancri, also named Tarf, is the brightest star in the zodiacal constellation of Cancer. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +3.5 and an absolute magnitude of −1.2. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 290 light-years distant from the Sun. An exoplanet, designated Beta Cancri b, is believed to be orbiting the star.

46 Leonis Minoris, also named Praecipua, is the brightest star in the constellation of Leo Minor. It is of spectral class K0+III-IV and of magnitude 3.83. It is a red clump giant. Based upon parallax measurements, its distance from the Sun is approximately 99.1 light-years. It is a suspected variable with an amplitude of about 0.05 magnitudes.
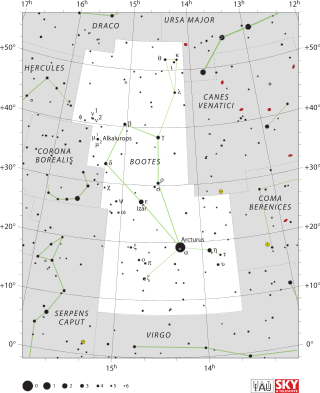
Beta Boötis, Latinized from β Boötis, and also named Nekkar, is a star in the northern constellation of Boötes. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.5, making it one of the brighter members of the constellation. In the modern constellation, it marks the head of Boötis the herdsman. Based upon parallax measurements obtained by the Gaia spacecraft, this star is approximately 235 light-years from the Sun. The magnitude of the star is reduced by 0.06 from extinction caused by intervening gas and dust.

Zeta Canis Majoris, or ζ Canis Majoris, also named Furud, is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Canis Major. This system has an apparent visual magnitude of +3.0, making it one of the brighter stars in the constellation and hence readily visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements from the Hipparcos mission yield a distance estimate of around 362 ly (111 pc) from the Sun. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +32 km/s.

Iota Canis Majoris, Latinized from ι Canis Majoris, is a solitary variable supergiant star in the southern constellation of Canis Major. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that varies between +4.36 and +4.40. The distance to this star is approximately 2,500 light years based on spectroscopic measurements. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +42 km/s.

Delta2 Canis Minoris is a main-sequence star in the constellation Canis Minor, about 141 ly away.

Delta3 Canis Minoris, Latinized from δ3 Canis Minoris, is a solitary, white-hued star in the equatorial constellation of Canis Minor. Based upon a parallax of 4.46 mas as seen from Gaia spacecraft in its repeated orbits around the Sun, just beyond the Earth. This star is about 730 light years from the Solar System. At that distance, the visual magnitude of these stars is diminished by an extinction of more than 0.15 due to interstellar dust. With an apparent visual magnitude of +5.81, it is just bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye.

Epsilon Canis Minoris is a suspected binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Canis Minor. It is a fifth magnitude star, which means it is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of just 3.13 mas as seen from Earth, this star is located roughly 770 light years from the Sun, give or take a 40 light year margin of error.

Eta Canis Minoris is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Canis Minor. It is approximately 318 light-years from Earth.
1 Canis Minoris is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Canis Minor, located about 287 light years away from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, white-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.37. The radial velocity of this object is poorly constrained at −1.0±4.2 km/s.
11 Canis Minoris is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Canis Minor, located around 313 light years away from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, white-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.25. This object is moving away from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +28 km/s, having come to within 157 light-years some 2.35 million years ago.

Beta Piscium or β Piscium, formally named Fumalsamakah, is a blue-white hued star in the zodiac constellation of Pisces. Its apparent magnitude is 4.40, meaning it can be faintly seen with the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements taken during the Hipparcos mission, it is about 410 light-years distant from the Sun.

YZ Canis Minoris is a red-hued star in the equatorial constellation of Canis Minor. With an apparent visual magnitude of 11.15, it is much too faint to be viewed with the naked eye. The distance to YZ CMi can be estimated from its annual parallax shift of 167 mas, yielding a value of 19.5 light years. Presently the star is moving further away with a heliocentric radial velocity of +26.5 km/s. It made its closest approach some 162,000 years ago when it made perihelion passage at a distance of 10.2 ly. YZ CMi is a potential member of the Beta Pictoris moving group.














