
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 485.4 Ma.
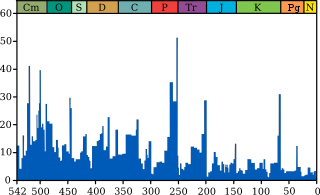
An extinction event is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp fall in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It occurs when the rate of extinction increases with respect to the background extinction rate and the rate of speciation. Estimates of the number of major mass extinctions in the last 540 million years range from as few as five to more than twenty. These differences stem from disagreement as to what constitutes a "major" extinction event, and the data chosen to measure past diversity.

The Silurian is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at 443.8 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, 419.2 Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of the Paleozoic Era, and the third of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out.

The Triassic is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era and the seventh period of the Phanerozoic Eon. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic.

The Archean Eon, in older sources sometimes called the Archaeozoic, is the second of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic. The Archean represents the time period from 4,031 to 2,500 Mya. The Late Heavy Bombardment is hypothesized to overlap with the beginning of the Archean. The Huronian glaciation occurred at the end of the eon.

Foraminifera are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment, while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths, which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA.

The Cryogenian is a geologic period that lasted from 720 to 635 million years ago. It is the second of the three periods of the Neoproterozoic era, preceded by the Tonian and followed by the Ediacaran.

The Ediacaranbiota is a taxonomic period classification that consists of all life forms that were present on Earth during the Ediacaran Period. These were enigmatic tubular and frond-shaped, mostly sessile, organisms. Trace fossils of these organisms have been found worldwide, and represent the earliest known complex multicellular organisms. The term "Ediacara biota" has received criticism from some scientists due to its alleged inconsistency, arbitrary exclusion of certain fossils, and inability to be precisely defined.

The geology of China consists of three Precambrian cratons surrounded by a number of orogenic belts. The modern tectonic environment is dominated by the continued collision of India with the rest of Asia starting 40–50 million years ago. This has formed the Himalayas and continues to deform most of China. China has vast mineral reserves, a significant earthquake risk in its western regions and rare isolated active volcanoes throughout the country.

Government Central Model School, Lahore is a public school in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. More than 3,000 students study in the school.
The Institute of Geosciences is a unit of instruction of the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS). It includes the undergraduate courses of Geography, Geomatics Engineering, Geology. It has a department of study of vertebrate paleontology which has made great contributions to the geopark of Paleorrota.

Wolfgang "Wolf" Helmut Berger was a German-American oceanographer, geologist, micropaleontologist and emeritus professor at Scripps Institution of Oceanography and the University of California, San Diego. His research interests comprise "micropaleontology, marine sedimentation, ocean productivity, carbon cycle, ocean history, climate history, and history of oceanography."

The Washington Formation is a coal, sandstone, and limestone geologic formation located in Ohio, Pennsylvania and West Virginia. It dates back to the Lower Permian period, with its base at or near the Permian/Carboniferous boundary. The Washington formation and the Dunkard Group as a whole was deposited at a time when the continents were in the process of forming the "Super Continent" Pangaea as well as a gradual drop in sea levels. The result during this period was coals being thinner and impure with high ash content. The limestones found with in the formation are exclusively freshwater deposits.

The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event, also known as the K–T extinction, was the mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth approximately 66 million years ago. The event caused the extinction of all non-avian dinosaurs. Most other tetrapods weighing more than 25 kg (55 lb) also became extinct, with the exception of some ectothermic species such as sea turtles and crocodilians. It marked the end of the Cretaceous period, and with it the Mesozoic era, while heralding the beginning of the current era, the Cenozoic. In the geologic record, the K–Pg event is marked by a thin layer of sediment called the K–Pg boundary, Fatkito boundary or K–T boundary, which can be found throughout the world in marine and terrestrial rocks. The boundary clay shows unusually high levels of the metal iridium, which is more common in asteroids than in the Earth's crust.

Julie Brigham-Grette is a glacial geologist and a professor in the Department of Geosciences at the University of Massachusetts Amherst where she co-directs the Joseph Hartshorn Quaternary Laboratory. Her research expertise is in glacial geology and paleoclimatology; she has made important contributions to Arctic marine and terrestrial paleoclimate records of the late Cenozoic to recent periods, the evolution of the Arctic climate, especially in the Beringia/Bering Strait region, and was a leader of the international Lake El’gygytgyn Drilling Project in northeastern Russia.

Jean-Pierre Gattuso is a French ocean scientist conducting research globally, from the pole to the tropics and from nearshore to the open ocean. His research addresses the biology of reef-building corals, the biogeochemistry of coastal ecosystems, and the response of marine plants, animals and ecosystems to global environmental change. He is also interested in transdisciplinary research, collaborating with social scientists to address ocean-based solutions to minimize climate change and its impacts. He is currently a CNRS Research Professor at Sorbonne University.

Bruce William Hayward is a New Zealand geologist, marine ecologist, and author. He is known as a leading expert on living and fossil foraminifera.
Laura Frances Robinson, born November 1976, is a British scientist who is Professor of Geochemistry at the University of Bristol. She makes use of geochemistry to study the processes that govern the climate. In particular, Robinson studies radioactive elements, as these can be analysed in geological materials. She was awarded the 2010 President's Award of the Geological Society of London.
Maya Tolstoy is a marine geophysicist known for her work on earthquakes in the deep sea. From Fall 2018 through December 2019 she was the Interim Executive Vice President and Dean of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences at Columbia University. As of 2022, she is the Maggie Walker Dean in the College of the Environment at the University of Washington.
Paul Barry Wignall is a British palaeontologist and sedimentologist. He is best known for his research on mass extinctions in the marine realm., particularly via the interpretation of black shales.
















