| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 5,10,15,22,23,24-Hexahydro-21H-biline | |
| Systematic IUPAC name 11H,31H,51H,71H-1,7(2),3,5(2,5)-Tetrapyrrolaheptaphane | |
| Other names Bilinogen; Tetrapyrrolotrismethane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| 8008279 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H20N4 | |
| Molar mass | 304.397 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
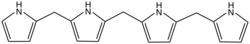
In organic chemistry, bilane is a compound with the formula C19H20N4 or [(C4H4N)−CH2−(C4H3N)−]2CH2. It is a tetrapyrrole, a class of compounds with four independent pyrrole rings. Specifically, the molecule can be described as four pyrrole molecules C4H5N connected in an open chain by three methylene bridges −CH2− at carbons adjacent to the nitrogens, replacing the respective hydrogens. [1]
The name is also used for the class of compounds formally derived from bilane proper by replacement of some additional hydrogen atoms by various functional groups. Natural bilanes usually have side chains substituted on the two carbons in each pyrrole ring that are not adjacent to the nitrogens. Artificial bilanes may be substituted on the bridging carbons (called meso positions). [2]
The parent (unsubstituted) bilane is difficult to prepare and unstable, [3] but substituted derivatives are synthesized by most living organisms as intermediates in the synthesis of natural porphyrins. Substituted bilanes may also be the starting point for the synthesis of artificial porphyrins. [2] [3]